The work of a kindergarten teacher is extremely important for the future of the entire country, because he is entrusted with the most valuable thing in every family - children. And today’s preschoolers are the future of the state, which is why the government pays so much attention to issues of education and training, starting from the very “starting” levels - nurseries and kindergartens. For the full development of pedagogy, each employee of a children's educational institution must know the main directions of the teacher, directly related to his work as a specialist in the education of young children.
The main activities of a preschool teacher
In preschool activities, mental, moral, labor, physical and artistic-aesthetic education are distinguished, but in recent years more and more attention has been paid to environmental and legal education. This is due to the fact that the socio-economic and political situation in the country and throughout the world is rapidly changing, and modern children in these areas are much better developed than their peers of previous years. In addition, the requirements for the development of a full-fledged personality provide for the all-round development of the child, so ignoring the issues of modern times will not bring anything good. Preschool teachers have to use much more knowledge and skills than in previous years, as this is required by the environment and the changed rules for assessing the activities of the teacher and the requirements for them.
The main directions of the teacher’s pedagogical activity include the following sections:
- Self-education.
- Organization of problem-search work for a children's team.
- Expanding the skills and abilities of students through the introduction of new information technologies into their activities.
- Expanding the educational space of pupils.
- The use of special classes to prepare students for school using ICT.
- Expanding the teacher’s own horizons and educational space using the latest information technologies.
The work of preschool teachers and educators is carried out in different directions, but, in essence, is aimed at one most important goal - the formation of a child as an integral creative personality. Therefore, one of the most important tasks of any educator is the harmonious unification of all areas of their activities to achieve their goal.
In the pedagogical literature, there are often 5 main areas of activity of a teacher in a preschool educational institution. These concepts resonate with the job responsibilities of a teacher, but do not copy, but complement them.
You can find many different definitions of the main directions of a teacher’s work, but they all, in essence, boil down to the following brief and succinct formulations:
1. Care.
2. Education.
3. Supervision.
4. Organization of educational work.
5. Conducting educational work.
This can be deciphered as follows:
- Care is caring, patronizing and providing assistance to a pupil. It concerns both training and education, and purely human feelings, as well as the health of the child. The teacher creates a psychologically healthy atmosphere in the children's educational institution, thanks to which the child feels calm, confident, and safe.
- Education is a broad concept that includes both the inculcation of universal human norms and the formation of a free, fully and comprehensively developed personality.
- Supervision involves monitoring not only behavior and academic performance, but also identifying various violations for the purpose of their subsequent correction and correction.
- Organization of educational work is planning and preparation of the entire learning process in a preschool educational institution. It includes numerous stages - from self-education to the production of the necessary visual material.
- Carrying out educational work is the actual learning process, which involves all the knowledge and skills accumulated by the teacher.
Also, the directions of the teacher’s work can be formulated as follows:
- Sports and recreation.
- Spiritual and educational.
- General cultural.
- General intellectual.
- Social.
The presence of several formulations does not introduce different interpretations into the definition of directions of educational activity, but only explains, “deciphers” them.
Rights
The rights of an employee are secured by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law “On Education”. Among those that employers list in the job description of a kindergarten teacher are the following opportunities:
- make proposals to improve the educational process;
- receive social guarantees and benefits in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- demand improved working conditions;
- have paid leave;
- with mutual agreement, exchange shifts with a second employee;
- demand the elimination of faults in the entrusted territory and the creation of normal working conditions.

The main activities of the senior preschool teacher

A methodologist, or senior educator, acts as a link between the state education system, pedagogical and psychological science, advanced professional experience and the practical activities of the teaching and educational staff of a children's educational institution. As a result, the main directions of the methodological work of the teacher-methodologist become the promotion of the formation, development and implementation of the professional creative potential of the teaching staff of the preschool educational institution.
According to the requirements of modern legislation and professional pedagogical standards, the main activities of the senior educator and the entire methodological service are the following:
- Education and training of preschool children in kindergarten in accordance with the requirements of modern standards of pedagogy and psychology.
- Formation of the educational standard of preschool educational institutions on the basis of universal human values, the free development of the child as a full-fledged individual, in compliance with the priorities of the health and well-being of pupils. In the work of preschool educational institutions, adhere to the principles of respect for human rights and freedoms, love for one’s native country, nature and the environment, the formation of the foundations of a healthy lifestyle, and the absence of bad habits. It also requires the formation of the principles of citizenship, hard work and social responsibility, taking into account the age of the students.
