Ekaterina Puchkina
Schemes and card index of buildings based on Lego construction
Card index of Lego building games.
1. Where is Matryoshka?
Visual material: buildings made from Lego (house, bed, car, toy matryoshka
Progress of the game: the teacher moves the Matryoshka in the building : puts it on the roof, puts it on the bed, hides it behind the house, behind the car.
The children explain where Matryoshka is - Matryoshka is standing on the roof.
2. Fourth wheel
Goal: to develop attention, intelligence, evidence-based speech
…
Target.
To train children in design using reduced-scale drawings, in planar modeling, and in the ability to build elementary diagrams; clarify spatial concepts.
Material.
Construction kits, scissors, felt-tip pens.
Progress
Working with the illustration “Buildings”.
Children look at the illustration (Fig. 47).
Rice. 47
Teacher
. Look at the reduced-scale drawings. What is drawn here? What parts does each building consist of?
Offer children a variety of construction parts and organize the construction of any buildings shown in the picture (optional).
Working with illustrations.
Look at the image of the building with your children (Fig. 48 a), analyze from what parts it is built and in what way.
Invite the children to determine which picture (Fig. 48 b, 48 c) shows the parts from which this building was constructed, and give reasons for their choice.
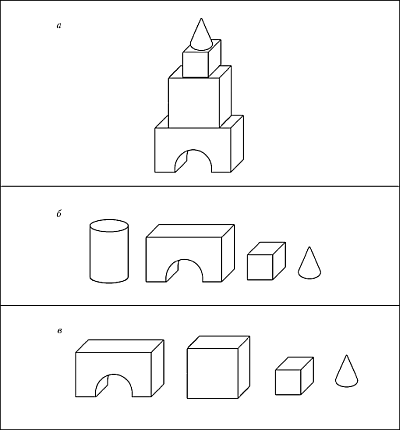
Rice. 48
Tips for a teacher
Play with your children using geometric shapes, building materials and Legos.
Working with illustrations.
Invite the children to find a sheet of paper on which a square is depicted, cut it into geometric shapes according to the markings, then lay out images from the shapes according to the proposed diagrams (Fig. 49, 50).
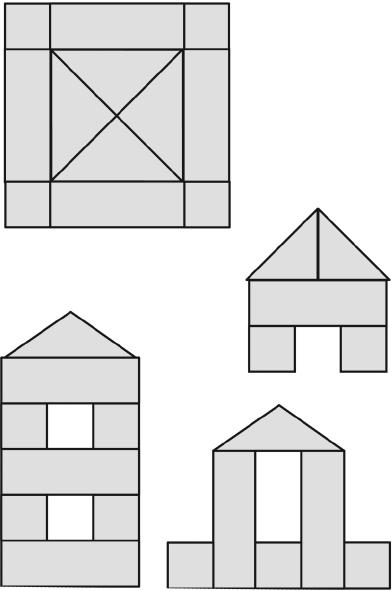
Rice. 49
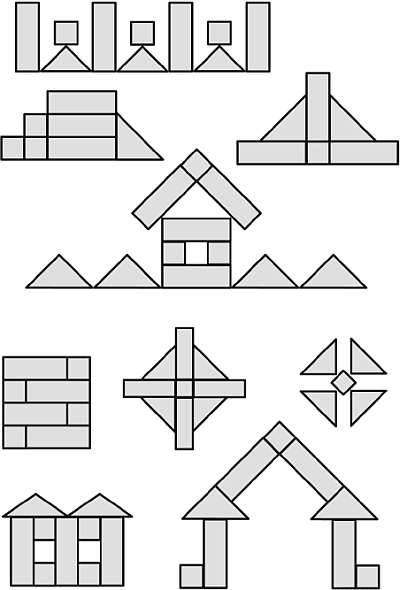
Rice.
50 Encourage children to come up with their own figures, make diagrams (trace the figures with felt-tip pens).
Working with the illustration “Inhabitants of Formandia”.
Invite the children to look at the “photos” of the inhabitants of Formandia (Fig. 51, 52) and ask: “What do the parts do? Who plays ball? How are the cylinders different? Etc.".
