Updated July 22, 2022 139 Author: Dmitry Petrov
Hello, dear readers of the KtoNaNovenkogo.ru blog. Today we will continue to introduce you to the terminology that exists in the Russian language.
In our “great and powerful”, almost all words can be classified into some category - depending on their origin, purpose, education, and so on.
Today we will talk about PROFESSIONALISM. Of course, first of all, many people know this word as a synonym for good work. It is about experienced and valuable employees that they say that they have a high level of professionalism.
But there is also the concept of PROFESSIONALISM in linguistics.
Professionalism is...
Professionalism is a group of words or expressions that are characteristic of a particular group of people involved in a particular field, or related to one profession.
Sometimes these words emerge from a certain “narrow circle” and begin to be used en masse. But some PROFESSIONALISM remain little known.
Well, for example, we all know exactly what antibiotics are. These are medicines that have a very strong effect and help with various colds.
But the word itself has a medical origin and came out of this area. That is, previously only doctors used it, but at some point it became publicly available.
But the word “Snow Maiden” in medical language means a person who has a low temperature. It sounds funny, of course. But if you hear from a doctor, “This Snow Maiden just doesn’t want to get better,” you’re unlikely to understand what they’re talking about.
Professional and personal qualities of a preschool teacher
Professional and personal qualities of a teacher
Professional qualities are often considered as a manifestation of the mental characteristics of an individual necessary for the acquisition of special knowledge, the formation of skills, as well as for the achievement of socially recognized effectiveness in professional work. The professional qualities of a specialist are based on knowledge of fundamental, professionally oriented and humanities sciences, skills and abilities to perform professional duties. In addition, the specialist must have a high level of professional knowledge in the chosen industry; be able to plan your further professional development; possess the skills of moral and legal responsibility for the quality and results of their work. Professional qualities in general terms are understood as individual properties of a subject of activity that are necessary and sufficient for its implementation at a normatively specified level and that significantly and positively correlate with at least one (or several) of its main performance parameters - quality, productivity, reliability [18] .
Personal qualities according to V.D. Shadrikov [64] represent a fixed form of behavior, behind which there is a personal motive. As I.N. points out. Gorbach, personal qualities are generalized personality properties, including the following structures: biologically determined substructure (temperament - strength, mobility, poise; pathological changes); individual abilities (emotions - excitability, stability, sthenicity; attentiveness, memory, intelligence, critical thinking, creative imagination, will - self-control, perseverance, determination, discipline), abilities of various types, orientation (labor, professional, general), experience (professional , culture), character (ideology, honesty, adherence to principles, initiative, organization, optimism, collectivism, compliance, etc.) [17].
In this regard, professional and personal qualities are understood as individual properties of a subject of activity that are necessary and sufficient for its implementation at a normatively specified level and that significantly and positively correlate with at least one (or several) of its main performance parameters - quality, productivity, reliability . The content and essence of professional and personal qualities vary depending on the specialty of the professional. As part of this work, we turn to the professional and personal qualities of the teacher.
Features of the development and formation of the readiness of a preschool teacher in professional activities is an extremely pressing problem, since no other profession puts such demands on a person as the profession of a teacher, teacher, educator. The kindergarten teacher is the main figure. It is on his professionalism that the intellectual, spiritual, social, and emotional development of the personality of preschool children depends [45].
Undoubtedly, the effectiveness of preschool educational organizations depends not only on training and education programs, but also on the personality of the teacher, his relationship with children and professionalism. Each talented, highly qualified, thoughtful teacher combines in his practice the general theoretical achievements of pedagogy, his own experience, personal preferences and characteristics of the children with whom he works. Not a single best theory can give a comprehensive answer to what a teacher should be, but it is the basis on which even the most gifted specialist should rely [13].
The professional and personal qualities of a teacher are a set of socio-psychological formations that have a factorial influence on the professional result of the teacher’s activities.
Federal state educational standards for preschool education and the professional standard of a teacher change the requirements for the professional and personal qualities of a teacher. A modern teacher is the initiator of his own activity - practical activity, communication, behavior, cognition, and also capable of self-improvement [11].