- Adaptation of kindergarten activities to the characteristics of the physiology and psychology of preschool children, as well as to social orders.
- Ensuring the secularity of the educational process.
In his activities, the senior teacher of a preschool institution carries out methodological and educational work in order to achieve the following indicators:
- Introducing proposals and changes to the work plan of the preschool educational institution.
- Improving the qualifications of teachers and educators.
- Support and assistance to the teaching staff in self-education and improvement of professional knowledge.
- Drawing up a schedule of classes taking into account the age groups of students.
- Providing methodological assistance to educators, primarily young professionals and newcomers to the work of a particular preschool educational institution.
- Exchange of employee experience.
- Working with parents.
- Providing groups with the necessary aids, books and toys.
- Analysis of the state of educational, educational and methodological work in preschool educational institutions and the adoption of measures to improve and improve it.
- Certification of educators and teachers of children's educational institutions.
Ensuring the fulfillment of all these complex and multifaceted tasks is possible only with coordinated collective work of all representatives of the educational and educational process.
What does he do?
In general terms, upbringing, education, care, and supervision of children is what a kindergarten teacher does, regardless of the form of ownership of the preschool educational institution. But to complete all the documentation, the employer will need a professional standard from the Ministry of Labor, which clearly states the functional requirements for the employee. The order of the Ministry of Labor indicates, among other things, what is the responsibility of a kindergarten teacher and teacher when admitting children to a group:
- regulating children's behavior to ensure a safe educational environment;
- implementation of educational opportunities for various types of child activities (educational, play, work, sports, artistic, etc.);
- development of students' cognitive activity, independence, initiative, creative abilities, formation of citizenship, ability to work and live in the modern world, formation of a culture of healthy and safe lifestyle among students;
- the use of constructive educational efforts of parents (legal representatives) of students, assistance to the family in resolving issues of raising a child.
Responsibility
The legislation defines not only the duties, but also the responsibilities of employees. In particular, the teacher is responsible for:
- preserving the life and health of children in the group;
- safety of pupils’ personal belongings;
- compliance with safety and labor protection instructions;
- the use of unacceptable methods of education, violence and rudeness;
- inappropriate performance and failure to complete one's work;
- use of working time for personal purposes;
- abuse of authority.
Violation of assigned duties may result in disciplinary action, and for “particularly serious” offenses the teacher may be dismissed.
Social orientation of the work of a preschool educational institution
A preschool educational institution (PEI) is the next institution for the socialization of a child after the family. His further progressive development, adaptation to new living conditions and socialization largely depend on the results of this work.
The problem of social adaptation of a preschooler to life in society is very relevant today. It includes several areas of working with children. One of the directions is familiarization with the outside world, which makes it possible to get acquainted with society. The staff of kindergarten No. 633 of the Kalininsky district builds its work with children on the basis of the basic state “Program of education and training in kindergarten edited by M. A. Vasilyeva.” In addition, other programs are used for certain problems, work technologies are used taking into account the capabilities of the team of employees and the characteristics of children.
Currently, activities to familiarize with the outside world in preschool educational institutions are intensively developing. The content of the programs and methodological manuals are considered and the tasks of working with children are identified in several blocks. The work of a preschool institution on the social development of children includes a number of aspects. The content of this work includes the study of the history and culture of the native city, environmental problems, people's livelihoods, and forms of their communication. Much attention is paid to the environment and the interaction of different groups of people. Preschoolers receive primary knowledge about the value of health, the rights of the child, and the surrounding reality (Fig. 1).
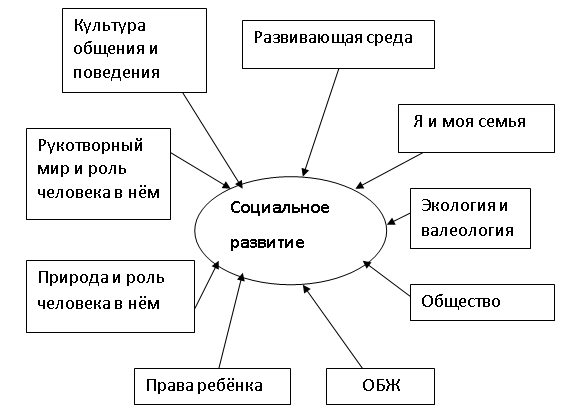
Rice. 1. Directions of social development of the child
It is known that the existence of an individual outside of society is impossible. A person who does not have responsibilities to the collective loses the meaning of his development as a social being. The process of personal socialization begins in childhood and continues throughout life. A holistic picture of the world for a child consists of the unity of its spatio-temporal and qualitative-quantitative forms. Preschoolers are not yet able to independently build this picture in their own minds and determine their place in it - they need the help of adults. By the end of the preschool period, children develop a primary system of value orientations.
