Published: 10.20.2020 Category: DevelopmentAuthor: editor
- Games by theme
- Interesting for everyone
- Progress of the game: The teacher asks:
- Table: features of choosing games for children of different ages
- Card index of didactic games for middle groups of kindergarten
- Timing game plan
- Tips for choosing
- Handy materials
- Games for preschool and primary school children
- The benefits of educational games
- Types of homemade board games
- Progress of the game. The teacher explains the rules of the game:
- DIY toys for primary school children
Games by theme
- For preschoolers (senior and preparatory groups). Games with rules. Board games, card games, lotto, dominoes, construction sets, puzzles, checkers and chess...
- For young children (junior and middle groups). Development of fine motor skills and coordination, first acquaintance with color, shape and size. Choose by color, screw on the lid, insert a button, braid your hair, games with clothespins, lacing, find a pair, sensory mats and corners, collect beads, felt toys...
- REMP. Formation of ideas about number and quantity, size, shape. Development of spatial orientation, familiarity with time. Count, find the figure, determine the size, logic problems, counting sticks, geocont, tangram, puzzles, geometric lotto, abacus, clock...
- Formation of a sense of rhythm, development of musical perception, familiarity with notes. Musical instruments, homemade noise instruments, games with notes and sounds, musical corners.
- Acquaintance with folk art, artists and paintings. Development of aesthetic perception, color perception, familiarity with the rules of composition. Arts and crafts, patterns and ornaments, palette, drawing games, make a portrait, put together a landscape...
- Homemade baby books, albums, soft, tactile, lapbooks...
- Consolidating knowledge about natural objects and phenomena, animals and plants. Plants, animals, insects, planet Earth, weather, space, water, sand...
- parts of the day, routine and routine...
- Ecological (landscape), traffic regulations, historical, local history, seasonal...
- Traffic rules, signs, traffic lights, cars, street layouts...
- Development of breathing, articulation, formation of correct sound pronunciation, learning to read and write, sounds, letters. Automation of difficult sounds, exercises with sounds, letters and syllables, vowels and consonants, make up a word, games for breathing development...
- Development of coherent speech, grammatical and lexical structure. Based on literary works, based on reference pictures. Mnemonic tables We form adjectives, coordinate words, use prepositions, formulate questions, games based on fairy tales and literary works...
- Attributes and aids for role-playing games, accessories, clothing, furniture
- Do-it-yourself puppet, finger, tabletop and other types of theaters, masks. Theater corners.
- Carnival, theater, dance and other homemade costumes for children and adults
- Clarification of ideas about the Motherland, native land, its history, the Second World War. Regional component.
- Games of different nations. Games of our grandmothers, our childhood, round dance games.
- Invention games. We train analytical thinking, learn to identify, compare, and solve problems.
- Development of emotions, communication skills. Games for a good mood, little girls, for dating. Mood corners
- Active games outdoors and at home.
- Physical exercises, attributes, finger games.
- Sports and physical education corners, equipment for physical education, sports competitions, relay races. Massage paths
Interesting for everyone
What you should pay attention to:
- age of the baby;
- interests;
- possibilities.
Why is it important? Because for some these will be exciting and developing projects, while for others they will be primitive, like completed material, which no one will like and which should not be allowed. Guys, do you know what is interesting to your little one personally? It would be good to take into account children's needs
Some people are crazy about trains, others need bunnies and monkeys. And others need to be taught how to count in a game or checked by traffic rules to see how much they know the rules, so that we remain calm when they go somewhere on their own
Guys, do you know what is interesting to your little one personally? It would be good to take children's needs into account as well. Some people are crazy about trains, others need bunnies and monkeys. And others need to be taught how to count in a game or checked by traffic rules to see how much they know the rules, so that we remain calm when they go somewhere on their own.
We are proud of our children! Their abilities are a reason for our little boast. And homemade strategy board games are a way to unlock a child’s potential and develop it.
Progress of the game: The teacher asks:
Children, do you know what grows in the garden? Let's play a game. I will name different objects, and you listen carefully. If I tell you what they plant in the garden, you will answer “YES”
, if something doesn’t grow in the garden, you say
“NO”
. Whoever makes a mistake loses. The teacher begins:
Carrot. (Yes)
;
tomatoes (yes)
Cucumbers. Yes.
Domino
Goal: to consolidate children’s knowledge about different machines that help people, name them correctly and select paired images: passenger car, truck, combine harvester, crane, etc.
Progress of the game: The teacher shows the cards to the children, names the cars and draws attention to the fact that the card shows two cars separated by a vertical stripe. Then he distributes 4-6 cards to the children. Here I put my card, what cars are drawn here
Tractor and crane. If you have the same ones, put your pictures next to the cars.
Now what are the pictures here? Who has these? Place them in one row. Children find identical pictures and place them at the end of the resulting row. The game continues until the children have no pictures left. Then a new rule is introduced, the children are again given the mixed pictures and the order is established, the pictures are laid out one after another. Whoever does not have a suitable one misses his turn, the one who puts all the pictures first wins.
What grows where?
Goal: To consolidate children's knowledge about plants; develop the ability to establish spatial connections between objects; group plants according to their place of growth, develop activity and independent thinking.
Progress of the game: Players receive a large map with different landscapes; small cards are in a box. At the driver’s signal, the children select small cards in accordance with the pictures on the large card. The winner is the one who quickly closes all the empty cells and names the plants correctly (on large cards there are forests, fields, gardens, and vegetable gardens.)
The names of cereals and mushrooms will be difficult. The guys exchange cards, small cards are shuffled, the game continues.
Let's plant a flower
Goal: To navigate in space, to distinguish between the concepts of “edge”
and
"middle"
.
How to play: 5-6 children sit at the table. On each table there is a tray filled with sand and a box containing many colorful paper flowers. “Children, now we will plant flowers,” says the teacher. -You have a lot of flowers in the box, you need to plant them beautifully, in a row, and not haphazardly. The teacher monitors the work of all the children, and each child says where he will plant the flower in the middle or on the edge.
Card index of board-printed games in kindergarten
The card index of ready-made games is grouped according to the age of the children, which is reflected both in the tasks being solved and in the content of the game.