The problem of the formation of professional and personal qualities of a teacher was facilitated by the research of B.G. Ananyeva, Yu.K. Babansky, I. Bekh, V.A. Bogoslovsky, A.A. Bodalev, L.I. Bozhovich, F.I. Gonobolina, E.F. Zeera, I.A. Zimnyaya, E.P. Ilyina, E.A. Klimova and others, which state that the qualities of a person are expressed in the organic unity of her needs, consciousness, knowledge, emotional-volitional sphere and practical actions aimed at personal and professional development. Professional and personal qualities as a component of a teacher’s professionalism, skill, culture, and creativity are considered by A.E. Bondarevskaya, V.A. Grineva, I.S. Zyazyun, E.I. Isaev, A.Yu. Kapskaya, A.K. Markova, L. Mitina, E.I. Rogov, S.A. Sysoeva, V.A. Slastenin, I.M. Yusupov and others. Personal qualities necessary for the successful performance of professional activities are called professional A. Gura, V.I. Royalian; professionally significant - Yu.K. Babansky, A.S. Borisyuk, V.A. Grineva, S.I. Goncharenko, I.K. Zyazyun, Yu.M. Kulyutkin, A.K. Markova; professional and personal - V.S. Vityuk, F.R. Gonobolin, L.M. Mitina; personal – E.A. Klimov, A.R. Infantry, I.P. Podlasy.
A number of publications by domestic researchers clearly illustrate that the training of a preschool teacher, first of all, must meet the requirements of our time, because this is the first educational link on which the level of education and upbringing of the future generation depends. It has its own specifics and is based on the basic didactic principles of constructing the process of professional training in a preschool educational organization [42].
An analysis of the scientific literature has shown that there is no single point of view in understanding the complex and essence of the professional and personal qualities of a teacher-educator today.
Requirements for the professional activities of a teacher are an imperative system of professional qualities that determine the success of teaching activities. Scientists offer various designs of requirements for the professional activities of teachers: pedagogical (professional) skill, pedagogical professionalism, teaching abilities, pedagogical culture, readiness for teaching activities, pedagogical creativity [30]. Let's reveal some of them.
Pedagogical excellence is understood as a high level of pedagogical activity, as a complex of personality traits of a teacher, ensuring a high level of self-organization of pedagogical activity, and is understood as a synthesis of scientific knowledge, abilities and skills of methodological art and personal qualities of a teacher.
Experts identify the following components of pedagogical mastery: humanistic orientation of activity, professional competence, professionalism, pedagogical abilities, pedagogical technique. The criteria for pedagogical excellence are humaneness, scientific character, pedagogical expediency, optimal character, effectiveness, democracy, and creativity [15].
We find a scientific interpretation of the term “pedagogical skill” in many modern researchers of the problems of teacher education, professional activity, teacher training and retraining.
So, the pedagogical skill of a teacher is a set of psychophysiological, mental and personal changes that occur in a person in the process of mastering knowledge and long-term activity and provide a qualitatively new, higher level of solving complex professional problems [16].
Pedagogical skill presupposes a set of professional properties and personality traits of a teacher that meet the requirements of pedagogical activity. A teacher must have a wide arsenal of intellectual (intelligence, professional direction of perception, memory, thinking, imagination, manifestation and development of children’s creative abilities), moral (love for children, faith in their capabilities and abilities, pedagogical fairness, exactingness, respect for the student - all , which forms the basis of the professional ethics of the teacher) and spiritual means (the basis of his general and pedagogical culture), providing a pedagogical impact on the student.
Professional and personal qualities are characterized by intelligence, humanism, broad outlook, intelligence, tolerance, and the ability to be creative. Professional and personal qualities allow the teacher to rise to the heights of professional excellence [33].
The pinnacle of development of a teacher’s professional and personal qualities is a constant focus on pedagogical, methodological, moral and spiritual self-improvement. The components of a teacher’s professional and personal qualities include: erudition (general and scientific), culture of communication, culture of speech, pedagogical ethics, spiritual wealth, desire for self-improvement [22].