For many years, preschool education in Russia was focused on the development of the cognitive sphere of children. However, its purpose is not so much to master the child’s knowledge, but to develop the basic properties of his personality: self-esteem, emotional needs of the sphere, moral values, meanings and attitudes, as well as socio-psychological characteristics in the system of relationships with other people.
A kindergarten is the next institution of socialization of a child after the family, and the kindergarten group often acts as the first level of its membership. For the personal and social development of a child, the established relationship with the first social formation in his life - the kindergarten group - is very important - his subsequent path, his future fate largely depends on this. The teacher is like a distant adult who is not related to the child, in communication with whom the child acquires a certain experience of social interaction. A psychologist, a music worker, a physical education worker and a social work specialist are also involved in raising a child in a Danish preschool.
In preschool educational institutions
The activities of a social work specialist are based on age (3–7 years) and preparation for school. A social work specialist organizes work with parents of undisciplined children, since they create a problem for their peers. He develops preventative measures for behavioral disorders, applies measures to eliminate symptoms of deviant behavior, and also plays the role of an intermediary communicator between the preschool institution and the family. A social work specialist has the right to contact social institutions, involve medical workers, psychologists, the police, etc. Prevents children from becoming at risk.
A variety of activities in a preschool educational institution is at the same time an important condition and means of introducing a child to social reality, which provides children with the opportunity to actively learn about the world around them, as well as to become part of it themselves. Activities organized in a preschool institution are a condition and means for a child to master methods of understanding the world: motor, play, communicative, artistic and aesthetic, scientific research, creative. Through various types of activities and mastering methods of cognition, children learn more and more new information, express their attitude to what they have learned, accumulate emotional and sensory experience, which encourages them to act, but at a higher level.
It is the joint meaningful activity of an adult and a child that is a school for the transfer of social experience - a school of socialization. The main thing in socialization is activity. Activities in a preschool institution act as a condition and as a means of socialization. Socialization is carried out through games, activities, walks, excursions. In preparation for practical life, much attention is paid to the child’s communication abilities: interpersonal communication, reading stories, dramatization, and drawing competitions. As a result of the implementation of this program, children gain knowledge, they have emotional experience in communication, they begin to evaluate different situations, and they become active in various types of activities.
One of the types of knowledge of reality is communication. Communication, as an activity, takes on a significant burden in the socialization of the individual. By communicating with teachers, parents, and peers, the child receives and deepens his knowledge about objects, their meaning and purpose, about phenomena in nature and social life, about the relationships of people, their variability and dependence.
Communication in joint activities provides a condition for the formation of many personal qualities. This is a school of feelings and emerging assessments; school for the development of cognitive interest, communication with other people; a school of positive and negative experiences of living among people. On this basis, the child’s character traits are formed, he masters the norms and rules of behavior, which are then reflected in deeds and actions. The interrelation of all types of activities of children in a preschool institution is an important component of the socialization of the individual.
Socialization is the process of mastering socio-cultural experience by an individual preparing for independent life in society, the results of which allow him to actively, competently and responsibly participate in various types of social activities. It includes a certain system of values, attitudes, knowledge and skills, norms of interpersonal interaction and rules of behavior [44].
The social process is complex. This is manifested in the fact that the tasks of developing the intellect, feelings, and moral foundations of the individual are formed in interconnection, and it is impossible to separate one from the other. This comprehensive approach, carried out in preschool educational institutions in the process of social adaptation, is especially important for children from disadvantaged families, as they exhibit shortcomings in family upbringing. The readiness of each team member to accept and understand the child’s message, regardless of the form of presentation, is important. This approach helps create a favorable background for communication at various levels.
One of the tasks is the development of communication abilities, since children from disadvantaged families have a disrupted communication system. In a comprehensive approach to the socialization of the individual, techniques such as sketches, writing stories, modeling and analysis of given creative situations, creative tasks for children, mini-competitions, improvisation, etc. are used. Corrective and developmental games that recreate relationships between people teach children to communicate with each other, help them master universal human values, and teach them to treat their peers with respect.