First junior group
For this category of kids, it is appropriate to use materials that involve putting together whole pictures from individual pieces, usually an even number (from 4 to 6). In addition, you need to use mosaics that develop fine motor skills. This type of game involves folding pictures based on a pattern.
Mosaic “Fold the picture” develops fine motor skills of children
Another important nuance regarding the method of playing the game: at first, the kids complete the task themselves with the help of an adult, then without an assistant. The last, most difficult stage of the work can be folding pictures at speed, but without a competitive moment. Paired or group games are not introduced in classes; each participant must have their own set of materials to avoid the possibility of quarrels.
“Who hid in the cubes?”
- introduce children to the main representatives of domestic and wild animals; develop the skill of combining elements into a single plot;
- increase cognitive motivation.
Instructions:
- “Guys, here is a picture of an animal, but it has split into 4 parts. Consider them." Note: if this is not the first time that children have performed such a task, then you can ask them to name those parts of the body that are on the faces of the cube.
- “Now try to fold the little animal. To do this, find a cube with a head on it and place the rest on it.”
- Together with the children we name the resulting animal.
Mosaic, geometric shapes
- consolidate knowledge of basic geometric shapes (square, circle, triangle, oval);
- help kids learn to correlate a verbal image with an image;
- develop attention and memory;
- cultivate persistence in work.
Instructions:
- Children receive a set of geometric shapes and a base (cardboard or wood or plastic) with indentations. “Guys, name the shapes corresponding to each indentation.”
- “Now find among your figures those that fit the shape on the base.”
In the first junior group, children do not play together, but side by side
Second junior group
In addition to the methodological subtleties characteristic of the first junior group, an element of team play is added.
Dominoes "Animals"
- consolidate children's knowledge about domestic or wild animals;
- teach to correlate the visual and auditory images of a word;
- develop attention, speech;
- develop the ability to work in a team.
Instructions:
- Each kid gets 4-5 dominoes.
- The teacher places the first bone.
- The kids take turns putting matching pictures of animals.
At this stage, you can assign tasks to complete in pairs.
In the second younger group, you can gradually introduce elements of work in pairs
“The Third Wheel” (theme “Dishes”)
- teach children to separate an extra element from those united by some characteristic;
- develop logical thinking;
- cultivate patience.
Instructions:
- Children receive 3 pictures.
- “Guys, look at the pictures, name the objects.”
- “Which element and why is extra?”
Middle group
When working with this age group, the emphasis is on speech development.
Therefore, all games involve detailed commentary along the way.
"What season?"
- consolidate children’s knowledge about the seasons and their defining features;
- develop speech and logical thinking.
Instructions:
- The teacher gives the children 2-3 pictures depicting characteristic signs of a particular time of year (for example, children are making a snowman, trees in the snow, a janitor clearing paths).
- “Guys, don’t show your pictures to anyone. We will guess what is depicted on them.” Turning to the child, he asks him to describe what is drawn on the first card.
- Whoever guessed correctly names the time of year.
- The one who made the guess shows the picture to make sure that the season is guessed correctly.
Game "What time of year?" develops logical thinking and speech abilities of the child
"Paired pictures"
- train to find similarities and differences between two pictures, learn to select the same ones;
- develop the ability to follow the rules of the game.
Instructions:
- The teacher takes 2 pictures that depict the same objects. He asks what it is and also gives additional information (they are the same).
- Then the teacher hands out 6 cards to the children and asks them to find pairs.
The game “Paired Pictures” develops the ability to combine objects based on certain characteristics
To make it more difficult, you can arrange the pictures in a column, give the kids a set of 3-4 cards and ask them to find pairs for their children in a common column.
Senior group
A distinctive feature of working with children of this age is that children need to be taught to compare objects according to a unifying characteristic.
"Numbers"
- teach ordinal counting from 1 to 10;
- learn to compare the number with the number of objects in the picture;
- train voluntary attention, cultivate patience.
Instructions:
- Children receive 2-3 central blocks with images of numbers and 10 figured cards with images of objects ranging from 1 to 10.
- Kids must connect the central block with matching shapes to make a solid circle.
The game “Numbers” trains counting skills and voluntary attention
Preparatory group
“What does the doctor need?”
- generalize children’s knowledge about professions and expand knowledge about the purpose of certain work-related items;
- develop fine motor skills, speech, and the ability to logically construct statements.
Instructions:
- There are cut-out pictures (for example, tools) on the table.
- Children collect entire episodes.
- Explain the purpose of the images obtained.
“When does this happen?”
- consolidate children’s ideas about the times of day;
- cultivate patience and attention.
Instructions:
- The child receives a set of pictures depicting scenes related to different times of the day.
- Children take turns saying what time it is and describing their picture (for example, “This is morning because we are doing exercises”).
Game "When does this happen?" reinforces preschoolers’ ideas about the times of day
Table: features of choosing games for children of different ages
| Age/group | Features of development | Games | Examples | Time | Notes |
| 2–2.5 (first minor) | Games must have plot pictures |
|
| Up to 5 minutes | If the regime allows (there is time before bed or before meals), then it would be good to change this activity to a more active one |
| 3–4 (second youngest) | Interest in games in pairs |
|
| 7 minutes | The work is aimed at speech development |
| 4–5 years (average) | Work in small groups (3–4 people) |
|
| 7–8 minutes | |
| 5–6 years old (older) | Conscious participation in team games |
|
| 10 minutes | Combining physical activity of an adult and a child |
| 6–7 years (preparatory) | Intolerance towards adult help |
|
| 10–12 minutes | Children learn to comment on their actions with high independence in completing tasks |

The didactic game “Fold the Square” fosters patience and perseverance in children
7. Printed board games
- Cheerful pencil
- Magic wands
- Tic Tac Toe
- Sea battle (1st option)
- Sea battle (2nd option)
Board games are a special category of games that, unlike others, require from participants not only attention, logical thinking, reaction speed and observation, but also certain skills in using a pencil or pen. The game forces the child to think first and only then draw certain objects on a sheet of paper, since it will be difficult to erase the drawing later.
Printed board games are quite complex, so children can only learn to play them from the age of 5-6. But, despite this, they are very interesting and are always perceived by children with pleasure.
Purpose of the game:
develop attention, observation, memory, the ability to quickly find changes and missing elements in a subject.