A.S. Makarenko, a famous domestic teacher, was one of the first to draw attention to the fact that children need complex tactics and techniques; the teacher should be able to control their mood, style and tone of communication, intonation, smile, gaze, facial expressions, movements, gait... Thus, sometimes a gesture is more eloquent than words, and facial expressions in the shortest possible moment prove what would require monologues. So, a good teacher is always a bright personality who has his own technique of influence, interaction, communication, and self-regulation.
Let us turn to the definition of pedagogical technique. Pedagogical technique is defined as a system of teacher skills that allows you to use the culture and technique of speech, your own psychophysical apparatus to achieve effective pedagogical results, the ability of emotional self-regulation, and communication.
The main components of pedagogical technology include the following skills:
— communicate verbally (culture and speech technique)
- communicate non-verbally (facial expressions, pantomime, appearance);
- manage your psychophysical state (breathing, muscle tension, emotions, attention, imagination, observation) [34].
The most recognized integrated personal quality is teaching ability.
Pedagogical abilities are individual psychological properties of a person, which are integrally expressed in a tendency to work with children, love for children, and enjoyment of communicating with them [8].
The basis of a teacher’s professional skills are the following groups of abilities:
- organizational - manifested in the teacher’s ability to unite students, distribute responsibilities among them, plan work, sum up what has been done, etc.;
- didactic - manifested in the ability to select and prepare educational material, clarity, equipment, present the material in an accessible, clear, convincing and consistent manner, stimulate the development of cognitive interests and spiritual needs, increase educational and cognitive activity, etc.;
- perceptual - manifested in the ability to penetrate into the spiritual world of students, objectively assess their emotional state, and identify mental characteristics;
- communicative - manifested in the teacher’s ability to establish pedagogically appropriate relationships with students and their parents, colleagues, and the management of the educational institution;
- suggestive - manifested in the teacher’s ability to exercise emotional and volitional influence on students;
- research - manifested in the ability to cognize and objectively evaluate pedagogical situations and processes;
- scientific-cognitive - boil down to the ability to assimilate scientific knowledge in the chosen field [30].
N.D. Levitov [36] identifies five groups of pedagogical abilities: 1) the ability to convey knowledge to children in a concise and interesting form; 2) the ability to understand children; 3) the ability for independence and creative thinking; 4) a tendency to ingenuity, quick and accurate orientation; 5) ability for organizational skills.
In turn, V.A. Krutetsky [31] includes the following as part of pedagogical abilities:
1) didactic - transmission of educational information; 2) academic - possession of in-depth knowledge; 3) perceptual - the ability to penetrate into the inner world of the student; 4) speech - the ability to clearly and vividly express one’s thoughts; 5) organizational - the ability to create an atmosphere of team vitality; 6) communicative and authoritarian - the ability to establish contact and influence children; 7) pedagogical imagination and attention [18].
Pedagogical abilities according to N.V. Kuzmina is a manifestation of special sensitivity to the object, a special result of pedagogical activity. They are represented by a special organization of this sensitivity: 1) gnostic - study of an object, process, results of one’s own activity; 2) design - selection, distribution of tasks; 3) constructive - compositional construction of the work system; 4) communicative - establishing relationships with children; 5) organizational - inclusion of children in various types of activities.
Certain pedagogical abilities, without which pedagogical activity is impossible, have become the leading qualities of a teacher. These include, for example, communicativeness (a set of essential, relatively stable personality traits that contribute to the successful reception, understanding, assimilation, use and transmission of information) and pedagogically oriented communication (professional communication between a teacher and all participants in the educational process, which is aimed at creating optimal conditions for achieving the goals, objectives of education and training) [24].
A number of experts are of the opinion that the lack of pronounced abilities can be compensated for by the development of such important professional qualities as hard work, systematic work on oneself, and a conscientious attitude towards one’s responsibilities.
Pedagogical abilities are considered an important requirement for the professional activity of a teacher, but are not his decisive professional and personal quality.