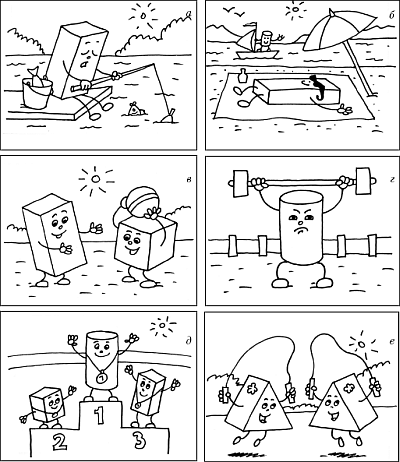
Rice. 51
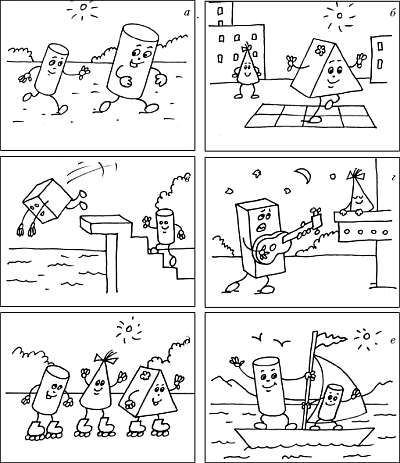
Rice. 52
During the conversation, practice children in defining the concepts: “near”, “far”, “up”, “down”, “above”, “below”, “above”, “down”, “far from each other”, “to the left” ", "right", "in the middle", "next to", "on", "above", "inside"; in determining the properties of objects (large, small, long, short, identical; wider, narrower, wide, narrow, thick, thin, heavy, light, tall, low).
Game tasks.
Remind the children about their friends - animals (Fig. 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10) and offer to visit them. Let the children meet their favorite characters again, remember and tell what construction parts the head of a bear, the body of a fox, etc. look like.
Game “Remove the figure (detail).”
Tasks: “Remove the extra one from three figures” (square, rectangle, circle, etc.); “Remove the extra one from three parts” (cylinder, cone, brick, etc.).
Game “Select the parts that have something the same.”
Children select details that have common characteristics.
Game “Match the figure (shape) with the same large (small) figure (shape).”
Tips for a teacher
Make tasks more difficult by offering children more elements.
Game "Transform the figure."
Practice children in drawing geometric shapes and giving them certain images.
Game "Shadow".
Place the table lamp in such a way that you can get shadows from objects on the wall. Invite children to select objects of different shapes and display them on the wall. Draw their attention to the ball (no matter how you turn it, a circle is always visible). Compare the ball with a flat round object: a plate, a pan lid (the circle is not always visible). Showcase the details of a large tabletop builder (cube, brick, prism, etc.). Encourage children to draw their own conclusions (“When an object has different sides (edges), they have different shadows,” etc.).
Place several parts on the table so that they cast shadows on the wall - clear geometric shapes, for example, put a thick plate on two cubes standing at a distance from each other, and a prism on it.
Invite the children to model a structure using geometric shapes (on tables).
Game "Lay out with figures."
Build elementary buildings on the table and invite the children to lay out their images in geometric shapes (front view). Lead the children to constructing elementary diagrams of buildings, asking them to then trace the shapes with felt-tip pens.
Organize construction using building materials and construction kits. Encourage children to build familiar structures and invent new ones. Point out to them that any object can be constructed in different ways; practice finding ways to design.
Play role-playing games with your children more often using building materials, Lego constructors, etc.
Keyword
Edge.
How to play: Look and tell me which detail is unnecessary.
3. “Describe the detail”
Target:
Lego pieces . The teacher shows a detail, the child must describe this detail. (what is it? what color? what shape? what does it look like)
4. "I am builder"
Target:
Progress of the game: In front of the child is a diagram for building an object . The child builds a building , speaking out his actions (I take a 2*6 green brick, next to it I put exactly the same green 2*6 brick, I secure these two bricks with blue 2*4 bricks, on the right I put a yellow 2*2 brick ,on the left I place a yellow cube 2*2, etc.)
5. "Colorful details"
Goal: Sensory development.
Progress: Children are offered a construction set of different colors (red, yellow, green, blue)
and baskets, you need to place the construction set of the same color into baskets.
6. "What changed?"
Goal: development of attention, coherent speech, ability to describe an object.
Progress of the game: Lego objects are placed on the table in a certain sequence.
Educator: look carefully at the objects, remember how they are located. Then, when you look away, I'll change something. When you turn back, you must carefully look at how the objects are lying and tell me what has changed?
Complication:
Describe an object that is missing
tell about the place where he stood
What sound does the name of this item begin with?
What other objects have this sound in their names?
7. "Multi-colored chest"
Purpose: to teach children how to agree on neuter (feminine)
gender with a pronoun, focus on the ending of the word.
