- Does your baby absolutely not want to look at the letters in the alphabet?
- Is your child about to start first grade, but can he be forced to read only under pain of being “excommunicated” from the computer?
- Don’t know how to organize classes with a preschooler in such a way as to save your nerves and not completely discourage his interest in reading?
These and other problems in teaching preschoolers to read can be solved by organizing classes in a playful way.
For preschool children, play is the leading form of activity. Therefore, engaging with a preschooler by playing different games is the easiest and most effective way to teach him to read. Before we talk about what games are best to play with your child when learning to read, we will give some general tips on organizing classes.
- Exercise regularly! Let the classes be short (5-10 minutes), but daily. This is much more effective for preschoolers than 45-minute lessons once a week.
- Exercise everywhere. To learn to read, you don't necessarily have to sit your child at a table with books. You can learn letters in the park while taking a walk, drawing them with chalk on the asphalt or looking at signs, helping mom make cookies in the shape of letters, or studying license plates of cars in the parking lot, etc.
- Exercise when your child feels well: he has slept, is active and is ready for new games and activities.
- Constantly create situations of success for your child, praise him more often, focus his attention on what he has accomplished, and do not dwell on failures. Classes should be a joy for the child!
And one more thing you definitely need to know when starting to learn to read is in the article at the link.
What games can be played at different stages of teaching preschoolers to read?
Learning letters.
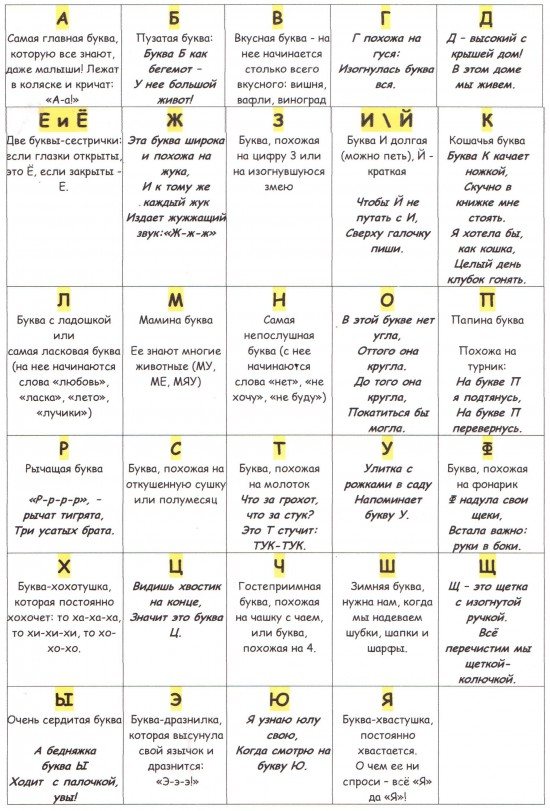
If a child has trouble remembering letters, the best way to learn them is to “revive” them, to create a vivid association with each letter. You and your child can come up with what this or that letter looks like, or use a variety of materials from the Internet and modern alphabet books.
For example, bright, memorable images of letters for children can be found in Elena Bakhtina’s primer (this book contains not only colorful pictures and recommendations on how to tell a child about each letter, but also colorful templates - letters from this primer can be cut out and played with) .
On the Internet, you can find a lot of coloring pages for children with letters similar to this or that object.
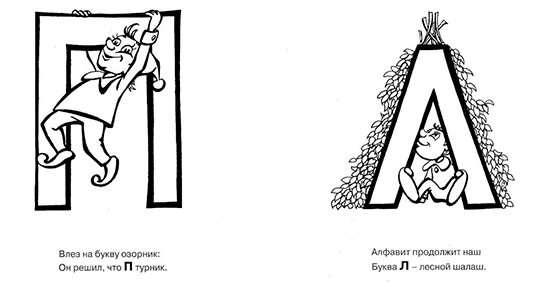
It is also useful in the process of learning letters to repeat short verses that help you remember each letter:
You see the tail at the end, so this is the letter C.
The letter B is like a hippopotamus - She has a big belly!
G looks like a goose - the whole letter is bent.
D - a tall house with a roof! This is the house we live in.
And the poor letter Y walks with a stick, alas!
In my work, I use various “reminders” that children associate with one or another letter. You can actively use them in home lessons or come up with your own.
It is very useful to have a special notebook or album in which the letter you have learned will “live” on each page. In this album you can also teach your child to write, paste pictures with words on the desired letter, add poems and coloring pages, creating a selection of materials for each letter. Children are very fascinated by the process of joint creativity, so actively involve them in creating such an album.