Professionally significant qualities of a teacher’s personality are stable general and specific traits that ensure the teacher fully fulfills his professional functions and responsibilities.
In general, an analysis of the literature shows that the most important professional and personal qualities of a teacher are recognized as: hard work, efficiency, discipline, the ability to determine a goal and choose ways to achieve it, organization, perseverance, systematic and systematic improvement of one’s professional level, responsibility, the desire to constantly improve the quality of one’s work [thirty].
In pedagogy, it is generally accepted that professional requirements for a teacher should include the following basic complexes: general civic traits (broad outlook, integrity and firmness of conviction; social activity and determination; patriotism and good attitude towards representatives of other nationalities and countries; humanism, high level of consciousness, optimism; love of work); features that determine the specifics of the teaching profession (moral - pedagogical, pedagogical, social-perceptual) special knowledge, skills and abilities in the subject (specialty).
In addition to these requirements, let us pay attention to the social competence of a teacher in a preschool educational organization. So, A.A. Kononko points to the following qualities that certify this formation:
1) respect for a preschooler - the child must be treated as a value, recognize his right to make mistakes, see his merits and achievements, perceive him as he is, believe in his capabilities, recognize his right to have his own point of view, secrets, not humiliate its virtues;
2) understanding the child - to navigate his weaknesses and strengths, feel his state, mood, predict probable behavior tactics, show insight and responsiveness;
3) help and support for the child - to promote the child’s full functioning, create an atmosphere of safety and trust, and rely on her strengths; do not emphasize the weak;
4) the ability to negotiate with a child, make a deal with him - to prevent conflicts and resolve them with the least emotional cost, avoid aggravation of relations, actively listen to the child, promote equal partnerships;
5) perceptivity - observation, receptivity, the ability to feel the state of another and respond adequately to it;
6) be yourself - maintain your individuality, originality, show integrity in situations of pressure, have your own personal and professional face [24].
The professional activity of a teacher has its own specifics, and, consequently, its own structure. The structure of pedagogical activity, according to A. I. Shcherbakov, includes the following components:
- informational - based on deep and fluent knowledge of educational material, methods and techniques of teaching it, etc.;
— developing — reflects the unity of training, education and development, ensures management of the main components of the student’s activity (mental, emotional, volitional components)
— orientational — forms in children ideas and ideals, motives of behavior and social actions;
— mobilization — activates knowledge and life experience in order to form their cognitive independence;
- research - the teacher must be a creator, a researcher;
- constructive - in his professional activities, the teacher has to select and arrange educational material in accordance with the age characteristics and capabilities of the students; plan and build the pedagogical process, the structure of one’s own actions and the actions of children;
- organizational - inclusion of pupils in various types of activities, organization of children;
— communicative — cooperation and communication with other people (pupils, parents, other teachers) [10].
The named components are the basis of a teacher’s professional activity, and therefore should be used in combination.
We also draw attention to the fact that for successful teaching activities, the teacher must acquire knowledge of preschool pedagogy, child psychology, developmental physiology, preschool pediatrics and hygiene, individual psychological characteristics, rules for protecting the lives and promoting the health of children. At the same time, he needs knowledge that, at a general theoretical level, reveals the goals, objectives, principles, content of raising and educating children, as well as optimal conditions, forms, methods and means of implementing the educational process, organizing games, intellectual and physical work, artistic creativity, arrangement of space life activity of children [7].
Psychological education is of particular importance in the work of a teacher. Knowledge of the individual characteristics of children, understanding of the psychological and pedagogical patterns of development of the personality of the child and the children's team will help to better realize the main pedagogical task - creating favorable conditions for the personal development of their pupils, ensuring the balanced development of each child, coordinating in his life the main tendencies towards self-realization, self-development and self-preservation , the formation of his life competence.
Let us separately dwell on the issue of pedagogical tact as a special ability of a teacher to build his relationships with students.
Tact is a concentrated expression of the mind, feelings and general culture of the teacher. In turn, pedagogical tact is maintaining a sense of proportion in relations with students, understanding students, choosing the optimal means of influencing them in a specific situation [5].