Equipment:
sheets of blank paper, preferably checkered, red and blue pencils for each participant in the game.
Age
: 5–6 years.
Progress of the game:
children sit at tables in pairs, receive sheets of blank paper and carefully listen to the rules of the game, which consist in the need to give instructions to a partner about drawing a particular line (for example, lead to the right, and now – up).
After this, each person is left with a certain broken line drawn in red pencil on the sheet. Now the participant who gave commands to his partner takes a blue pencil himself and begins to repeat the existing drawing on his sheet of paper. A special rule is that the length of the lines from which the polyline is constructed should be approximately the same.
The next stage is that the participants who played in pairs change roles, and now the other child gives instructions that must be followed. At the same time, children not only repeat concepts such as “up”, “down”, “right”, “left”, but also learn to repeat the drawing on another sheet on their own, which requires certain attention and the ability to navigate on a plane.
Purpose of the game:
teach children to group objects according to their properties and belonging to one category or another, improve the ability to generalize, develop memory, attention, and logical thinking.
Equipment:
10-15 counting sticks, a pencil, an eraser and a piece of white paper.
Age
: 5–6 years.
Progress of the game:
The teacher offers the children the following task: they need to fold the prepared sticks into a certain shape, for example a triangle or a rectangle. He then asks how many sticks it took.
When the guys answer the question, you should invite them to draw the same figure on a piece of paper, and it should be about the same size. If it is still difficult for the children to complete such a task, then a ruler can come to the rescue, which they usually already know how to use.
You can also offer to assemble a square from counting sticks, ask the children to name its distinctive features and show how they can turn it into 2 triangles using only one stick.
When the children complete this task, it is necessary to ensure that they correctly transfer these figures onto pieces of paper using a pencil. During the lesson, special attention should be paid to the rules of using a pencil and an eraser, and show how to use a ruler correctly so that the lines are straight.
Purpose of the game:
develop attention, memory, the ability to focus on a certain subject for quite a long time, teach children to distinguish concepts such as “diagonally”, “vertically”, “horizontally”, and systematize previously acquired knowledge.
Equipment:
sheets of paper for each participant, pencils or pens.
Age
: 6–7 years.
Progress of the game:
The leader invites the children to learn how to play a very interesting game and begins to explain the rules, which are that it is necessary to line up a series of crosses or toes diagonally, vertically or horizontally.
But first you should explain the meaning of these words, since not all children may be familiar with them.
At the next stage, the teacher shows how to draw the playing field so that it consists of 9 squares. Only then can we begin to explain the game itself. To do this, it is advisable to divide the group of children into 2 teams, one of which will be a “toe” and the other will be a “cross”.
Then the leader shows how the crosses or toes can be placed on the playing field, and which combination turns out to be winning.
It is better to do this on the board so that the children can see everything clearly.
When the children have mastered the rules of the game well, you can play as a whole group several times and only after that invite the children to play independently in pairs. But during a single-player game, the teacher must constantly monitor everyone and help if necessary.
In the summer, if the children have crayons and smooth asphalt on the playground, the game can be organized on the street.
Purpose of the game:
develop memory, attention, observation, quick thinking, the ability to find small changes that have occurred in objects, develop children’s speech, activate children’s vocabulary and teach the correct construction of sentences.
Equipment:
blank sheets of checkered paper with playing fields drawn, pens or pencils, a large sample of the playing field attached to a magnetic board.
Age
: 6–7 years.
Progress of the game:
The teacher invites the children to divide into small groups of 4–5 people. He gives each of them a piece of paper with playing fields 10 x 10 cm drawn on them, consisting of 100 cells.
Then the leader explains what the numbers from 1 to 10, located vertically to the left or right of the playing field, are for, as well as the role of the letters written on top of each cell from A to K.
Only now the children begin, with the help of the teacher, to place the ships on the field in such a way that they do not touch each other. There should be: single-deck - 4 pieces, double-deck - 3, three-deck - 2 and four-deck - 1.
The ships can be positioned however you like, the main thing is that they are within the boundaries of the field.
Now you can start the game, which involves two participants or two teams. The rules of the game are to determine the location of the ships as quickly as possible and hit them with a projectile that flies strictly along the specified route, for example A-5 or B-10.
If a player hits a ship, but there are still entire decks left, then the other player replies that the ship is wounded. When all the decks are hit, the ship is considered dead.
If the player hits, then he has the right to one more move, but if he missed, then he passes the move to the enemy. The winner of the game is the participant who can “sink” all the ships before the enemy.
Purpose of the game:
develop memory, attention, observation, quick thinking, the ability to find small changes that have occurred in objects. develop children’s speech, activate children’s vocabulary and teach them how to construct sentences correctly.
Equipment:
blank sheets of checkered paper, blue and red pens.
Age
: 6–7 years.
Progress of the game:
The teacher invites the children to divide into groups of 2–4 people.
After this, you should take pieces of paper and fold them in half so that the corners coincide with each other. You should unfold the sheet and randomly place 10 small ships in the form of boats (about 1 cm in length) on each half.
One side will be your field, and the other will be the enemy’s field.
Now you can start the attack. To do this, the child must place the mine (draw a small circle and color it well) so that it is located exactly opposite one of the enemy ships.
Then the piece of paper is rolled up again and the same child tries to draw a mine on the reverse side so that a trace of the paste remains on the opponent’s field.
If this trace is superimposed on one of the ships, then it is considered lost and is crossed out. This means that the baby gets the right to take a second turn.
But if the mine does not hit the ship, then the turn goes to the opponent.
There are special rules of the game, which are that you cannot draw a mine on your ship. If this happens, he is considered killed.
The player who is the first to identify all enemy ships wins the game.
Table of contents
Card index of didactic games for middle groups of kindergarten
In the middle group, a card index of games can be compiled according to the following topics:
"Child and health." To study the daily routine, children are asked to look at pictures with images of the daily routine and arrange them in order and comment: the morning begins with exercises, breakfast, etc.
This game introduces children to a healthy lifestyle, develops speech, attention and memory.
"Healthy foods". The following games will help you remember fruits and vegetables: children take a dummy of a product out of a bag and describe it (“this is an apple, it’s round, red and smooth); the teacher names the characteristics of the fruit/vegetable, and the children guess it; children try foods with their eyes closed and name them, say what the fruit/vegetable tastes like.