Material: box, subject pictures according to the number of children .
Move.
Educator:
I put the pictures
In a multi-colored chest.
Come on, Ira, take a look,
Take out the picture and name it.
Children take out a picture and name the building that is depicted on it.
8. “Tell me which one?”
Goal: To teach children to identify the characteristics of an object.
Move.
Teacher (or child)
takes objects out of the box, names them, and the children point to some sign of this object.
If the children find it difficult, the teacher helps: “This is a cube. What is he like?
9. "Assemble the Lego "
Goal: To consolidate knowledge of primary colors.
Equipment: Lego bricks of 4 colors .
Four children playing. The teacher scatters Lego , places the boxes, and distributes what color bricks should be put in the box. Children choose the color they will collect. At the command “Start!” children collect bricks. The one who collects the fastest wins.
10.“Assemble the model from memory”
The teacher shows the children a model of 3-4 parts for a few seconds, and then removes it. Children assemble the model from memory and compare it with the sample.
11. Didactic game “Count and name”
Purpose: helps to consolidate grammatical structures.
Progress of the game: - let's play a game, I have one Lego Christmas tree , but tell me how many there will be? For example: one cube - and there will be many - cubes.
-I have one Christmas tree, how many Christmas trees do you have?
-How many Christmas trees does Katya have?(4)
-Katya give one Christmas tree to Lisa. How many Christmas trees does Lisa have?
-Count how many Christmas trees you have?
12. Didactic game “Tower”
Goal: fix prepositions (on, under, between)
Construction in kindergarten according to Federal State Educational Standards
Developing children's imagination and creativity through the use of various types of construction.
The goal of training is not only to master basic manual labor skills, but also to develop the mental and aesthetic education of the child, the development of his creative and technical abilities Objectives: 1. To create in children an interest in design activities and a desire to experiment. 2. Develop imagination, the ability to see the unusual in ordinary objects, develop fine motor skills, thinking, and attention. 3. Develop children's artistic and creative abilities. 4. Develop aesthetic perception of artistic taste. 5. Develop the ability for self-analysis of designs, diagrams, and content of your toy sketches. 6. Teach children various techniques for transforming paper, fabric, natural and waste materials. 7. Learn to create joint decorative structures from different materials. 8. Teach how to construct from a variety of construction sets that have different methods of fastening. Develop installation and dismantling skills. Construction is a form of child activity that develops spatial thinking, allows him to foresee future results, provides an opportunity for the development of creativity, and enriches speech. Children's construction refers to an activity in which children create a variety of play crafts (toys, buildings) from various materials. Types of construction in kindergarten: Depending on what material children use to create their buildings and structures, they are distinguished: Construction from building materials: There are many sets for all age groups of kindergarten. When I go for a walk, I use sand sets; in winter, I use shovels and buckets for building fortresses and slides.

In the group we use ready-made board games for design and construction: various mosaics, lacing, small wooden cubes, paper constructor, tangram, etc. d. Games on the floor: modular cubes, large wooden, plastic cubes, sets: “Farm”, “Railroad”, etc., they are used as an independent type of material for construction, can be used together with each other (cubes and construction set )



Using natural material in my work, I introduce children to its properties, they learn to fill their free time with interesting activities. They learn that sand is free-flowing, but you can sculpt from raw sand, water can be poured into different dishes, and in the cold it freezes, etc. From branches, bark, leaves, chestnuts, cones, nut shells, straw, acorns, seeds etc., you can create entire compositions. By creating forest animals and trees, we immerse children in the world of play. The peculiarity of crafts made from this material is that its natural shape is used. Quality and expressiveness are achieved by the ability to notice similarities in natural materials with objects of reality, and to enhance this similarity and expressiveness by additional processing using tools. This activity is especially important for the development of imagination in a child. The list of different types of construction in kindergarten shows that each of them has its own characteristics. However, the basics of activity are the same: in each, the child reflects objects of the surrounding world, creates a material product, the result of children's activity is intended mainly for practical use.
We recommend watching:
Development of creative abilities of children of senior preschool age Construction for senior preschoolers Do-it-yourself Kuvadka doll for children Summary of a design lesson on the topic “Gzhel”. Preparatory group
Similar articles:
Children's aggression. What to do?
Independent activity of children in the younger group according to the Federal State Educational Standard during a walk
How to take into account the child’s temperament in the process of teaching activities
Methods for early teaching children mathematics
Maria Montessori's method of early childhood development