The main features of the pedagogical tact of V.V. Yagupov considers humanity without arrogance; demandingness without rudeness and pickiness; pedagogical influence without humiliating the personal dignity of the student, orders, suggestions, warnings; the ability to give orders, instructions and requests without insolence and arrogance; the ability to listen to the interlocutor without showing indifference; poise, self-control and a businesslike tone of communication without irritability and dryness; simplicity in communication without familiarity, familiarity, and showing off; integrity and perseverance without stubbornness; attentiveness, sensitivity and empathy without emphasizing them; humor without laughter; modesty without pretense. Thus, it should be noted that the work of a teacher is one of the most important and most difficult. Therefore, a person who strives to become a teacher must not only acquire professional knowledge, but also cultivate his own character, develop intellectually and emotionally [13].
Next, having examined these concepts in general, let us turn to the legal documents regulating modern requirements for the professional and personal qualities of a teacher (educator).
Today, the professional standard of a teacher [52] operates along with the document “Unified Qualification Directory of Positions of Managers, Specialists and Employees” (USC) [24], section “Qualification Characteristics of Positions of Education Workers,” which “is intended to resolve issues related to regulation labor relations, ensuring an effective personnel management system for educational institutions and organizations, regardless of their organizational, legal forms and forms of ownership.”
The Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation considers professional standards as additional elements of social and labor information, and over time plans a transition from the CAS to professional standards.
In this regard, we are convinced of the need to conduct a comparative analysis of these documents. The analysis is presented from the perspective of changes and continuity in the structure, content, and competencies of a teacher in the professional standard in comparison with the EKS.
First, let us highlight a number of important distinctive features of the professional standard:
— the main goal of the type of professional activity is highlighted (provision of educational services in basic general education programs by educational organizations);
- the main unit of description is the type of professional activity by describing generalized labor functions (in the CAS - position);
- labor functions are disclosed from the standpoint of labor actions, necessary skills and necessary knowledge (in the EKS - job responsibilities, must know);
— the list of necessary knowledge in all labor functions has been significantly expanded;
— significant attention is paid to psychological and pedagogical support of the educational process, knowledge of the socio-psychological characteristics of the child’s personality, patterns of development, laws of periodization and age-related crises, the foundations of psychodiagnostics.
Due to the fact that preschool education is of particular interest for our research, the identification of labor actions was carried out within the framework of labor function 3.2.1 “Pedagogical activities for the implementation of preschool education programs” of the professional standard.
Comparative analysis conducted by E.S. Gryaznova, S.F. Bagautdinova, made it possible to establish that there are a number of labor actions of the professional standard that are consistent with the job responsibilities of a CES teacher (Table 1).
Table 1
Continuity of labor actions of the professional standard and job responsibilities and knowledge requirements of the EKS for the position of “educator”
| Professional standard of a teacher | EKS |
| Planning and implementation of educational work in a group of children of early and/or preschool age in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standards for Preschool Education and the General Educational Standards for Preschool Education | Develops a plan (program) of educational work with a group of students, pupils |
| Participation in the creation of a safe and psychologically comfortable educational environment of an educational organization through ensuring security children’s lives, maintaining the child’s emotional well-being during their stay in an educational organization. Creating a positive psychological climate in the group and conditions for friendly relations between children, including those belonging to different national, cultural, religious communities and social strata, as well as those with different (including disabilities) health abilities | Promotes the creation of favorable conditions for individual development and moral formation of the personality of students and pupils, makes the necessary adjustments to the system of their education. Creates a favorable microenvironment and moral and psychological climate for every student and pupil. Helps the student or pupil solve problems that arise in communication with friends, teachers, parents (persons replacing them) |
| Organization and conduct of pedagogical monitoring of children’s mastery of the educational program and analysis of educational work in the group | Conducts observations (monitoring) of the health, development and education of students, pupils, including using electronic forms |
| Participation in planning and adjustment of educational goals (together with a psychologist and other specialists) based on monitoring results, taking into account the individual developmental characteristics of each child. Implementation of pedagogical recommendations of specialists (psychologist, speech therapist, speech therapist, etc.) in working with children experiencing difficulties in mastering the program, as well as with children with special educational needs | Works closely with teachers, educational psychologist, other teaching staff, parents (persons replacing them) of students and pupils. Based on the study of individual characteristics and recommendations of a teacher-psychologist, plans and conducts correctional and developmental work with students and pupils with disabilities (with a group or individually) |
| Organization of the educational process based on direct communication with each child, taking into account his special educational needs | In accordance with the individual and age interests of students, pupils, it improves the life activities of the team of students and pupils |
Along with this, a comparative analysis of these documents made it possible to identify newly introduced labor actions, the necessary skills and the necessary knowledge of the professional standard of a teacher, which is very important in view of the introduction of new requirements for the qualifications of a preschool teacher:
1. Participation in the development of the basic general education program of an educational organization in accordance with the federal state educational standard for preschool education.