"Dangerous Items"
The purpose of such games is to introduce children to dangerous objects that should not be played with or taken without the permission of adults. For example: the teacher prepares cards with dangerous and safe objects and asks the students to put them into two groups, explaining their choice. You can complicate the task by offering to tell the children what injuries dangerous things can cause (cuts, bruises, etc.).
Goals and objectives of board and printed games
A type of primary activity of preschool children, aimed at an analytical approach to solving a game situation, presented in the form of a visual aid, is called a printed board game.
Such games include:
- mosaics;
- didactic games in pictures (for example, a set of objects for the game “The Third Wheel”);
- folding cubes (in which the overall image is folded by turning over the faces of each cube);
- puzzles;
- lotto;
- domino;
- checkers, etc.
Board and printed games are an important part of the subject-development environment in kindergarten
The goals of introducing board-printed games into the educational process are:
- consolidation or development of acquired knowledge;
- development of thinking processes, attention, memory, imagination and speech;
- training in perseverance, discipline and the ability to finish a job;
- fostering compliance, a tolerant attitude towards partners, and the ability to cooperate.
To achieve these goals, it is necessary to systematically solve the following tasks:
- consolidate knowledge about objects, their purpose, species differences;
- teach preschoolers to generalize objects according to essential features and identify relationships between them, as well as to compose parts into a whole;
- identify children’s interests (for example, compiling collective pictures from mosaic parts, putting together puzzles on a particular topic, etc.);
- develop the ability to play in small groups (children play in pairs, in threes, but if there are many participants in the group, it becomes difficult for them to decide on their role in the team - showdowns and quarrels begin);
- develop the skill of choosing play partners (by temperament, mood, etc., and not just by appearance);
- methodically competently build a system of interaction between children (the teacher plays the role of guiding the game process, but not the leader);
- encourage children's independence.
This is interesting. Scientists have proven that the structure of the human brain in childhood makes it possible not to forget anything, but to put it away in a kind of “portfolio.” Over time, all lost situations will be consolidated, assimilated and become a habit of the baby’s behavior.
Timing game plan
All elements of the educational process in kindergarten must be strictly timed. Only in this case there will be no violations of discipline, and all new information will be perceived as efficiently as possible. The game plan consists of 3 important stages:
Introduction – 1–2 minutes. The teacher explains or reminds the rules of the game and distributes the necessary materials. If they are already prepared on the tables, then the purpose of each is explained. The game itself takes 3–7 minutes. The teacher helps and guides the children’s actions if necessary. Summing up - 1–2 minutes
At this stage, it is important to praise each participant, regardless of the success of the results of his game.
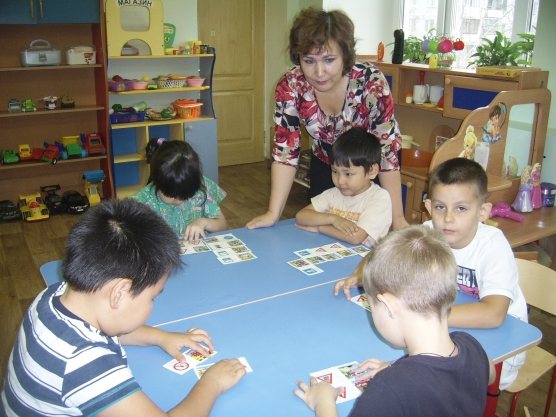

Even the lotto game is played under the supervision of an adult
An example of the timing of the game “Where can I buy this?”
When studying the topic “Shopping,” the teacher explains to the kids in which departments of the store this or that product is sold. The purpose of this game is to consolidate children’s knowledge about various products and departments of stores (grocery, hardware, etc.), develop the ability to navigate the environment, and cultivate a desire to help adults.
- Explanation of the rules: children discuss where mothers buy certain products, then the adult hands out small pictures of the products, and hangs a large poster on the wall depicting various departments of the store (2 minutes).
- Children arrange the pictures into the appropriate sections, explaining their choice (2 minutes).
- Summing up (3 minutes).

Game “Where can I buy this?” develops the preschooler’s ability to navigate the world around him
Example of a summary of the games “What Shape” and “Loto”
Author Makrushina Tatyana, MDOU kindergarten "Fairy Tale", Saratov region, r.p. Dergachi Name Fragments of board and printed games “What kind of shape” and “Loto” Age of children, group 3–4 years old, junior Description of the game “What kind of shape”
Draws children's attention to the sizes of “building materials”. The teacher asks each child to take one geometric shape and name it. Children play independently, constructing any buildings from existing objects...>
Description of the game "Loto"
Then he clarifies where the cherry tree grows. The children answer that they are in the garden. The teacher asks where flowers grow (in the forest, in a flower bed, in a meadow), cucumbers (in a garden bed) and other vegetables. The teacher gives the children to look at cards that depict a vegetable garden, a garden and a flower garden. “Now you will play so that everything that grows in the garden appears in the garden, everything that grows in the flower garden ends up in the flower garden, and everything in the garden ends up in the garden. All objects must fit into their squares on the map.” Whoever closes all the squares first wins. Children exchange cards and the game continues. This game is used when the task is to systematize and consolidate knowledge about other objects, for example, dishes, furniture, clothes, shoes, etc...>
Quote from: https://www.maam.ru/detskijsad/nastolno-pechatnye-igry-chast-3.html
Printed board games in kindergarten are actively used both directly in the classroom and during leisure time. This type of activity helps not only to practice and consolidate acquired knowledge, but also develops cognitive processes, speech, fine motor skills, develops patience and the ability to follow rules. In addition, children enjoy mastering different forms of games: individual, pair and collective, which develops the skills of constructive interaction with peers.
On the issue of developing attention in children of the younger group in board-printed games
The article discusses the features of the development of attention in early preschool age, the role of board and printed games and the conditions for organizing work with them for the development of attention.
Keywords: attention, primary preschool age, didactic games, board-printed games
At preschool age, the child actively develops in various types of activities. The most important component of activity regulation is attention. Developed attention creates the necessary basis for successful learning and development.