Another option is to make a letter house. Choose any size: it can be very small, made from a couple of cardboard sheets, or huge, as tall as a child. The main thing about it is the special pocket windows for letters. In each “apartment” of the letter house, place a letter with your child. To do this, you will need cardboard letters slightly smaller than each window. Mark in any way which apartments already have “residents” and which ones are still empty.
Attach the already learned letters to the outside of the windows (using paper clips) and invite the child to arrange pictures with words into the studied letters in the windows. For example, “treat” the letters: give the child images of products that he must distribute to the desired “apartments”: put a watermelon/apricot in the window with the letter A, a loaf, an eggplant - in the window with the letter B, waffles / grapes - with the letter B and etc.
Similarly, you can visit letters with fairy-tale characters (Pinocchio - to the letter B, Thumbelina - to the letter D, Mowgli - to the letter M, etc.), “dress” the letters (take the T-shirt to the letter F, jeans to the letter D, pants - letter Ш, etc.).
The main goal of this game is to teach the child to identify the first letter in a word and easily recognize letters already completed.
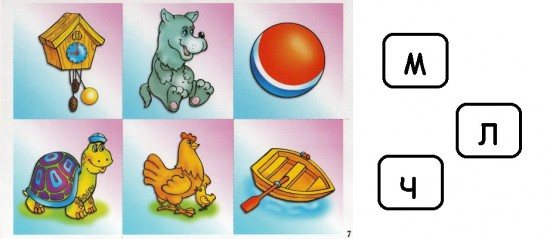
Various lotto and domino games are also great for learning letters. It is better to use lotto without picture prompts, this way learning will be much more effective. You can easily make such a lotto yourself. To do this, prepare sheets with 6-8 pictures on each and cardboard cards with the necessary letters. Let the child draw cards, read the letters and show which player has the picture for the dropped letter.
We add the syllables.
Teaching your child to form syllables may take a little longer than learning letters. The child will have to repeat various syllables many, many times before he masters this skill. So that learning is not a burden for him, but a joy, we continue to play with him. Only now we are playing games with syllables. The main task of this stage is to teach the child to pronounce two letters together.
In addition to syllable lotto, which can be made using the same principle as letter lotto, you can use other homemade games for children to teach them how to add syllables.
— Adventure games (“tracks”).
Adventure games have been and remain one of the most exciting games for children. To make such a game with syllables, take the playing field from any board game. Write various syllables in the empty cells/circles (write in more of those that are difficult for the child). Then play according to the usual rules: roll the dice and go through the squares, reading what is written on them. This way, the child will be able to read fairly long passages with syllables that he would “overcome” in a regular primer with great difficulty.
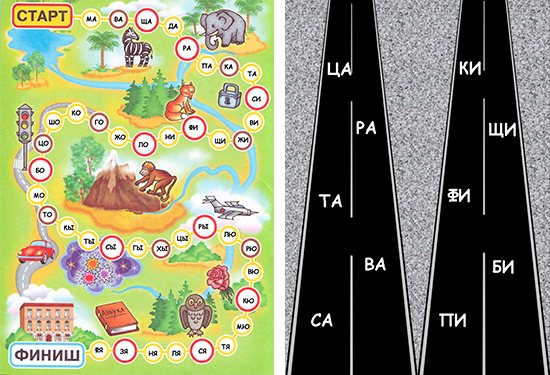
By analogy with adventure games, you can make various tracks with syllables, on which various vehicles will compete: who will pass the track without mistakes and as quickly as possible. To do this, you will need cardboard / whatman paper on which a route with syllables will be drawn, and toy cars / trucks / trains / airplanes. Remember that it is very easy to captivate children by adding a competitive aspect to the lessons.
— Games “Shop” and “Mail”.
Prepare coins - circles with written syllables, as well as goods - pictures with products / things that begin with these syllables. You play first as a seller: invite your child to buy something from you on the condition that he will offer the correct coin for the chosen product (for example, he can buy cabbage for a coin with the syllable KA, kiwi for a coin with the syllable KI, corn for a coin with the syllable KU, etc.).
Then you can switch roles: you are the buyer, the child is the seller. He must carefully monitor whether you are giving the correct coins for the selected product. Sometimes make a mistake, let your child correct you. The buyer can also be any toy; invite your child to teach her how to correctly name coins with syllables.
A very similar game is “Mail”, only instead of coins you prepare envelopes with syllables, and instead of goods - pictures with animals or fairy-tale characters. The child will be a postman, he must guess from the first syllable written on the envelope who the letter needs to be delivered to. In this game, it is best to read syllables that begin with the same consonant, so that the child does not guess the recipient by the first letter.
— Houses with syllables.
Draw several houses, write one syllable on each. Place the houses in front of the child. After that, take several figures of people and, calling the name of each of them, invite the child to guess who lives in which house (Vasya needs to be placed in the house with the syllable VA, Natasha - with the syllable NA, Lisa - with the syllable LI, etc.) .