2. Development of professionally significant competencies necessary for solving educational problems in the development of children of early and preschool age, taking into account the characteristics of the age and individual characteristics of their development.
3. Formation of psychological readiness for schooling.
4. Organization of activities carried out in early and preschool age: subject-based, cognitive-research, games (role-playing, director's, with a rule), productive; design, creating ample opportunities for the development of children’s free play, including providing play time and space.
5. Organizing constructive interaction between children in different types of activities, creating conditions for children to freely choose activities, participants in joint activities, and materials.
6. Active use of non-directive assistance and support for children's initiative and independence in various activities.
Thus, the existing continuity of labor actions, necessary skills, necessary knowledge of the professional standard and job responsibilities of the EKS acquires special importance in the conditions of a gradual transition to the professional standard “Teacher”. The presence of newly introduced labor actions, necessary skills, and necessary knowledge convinces that the professional standard of a teacher significantly expands the characteristics of a teacher’s activities, opportunities for increasing professional competence, and changing his internal position.
The professional standard sets requirements for the professional competencies of a preschool teacher (educator), reflecting the specifics of work at the preschool level of education [22].
A preschool teacher must:
1. Know the specifics of preschool education and the features of organizing educational work with children of early and preschool age.
2. Know the general patterns of child development in early and preschool childhood; features of the formation and development of children's activities in early and preschool age.
3. Be able to organize the main types of activities in preschool age: object-manipulative and playful, ensuring the development of children. Organize joint and independent activities of preschoolers.
4. Know the theory and pedagogical methods of physical, cognitive and personal development of children of early and preschool age.
5. Be able to plan, implement and analyze educational work with children of early and preschool age in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard for preschool education.
6. Be able to plan and adjust educational tasks (together with a psychologist and other specialists) based on monitoring results, taking into account the individual developmental characteristics of each child of early and/or preschool age.
7. Implement pedagogical recommendations of specialists (psychologist, speech therapist, speech pathologist, etc.) when working with children who have difficulty mastering the program or children with special educational needs.
8. Participate in creating a psychologically comfortable and safe educational environment, ensuring the safety of children’s lives, preserving and strengthening their health, supporting the child’s emotional well-being during their stay in an educational organization.
9. Be proficient in methods and means of analyzing psychological and pedagogical monitoring, which allows assessing the results of children’s mastery of educational programs, the degree to which they have developed the necessary integrative qualities of preschool children necessary for further education and development in primary school.
10. Know the methods and means of psychological and pedagogical education of parents (legal representatives) of children of early and preschool age, be able to build partnerships with them to solve educational problems.
11. Possess ICT competencies necessary and sufficient for planning, implementation and evaluation of educational work with children of early and preschool age [52].
Thus, the professional and personal qualities of a teacher include knowledge in the field of preschool pedagogy, knowledge of the age characteristics of children of early and preschool age, organizational skills, knowledge of methods of development and education of children, knowledge of methods of psychological and pedagogical monitoring, knowledge of methods of educating parents, ICT competencies .