The problem of attention in Russian psychology has been considered from different theoretical positions. Attention is direction and concentration on any activity. Features of the development of attention in preschool age were considered by L. I. Baskakova, L. S. Vygotsky and others [1,3].
Early preschool age is a period characterized by rapid distractibility, instability of attention, and difficulty concentrating on unattractive objects.
In early preschool age, an adult directs the child’s attention with the help of words, creating additional “arrow” instructions for him to the things around him and developing stimulus-instructions from words. The child begins to participate in this direction and himself begins to use this word or sound as a means of direction, that is, to draw the attention of adults to the object of interest to him.
Children of primary preschool age are able to distribute their attention to a small extent. Switching attention in younger preschoolers can also be difficult, especially if this switching is frequent and to different objects. The volume of attention allows you to keep a minimum number of objects in your field of activity.
The lack of targeted work on developing the attention of younger preschoolers can lead to insufficient development of attention in older preschool age. Therefore, it is necessary to use a variety of means, methods and techniques of working with children that will contribute to the development of voluntary attention. In our opinion, one of such means can be a didactic game.
Today, it is undeniable that didactic play is a powerful means of comprehensive development of a child’s personality, a source of mastering various knowledge and skills. The foundations of the theory of play activity were developed by such prominent psychologists as L. S. Vygotsky, D. B. Elkonin [3,7]. The issues of substantiating the psychological mechanism of didactic games and the peculiarities of the influence of the game on the mental development of children were given special attention in the studies of A. K. Bondarenko and others [2].
One of the types of didactic games in which favorable conditions are created for the development of attention of children of primary preschool age are board-printed games. This is due to the fact that in them the child naturally concentrates attention on the material of the game, looking at the pictures; switching of attention develops when changing game material; Distribution of attention is formed when the child simultaneously holds several objects in the field of attention.
D. V. Mendzheritskaya defines didactic games as a type of games with rules, specially created by pedagogy for the purpose of raising and teaching children. These games are aimed at solving specific problems of teaching children, but at the same time, the educational and developmental influence of gaming activities is manifested in them. It contains opportunities for developing the attention of preschoolers, there is a subordination of motives and purposefulness of actions, which has a positive effect on the development of concentration, volume, and switchability of attention of older preschoolers [6].
The basis of printed board games is printed material, presented in the form of paired pictures, lotto, and dominoes. The key principle in printed board games is the principle of clarity, when children are offered not the object itself, but its image.
In early preschool age, the use of printed board games is quite effective, since not all children have well-developed speech to explain something or answer questions. At the same time, on a non-verbal level, a child can fully cope with many tasks. In addition, in early preschool age, the use of board and printed games is closely related to the development of children's thinking, which is characterized by a high degree of specificity. In accordance with this, children need to operate with concrete rather than abstract images.
The main types of board and printed games in early preschool age include the following:
- Selection of pictures in pairs. In this game, a child can select identical objects based on some characteristic, and can also perform a more complex task when he needs to combine pictures not only by external features, but also by meaning, for example, if he needs to find two cars among all the pictures, etc. etc. To do this, he needs to combine them according to a key characteristic into one type of object.
- Selection of pictures (classification). In these games, children are asked to establish connections between individual objects and correlate pictures based on common features. Various board and printed games contain memorization tasks. In accordance with this, the following type of board and printed games is distinguished.
- Games for remembering the composition, number and location of pictures. In these games, children need to remember the content of the picture and then guess, for example, the picture that was turned down, or they need to remember the picture and then recognize it from a number of other images.
- Making cut up pictures and cubes. This type of games is aimed at developing children’s logical thinking, developing their holistic perception, and the ability to compose a whole object from parts. The options for conducting these games are varied: from individual to pairs and subgroups. It is important for the child to become familiar with the content of the material, since understanding what is shown in the picture helps the child complete the tasks assigned to him.
- Description, story based on a picture showing actions. In such games, children are asked to illustrate what is shown in the picture, for example, to illustrate what sounds this or that animal makes, etc.
- Domino. In games of this type, children select a pair based on the principle of similarity, that is, they find the same picture and build a sequential row by selecting identical pictures.
- Lotto is a game in which you need to make certain moves and select the correct pictures. This game teaches children to interact with each other, to be attentive and to pay attention to the actions of other children.
All types of board and printed games can have a positive effect on the development of children's attention.
Let's consider how you can develop individual properties of attention in children of primary preschool age when using board and printed games.
The development of the volume of memorized material will be facilitated by board-printed games in which children need, for example, to sequentially remember several objects depicted in pictures; gradually this volume of pictures can increase. Also, the development of children’s memory capacity can be facilitated by working with several pictures at once, for example, in the process of classification, when the child, on the one hand, performs a task to find the necessary picture, and on the other hand, he needs to keep other pictures in the field of attention and correlate the main one with them, according to essential features.
A. V. Zaporozhets believes that the development of stability of attention of children of primary preschool age in board-printed games can be facilitated by solving problems associated with comparing pictures according to one or another attribute, when the child needs to focus on the content of the picture, analyze it, identify features and compare their. It will also contribute to the development of sustained attention by conducting board-print games in a subgroup of children, in pairs, when the child needs to monitor not only his own actions, but also the actions of his peer [4].
L. I. Baskakova believes that the development of attention distribution in board-printed games can be ensured by moving from one step of the game to another step, changing pictures, playing games with several pictures at once, among which it is necessary to carry out sequential analysis and select the desired one, can be facilitated picture [1].
According to O. N. Zemtsova, switching attention in printed board games develops when the printed material itself changes, when a child, having completed one task, picking up one paired picture, takes the next step and picks up another picture. It should be noted that the process of gaming activity in a printed board game requires sufficient concentration of attention [5].
At primary school age, a natural condition for holding a child’s attention is the presence of pictures that are sufficiently bright, colorful, understandable and attract the child’s attention. At the moment when children look at pictures, they involuntarily keep their attention on the content of this picture. In addition, it should be noted that since printed board games are a type of didactic game, the main components of the didactic game management methodology are applied to them.
A.K. Bondarenko points out that when conducting board-printed games, the child is also given a game task, and a game rule applies, according to which the child performs certain actions.
- The game task is the main element of the game, to which all other elements are subordinated. For children, the learning task is formulated as a game task. It reveals a program of game actions, and with its help stimulates the desire to carry them out. Often the game task is embedded in the name of the game itself.