Education of environmental culture in children is carried out in preschool educational institutions on the principles of developmental education, that is, older preschoolers develop a holistic view of nature, an understanding of the role and place of man in it [15].
The child’s intelligence is formed in proportion to the information received. In the content of knowledge on each topic, much attention is paid to the role of man in the creation and development of the surrounding atmosphere. The expansion of the existing knowledge of preschoolers occurs in parallel with the development of interest in the world of adults. Based on stories, children get acquainted with the professional activities of adults, learn about the significance of their work for others, and about the results. For example, together with adults, children can go on a journey into the past and present of various objects: a hammer, a watch, dishes, a book, etc.
A child’s self-knowledge occurs when he realizes his social role in the family, understands connections with loved ones, belongs to his family, to his family tree. In this direction, the topics “Who am I?”, “Me”, “Me and my parents”, “Family”, “If I’m alone at home”, “Good and bad” are studied. Studying these topics allows not only to give children knowledge, but also stimulates their evaluative attitude towards various kinds of actions. During the conversation, an appropriate question is: “What would you do?” and so on.
In stories and conversations about family relationships, children are shown the importance of family for a person. (“Family is attention, care, kindness, love, warmth, help”). This is how children first think about complex but interesting questions for them: “Who was I?”, “Who have I become?”, “Who will I be?”
In modern conditions, especially in the city with the development of the transport system and the growth of crime, the problem of developing independence is especially important. Children at their own level master the basics of life safety during classes in a preschool institution. They become familiar with the rules of relationships with adults outside of kindergarten. “Minutes of safety and health” are held. In the senior group, they study the rules of life safety, in particular the rules of behavior on the street, on the roads, in a public place, in interaction with a stranger (you cannot come into contact with a stranger, let strangers into your apartment, tell them your home address).
Hygiene skills are instilled as part of social and everyday socialization. For example, the topic “Vegetables and Fruits” teaches you to wash fruits and vegetables before eating. Children learn that some vegetables can be eaten raw, while others need to be cooked. They are told about the benefits of fruits and vegetables, all this develops sanitary and hygienic skills. Taking care of things is learned when studying the topic “Furniture” (take care of furniture, do not lift heavy objects, do not swing on furniture - this is dangerous).
The most important area of social adaptation is holding mass events. For example, a competition was held for the best drawing “My four-legged friend.” Teachers, children and parents jointly took an active part in competitions and exhibitions. The competition “Mini-Museum of the Group and the World of Children’s Discoveries” made it possible to develop the creative abilities of children. The mini-museum contains the exhibitions “Museum of Balls”, “Museum of Postcards”, “Museum of Small Sculptures”. The holidays “Older People's Day” (respectful attitude towards the older generation), “Firefighter is the one who puts out the fire” (introduction to the firefighter profession, careful handling of fire) were also held.
The problem of environmental education is being solved. A thematic competition “Queen of Water” was held (the water cycle in nature, the benefits of water and respect for it).
The conditions of a preschool educational institution, the level of qualifications of workers, the social and moral content of programs and their methodological support make it possible to create conditions for effective personal growth of children and social adaptation, continuous improvement of educational work.
Literature:
1. Fundamentals of social work. / Ed. P. D. Pavlenka - M., 2004.
2. Fundamentals of the theory and practice of social work. / Ed. S.I. Grigorieva, L.G.
3. Guslyakova et al. - M., 1999.
4. Plotkin M. M. Social and pedagogical assistance to children from disadvantaged families. //
5. Pedagogy 2001, No. 1.
6. Problems of social work: theory and practice. - St. Petersburg, 2007.
7. Psychology of social work. / Ed. M. A. Gulina - St. Petersburg, 2002.
8. Savinov L.I., Kuznetsova E.V. Social work with children in families of divorced parents. - M., 2007.
9. Dictionary-reference book for social work. / Ed. E. I. Kholostova - M., 2000.
10. Social work. Brief dictionary-reference book. – St. Petersburg, 2006.
11. Social work. / Ed. V. I. Kurbatova - Rostov-on-Don, 2003.
12. Social work: theory and practice. / Ed. E. I. Kholostova, A. S. Sorvina.
13. Terentyeva A.V. Features of the development of a child in an alcoholic family and the possibilities of rehabilitation work. – M., 1998.