So, the presented analysis of scientific and pedagogical literature made it possible to determine modern psychological and pedagogical requirements for the professional activities of educators. Specialists working in the field of preschool education first of all need to work on developing their teaching abilities, which is the basis of their professional skills. In accordance with the analysis, the professional standard imposes new requirements for the professional and personal qualities of a teacher, in particular the development of professionally significant competencies, participation in the development of educational educational programs for preschool educational institutions, organization of activities for preschool children, constructive interaction of children, ICT competence. In general, the introduction of a professional standard for a teacher significantly expands the characteristics of a teacher’s activities, opportunities for increasing professional competence, and changing his internal position.
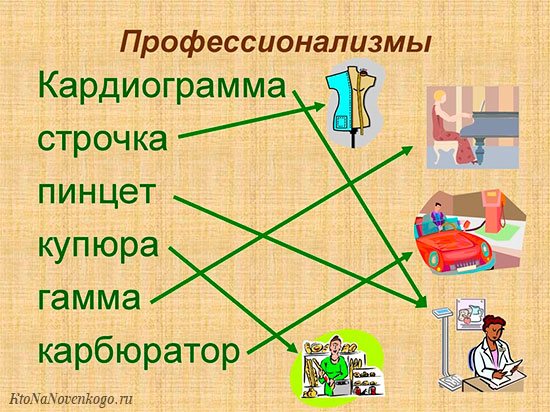
Examples of professionalisms
To make it even clearer, let's give other examples.
As we have already said, PROFESSIONALISM exists in absolutely every field of activity or profession .
Let's look at the most famous ones.
Medicine
Here is an example of well-known PROFESSIONALISM:
- scalpel - a sharp knife for operations;
- vaccine is a preventive medicine against viruses;
- injection is a professional synonym for injection;
- hematoma - people simply say “bruise”;
- diagnosis - determining what exactly a person is sick with;
- resuscitation - a set of measures to restore vital functions;
- symptom – various signs of a disease.
Even the names of specific types of doctors can be considered PROFESSIONALISM. Previously, everyone was simply called a doctor - general, children's, eye, ear, dental, heart, and so on.
And now a therapist, pediatrician, ophthalmologist (what kind of doctor is this?), ENT, dentist, cardiologist and many others.

But these are words that only a doctor will understand :
- Lyuska is a patient infected with syphilis;
- Deadwood is a person who has been in the hospital for a very long time;
- Skiers are patients who walk poorly and therefore shuffle their feet;
- Parachutist – a patient who received fractures in a fall;
- Coal is a patient with burns.
In general, doctors are known for their “professional humor,” which is often very dark. But nevertheless, this is just an example of such PROFESSIONALISM.
Sailors and pilots
A couple more professions in which there is a lot of PROFESSIONALISM. And most of them are understandable only to a certain circle of people .
Among the famous ones we can remember:
- Chapat is synonymous with a sea voyage;
- Landing stage - a vessel permanently moored at the pier;
- Fly around - get used to the plane.

And a completely different matter:
- Beska - a cap without a visor;
- Certificate – duffel bag;
- The jacket is an officer who did not graduate from a naval university;
- Under-smear and over-smear - not reaching a certain point or flying over it;
- Goat - a small jump of the plane during landing;
- A bubble is a weather balloon that is shaped like a ball.
Intuitively, some PROFESSIONALISM can be understood. Especially in the context of some kind of proposal. But some words remain a mystery to the uninitiated.
For example, sailors say the word “helicopter” and you will never guess what it means. But in fact, this is the name of the shovel used to clear snow on the deck.
Heartfelt congratulations on Teacher's Day in your own words

Happy Teacher's Day and all preschool workers. The education of all generations is in your hands and in your power, you open the doors for children to the land of happy childhood and dreams, you give children the necessary knowledge and opportunities to show their talents. With all my heart I wish you never to lose the kindness of your heart and inspiration for your work. Be happy and healthy.
Thank you for your work, difficult and sometimes invisible. Thanks to your love for kids, your sincere care and professionalism, it is much easier for us, parents, to raise children. We wish you an inexhaustible source of strength, health, inspiration and creativity! Happiness, warmth, prosperity to your families!