- Play activities are ways of demonstrating a child’s activity for play purposes. Depending on the age and level of development of children, play activities also change. The effect of the game depends on how varied and meaningful the game actions are.
- Rules - they ensure the implementation of game content. Within the same game, the rules vary. They can guide behavior and cognitive activity, determine the nature and conditions for performing game actions, establish their sequence, and regulate relationships between players. They can also limit the amount of physical activity, etc. [2].
Thus, we can conclude that board and printed games create favorable conditions for the development of attention in children of primary preschool age. In accordance with this, we can identify a number of pedagogical conditions, the consideration of which when conducting board and printed games will contribute to the development of children’s attention. These conditions include the following: selection of a set of board and printed games for the development of all properties of attention; development of content and techniques for step-by-step guidance in the development of attention in board and printed games; taking into account the level of development of children's attention when playing games
Literature:
- Baskakova L. I. Attention of a preschooler, methods of its study and development. Studying the attention of preschool children. M.: Voronezh, 2005. 98 p.
- Bondarenko A.K. Didactic games in kindergarten: Book. for a kindergarten teacher / A. K. Bondarenko. -2nd ed., revised. M.: “Enlightenment”, 2011. 148 p.
- Vygotsky L. S. Psychology of child development. M.: “Sense” 2008. 512 p.
- Zaporozhets A. V. Psychology and pedagogy of preschooler play. M., 2003. 162 p.
- Zemtsova O. N. Find the differences (we develop attention for 3–4 years). M., 2007. 109 p.
- Mendzheritskaya D.V. To the teacher about children's play. M., 2008. 128 p.
- Elkonin D. B. Psychological development in childhood. - M: NPO “Modek”, 2005. 416 p.
Tips for choosing
A board game is usually perceived as a pretty good gift, but (like any other product) it can be chosen either well or inappropriately.
Since it is given so that the child receives useful skills of his own free will, and not when he is forced, it is very important that the child likes the game, so that he becomes interested in it and begins to play regularly

There are some simple tips on how to achieve your goal:
For a child, play is a holiday. Even if she makes him think deeply, he himself still gets pleasure not from the process of solving a complex problem, as in chess, but from the surroundings. For this reason, a board game for a small child should be bright and beautiful, and also involve a certain legend, reminiscent of an interesting fairy tale.
Handy materials
Can I ask your opinion? Friends, what material do you prefer for crafts?
I will probably express the general point of view that this is the one with which it is easier or more interesting for you to create something at home.
And I will voice one more point. Sometimes I don't take new or valuable material. Even junk is used. Something that is kept by chance, or in anticipation that I can make something useful out of it. For example, corks from plastic bottles or wine, an old chessboard whose pieces are lost, buttons, pebbles, etc.
Well, when we have gathered everything: an understanding of what we have to construct with the children, for what purpose and for what purposes. We found out what materials we could use. We didn't forget the good mood. Now all that remains is to get down to business.
Games for preschool and primary school children
- Educational games
- Didactic games with the keyboard
- Senior group
- Preparatory group
- Middle group
- Junior group
Showing publications 1-10 of 69745.All sections | Children's games
New
Playing with natural materials while walking

Everyone has long known that in preschool age the leading activity is play. Through play, children gain the necessary knowledge, skills and abilities for further development. Many different educational games for preschoolers have been invented. Playing with natural materials evokes...
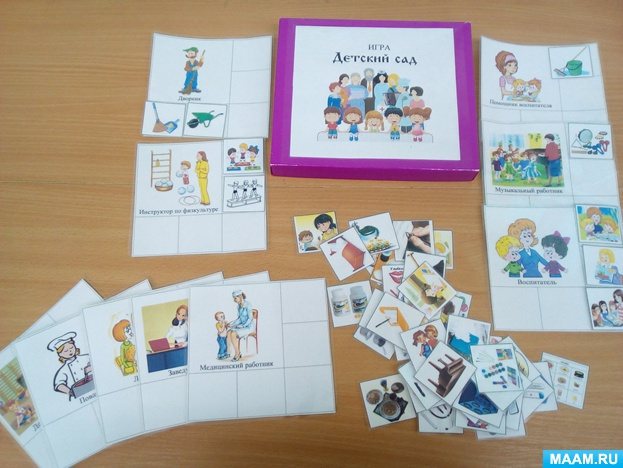

Theatrical and play activities as a means of developing the communication abilities of young children Educator Ilyunicheva Svetlana Alekseevna MDOU combined kindergarten No. 58 “A child’s ability to communicate positively allows him to live comfortably in the company of people...” What are communication abilities? Communication is an element of communication during which an exchange takes place...
Visual material
Visualization is one of the main principles of gaming activities and the entire educational process in kindergarten. To carry out this work, certain visual aids are required. In other words, to create a picture from a mosaic, you need its diagram, and to create a picture from a puzzle, you need a solid image as a hint.
Games based on visual perception of information are associated with games such as:
- plot or symbolic pictures, images for the development of speech, mastering the basics of mathematics, familiarization with the world of things and nature, etc.;
- puzzles (including three-dimensional ones);
- lotto and domino sets;
- cubes;
- mosaics;
- “Adventure games” with chips and dice.
Puzzles can be of different shapes, but it is important that each child receives a separate set
This is interesting. You can make simple puzzles with your own hands. It is enough to cut postcards with a plot that is understandable to everyone into several uneven parts.
In order not to lead to hysterics, immediately stipulate that each child will have his own set of props, for example, a separate puzzle. If kids see such toys for the first time, then you need to give them time to get to know each other, and only then move on to playing. Please note that in younger groups, the folding process itself is important for children, so the picture should be the same - then there will be no tears. In older groups, you can give each student their own puzzle, and the pictures will be different. If time allows, then include in the game the stage of exchanging details: this way the kids will be able to put together different stories, and training motor skills and thinking will be more productive.
Another important point. For some games, for example, lotto, dominoes, it is assumed that there is one set for a certain number of players. But there may be more children in the group. In this case, you should take care of purchasing not one, but two sets. And divide the playing chips (or other game materials) equally.