Another option for this task: let the child come up with names for the little men, place them in houses and write the first syllable of the name on each of them.
- Game “Make a syllable from halves.”
Prepare cardboard cards with syllables, cut them into two equal halves horizontally. The child must put these “puzzles” together and name the resulting syllables.
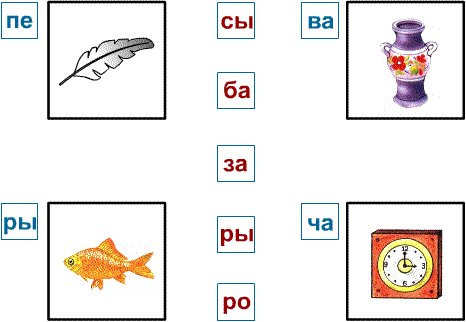
— Game “Finish the word.”
Take several cards with two-syllable words (for example, FEATHER, VASE, CLOCK, FISH). To the left of the picture, place the first syllable of the word. You need to read it clearly, and the child must choose the last syllable correctly. 3-4 possible endings are laid out in front of the child.
More games for learning to read by syllables are in the article at the link.
From simple to complex

Speed reading training is based on the ability to perceive words as a whole, without dividing them into syllables. At the initial stage, use short words consisting of two or three sounds. For example, “house”, “cat”. In the future, the baby will not read them or recognize them by letters. He will see this word in the text and immediately pronounce it. This is the meaning of the speed reading technique.
Preparation for the lesson: write the simplest words on a piece of paper, one at a time. Show them one after the other. As you complete the exercise, gradually increase the pace of changing words. Replace three-letter lexemes with words of four–five–seven letters after a solid assimilation of the material covered.
Words (“house”, “forest”) are replaced with complex ones (“tree”, “car”), then phrases and phrases. Compose sentences from vocabulary familiar to students. For example, he can read “who” and “house” separately. Suggest the phrase: “Who is in the house,” then add “lives” to this. You will get an offer.
You can start reading short texts when the student has mastered the ability to quickly read phrases and phrases. The pace of skill consolidation is different for all children. Do not rush if the student hesitates. Sometimes you need to return to simple, already covered material. This will increase interest in classes, reduce emotional stress, and set you up for success.
And only in this case will the fast reading technique produce results.
Important! For your first books, use bright literature, with pictures, and an interesting plot. A boring curriculum will not do.
We read words and sentences.
Learning to read words (and then sentences) presupposes that preschoolers are already actively working with books, but this does not mean that we stop playing in class. On the contrary, “dilute” learning with games as often as possible, switch from one type of activity to another so that the child gets less tired and learning goes more efficiently. Remember: it is not enough to teach a child to read, it is important to instill in him a love of reading. What games can be offered to parents of preschoolers at this stage of learning to read?
— Search for hidden words.
Lay out a trail of words in front of your child. Invite him to choose only “edible” words (or what is green / what is round in shape / only “live” words, etc.). If the track is long, you can take turns reading the words with your child.
— Traces with words.
Place cut out traces with words around the room (you can use ordinary sheets). Invite your child to walk from one end of the room to the other following these tracks: you can move further only by reading the word you are standing on. The child walks on them himself or with his favorite toy.
- Game "Airport" or "Parking".
In this game we train the attentiveness of preschoolers. Prepare several cards with very similar words so that the child does not guess the words, but carefully reads them to the end (for example, MOUTH, HORN, GROWTH, HORNS, ROSE, MOUTH, DEW). Place the cards around the room. These will be different airports/parking spaces. The child picks up an airplane (if you play airports) or a car (if you have a parking lot), after which you loudly and clearly call out exactly where he needs to land/park.
Skills that should be developed in a six year old child
The degree of readiness for reading depends on the level of intellectual development, mental and emotional maturity of the preschooler. After all, the ultimate goal of a parent is to teach the child not to mindlessly reproduce what is written out loud, but to understand the meaning of what is read. Therefore, before you start learning to read, it is important to make sure that:
- the baby has a sufficient vocabulary;
- his speech is correct and literate;
- The child has no obvious defects in sound reproduction.
If a preschooler's vocabulary is small, his speech is replete with errors or defects, it is too early to start reading. At home it is better to work on the overall development of the baby. Through speech therapy exercises, it is important to teach him to pronounce sounds correctly.

Preparation for school should begin at the age of 5
Reading requires long-term attention span. It is impossible to quickly teach reading or learn the multiplication tables with a child who is constantly distracted. A fidget's concentration skills can be developed in a variety of ways, including making pictures from puzzles, painting, and playing with a construction set.
It is important to teach your child to guide a book with his finger or pointer. If this was not enough, and the baby jumps from line to line or often loses the place where he stopped, it is worth cutting out a window in a white sheet and moving it to the desired area.
For most children, reading is hard work. It is important to ensure a positive perception of this process.

Familiarity with letters should begin at 2-3 years of age.
From the age of two or three, a child should be gradually accustomed to books. It is worth focusing on specimens with bright, detailed pictures that can be viewed and described verbally. At six or seven years old, books with large print will be useful for extracurricular reading.
Tip: It is important to read aloud to your child. Ideally, bedtime reading should become a daily evening ritual. On the one hand, this will bring a lot of pleasure to the child, on the other hand, it will become an example to follow.