Video: example of a printed board game “Opposites” in the form of a puzzle
The benefits of educational games
The games in question develop:
speech - children hear the speech of an adult and other preschoolers, therefore, their vocabulary is replenished
In addition, the guys answer questions, describe something, reason, therefore, the existing speech data are trained and improved;
thinking - preschoolers expand their knowledge about objects, phenomena, flora and fauna, learn new information, can compare existing experience with what they have received, train memory, logic, and mathematical abilities;
attention - children train listening skills and understanding what needs to be done, how to play the game correctly, therefore, they become more attentive, focused, and are able to regulate their actions;
physical qualities - the motor system develops, children become mobile, active, learn to control their movements, manage them, the child’s psyche is formed in terms of the ability to be active in life.
Katamino
Gigamic

When the child first saw this game away, I simply didn’t hear him for about an hour. Then we bought it, and every morning the day began with concentrated play. At the same time, my attention was not required; my son dealt with everything himself.

So. The set contains a wooden board and colorful figures of different shapes. Similar to Tetris, but you can rotate the pieces with your hands. The task is to fill a rectangular field with these figures. The game develops spatial thinking and allows you to understand the basics of geometry. You can play alone or together.
My kids enjoy playing one at a time.
There are different levels of difficulty, and there are ready-made cards with tasks.
Buy for 2810 rubles here
Types of homemade board games
In our unified information space, it makes no difference who is the manufacturer of board games. The same development can be popular both in European countries and in America or Australia. Types of entertainment are varied, many classifications are closely related. For example, economic theory turns out to be not only a logic game, but also an exciting adventure, and popular walkers are nothing more than a carefully thought-out strategy.
Joint activities bring the family together; at this time you can discuss plans and problems along the way. PHOTO: market.yandex.ru
There are several classifications of board games that are suitable for a wide variety of companies and ages:
- for kids, their main task is development and learning, they teach the child to remember the names of geometric shapes, shapes and sizes;
- fillers or card board games are exciting activities with simple rules that are understandable to both adults and children;
- logical board exercises are aimed at developing thinking, building an interconnected chain of varying degrees of complexity;
- walkers are fairy-tale characters moving sequentially. The themes can be different, for example, horror films, colorful adventures;
- fighting games – they feature direct conflict. The game is played on or without a field, cards with different teams are involved;
- tabletop activities for friendly parties are specially designed for several participants;
- large strategic missions are intended for those with a lot of time;
- wargames are military-tactical battles with a huge number of miniatures, fairly complex rules and a mandatory field.
Having chosen the theme, age and number of participants, you can start making it yourself.
Strategic battles for adults can be designed to hold several tournaments over a long period of time. PHOTO: tdko.su
DIY toys for primary school children
Children of this age also need educational toys. Various board games are very suitable here. Again, there are a lot of them sold in stores, but there is one caveat. Firstly, they are expensive and there is a possibility that if you buy a toy. The child will use it only a couple of times and then abandon it. Therefore, it is better to make it yourself, especially since you can come up with the idea yourself.
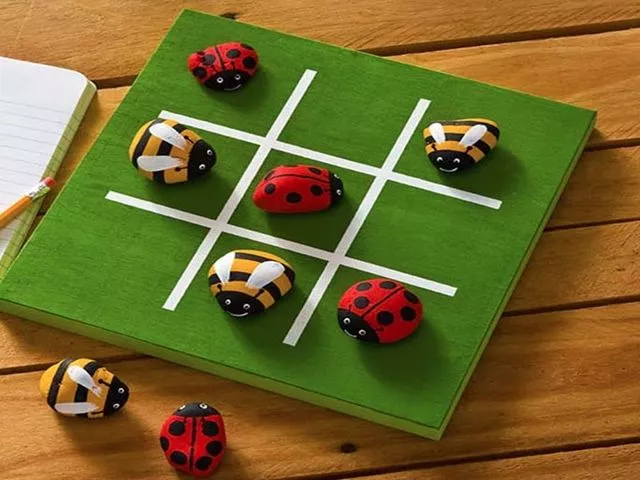
One of the fairly simple and standard options is “tic-tac-toe”. Of course, the paper version with a pen and piece of paper does not require any costs at all. But, you must admit that such a toy made with your own hands can even become a gift. And to make it you will need a sheet of plywood or cardboard, which we paint and divide into squares and round chips, also cardboard. On some we draw a cross, on others a zero.
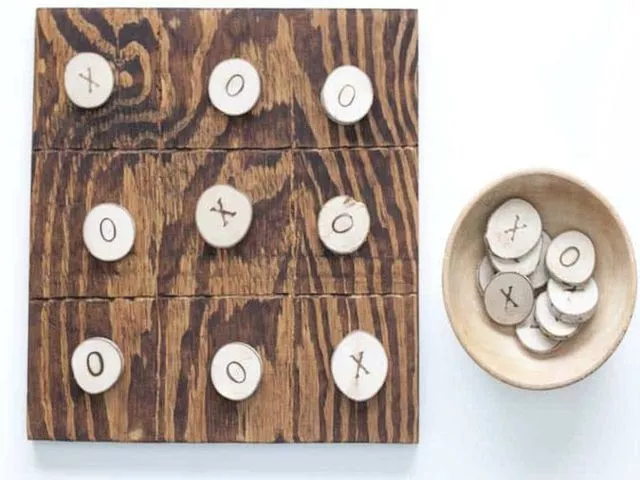

Both corks and flat buttons can be used for these purposes. The toy will turn out to be interesting, you can even take it with you to the dacha or on a trip.
As an option, instead of tiles with crosses and toes, you can make, for example, bees and ladybugs.

To spend useful time with children on trips, in addition to playing tic-tac-toe, you can make portable checkers. To do this, take an empty DVD box. Inside we attach a sheet of cardboard or any other material under the chessboard. Next, take flat buttons of the same size in two colors. You can choose any color, not necessarily black and white.
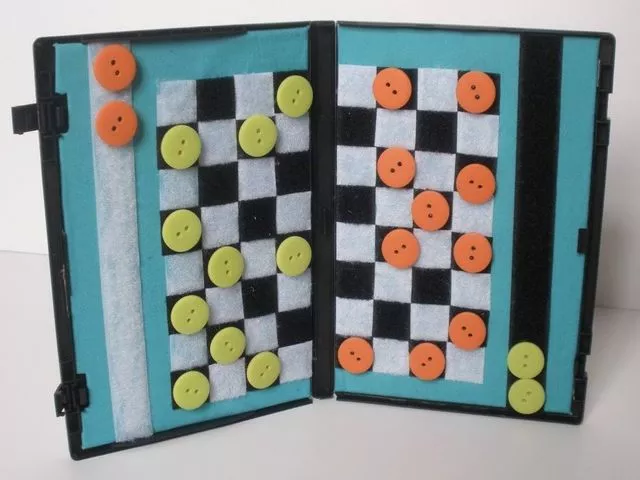

It turned out tasteful and original. With such a game, there is no shame in having a few “parties” with strangers.
If you want to play checkers like this at home, but want to have a larger field, well, take a large sheet of cardboard, paint it black and white checkered, take caps from plastic bottles in two colors and play.
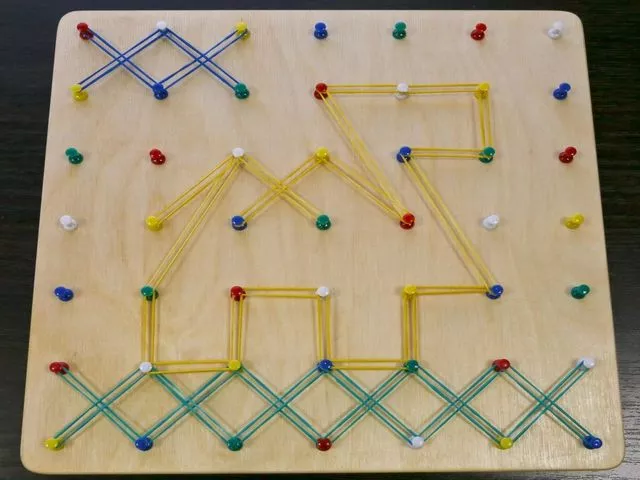
The next type of creative game is extremely simple in its implementation. We will need a board, even a kitchen board, pins and colored rubber bands. Place pins on the board in the correct order. As a result, we get the so-called geoboard. Using rubber bands, you can build various geometric shapes on such a board.
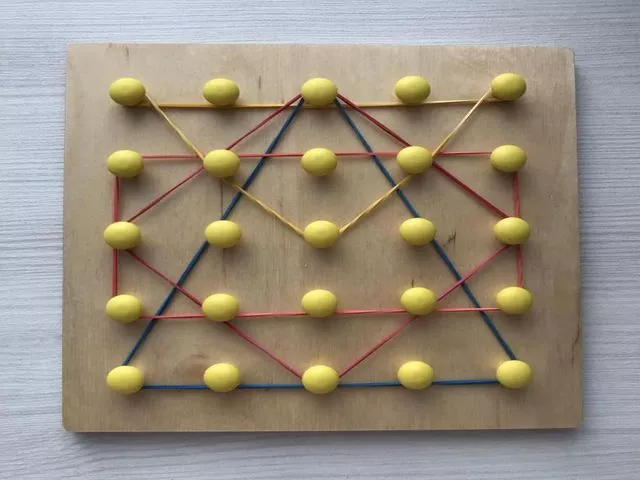
If you show your imagination, you can not only make squares and triangles, but even “draw” something. It turns out quite interesting, and most importantly, entertaining.
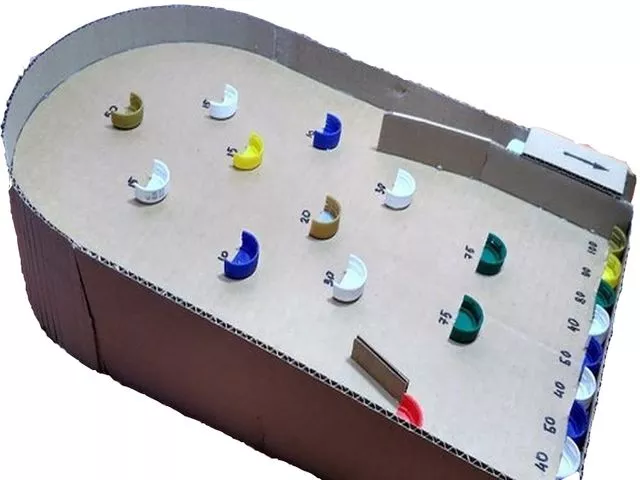
Back in the 20th century, pinball was a popular game. The field was marked with cells with numbers. The ball was shot onto the field using a spring and occupied a certain cell. Whoever scores more points wins. You can make this pinball yourself using cardboard and plastic bottle caps.

We have already talked about board games like football and hockey, but here I would like to present another interesting version of magnetic football. We take a lid from a shoe box and cut out gate holes on the sides of the opposite ends. In the corners we make legs from plastic tubes or all from the same cardboard. Then we cut out two small circles and glue a round magnet to them. We cut off two long narrow strips, to which we also glue a magnet. We are drawing out the football field. The game is ready.
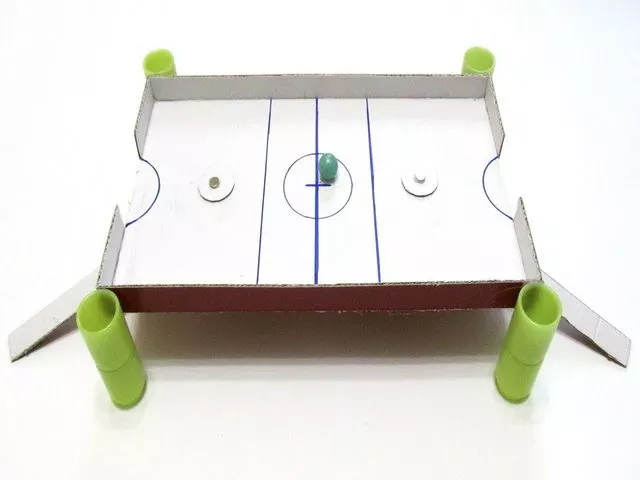

When you bring cardboard strips with magnets under the same magnetic circles and move the strips, the circles on the field will also move. Now we place the ball on the field and push it into the enemy’s goal.