Dear teachers and all preschool workers! Parents trust you with the most precious thing they have - their children. You surround your children with warmth, care, and smiles. I would like to thank you and wish you to be surrounded by the love and warmth of your loved ones, so that a smile always shines on your face. Happy holiday!
Being a teacher is a real calling. And even though your work is not at all easy, you do it perfectly. On your professional holiday, I would like to thank you for your warmth, care and attention to our children. I sincerely wish you good health, prosperity, patience, success, happiness and joy.
Today, on Teacher's Day, let me congratulate you with all my heart and express my sincere gratitude for your noble work! It is you who, coming to work every day, give children not only your love and warmth, but also invest valuable knowledge in them, help them become inquisitive, kind, smart and happy. Thank you for your work, we appreciate, are proud and wish you happiness! Happy holiday!
We all need your work so much. People of different professions trust you every morning with raising their children. You fully cope with your mission, giving children not only knowledge and skills, but also care and warmth. Your students feel your kind attitude towards them. And, believe me, with warmth in their hearts, they will remember the years spent next to you, many years from now. Thank you for everything!
Dear educators! The results of your work are not immediately visible. It bears fruit after many years. However, having met your students by chance on the street or read about them in a printed publication, you are filled with pride in your work. You want every grain you sprouted to become a strong shoot that can become a cultivated plant. Low bow to you for all your efforts and efforts! Thanks to you, our world becomes more humane, kinder, brighter. You are the foundation of our hearts. Glory to all preschool workers and teachers! Hooray! Hooray! Hooray!
Our dear and respected teachers and all kindergarten staff! On your professional holiday, we would like to say warm words of gratitude to you and wish you good health, good spirits and a positive mood! And also great patience and endless love for our little mischief-makers! And let them give you moments of happiness and fun. Be happy and let material problems pass you by. Love, respect, joy and happiness for many years to come!
Professionalism in business
Businessmen also have their own language. And it also contains a lot of incomprehensible words. But some still become popular:
- Cash – money, mostly paper;
- Non-cash – payment by credit card or transfer of money using banking and mobile services;
- A startup is a newly created company that is just beginning its journey in business and is associated with some kind of innovation (how is that?);
- Team building (how is that?) – work to unite the company’s employees into one friendly team;
- Manager (who is this?) – the person responsible for sales. Now the range of responsibilities for this profession has expanded significantly
- Bitcoins are a virtual currency.

But the expression “turn on the counter” or “white rollback” are more specific. The first means “raise the interest rate”, and the second means the commission to the intermediary.
Programmers and gamers
People who work with computers or constantly use them also have their own specific language.
From understandable PROFESSIONALISM:
- A flash drive is a portable mini-data storage device;
- User is an active computer user (how is that?) who spends a lot of time on it;
- Social networks, mobile applications, telegram channel, video hosting and websites - everything that fills the Internet today;
- Internet - even this word itself is PROFESSIONALISM;
- Freeze - suddenly stop working;
- Glitches are synonymous with errors;
- Save – save at a certain stage of the game;
- Gamer (who is this?) – a person who is interested in computer games;
- Likes and reposts (how is that?) are special marks on social networks.
It is interesting that many words from the computer sphere have acquired additional meaning in everyday speech.
For example, we can say about a person that he is “stuck,” “slowing down,” or “caught a glitch.” And everyone will understand that we are talking about very slow work or actions of this person or that he made a mistake.

Here are examples of uncommon PROFESSIONALISM :
- Tower – a computer case with a characteristic shape;
- Malware or Malicious - a computer virus;
- A soap dish is a very simple device from a technical point of view;
- The truck is a pumped up and strong character in computer games;
- Bot (what is it?) are characters in computer games that are not controlled by people.
Features of the profession
Being a teacher is not only an honor, but also very responsible.!
After all, it is at the age of 3 to 6 years that many skills and abilities are formed, your baby’s cognitive abilities are improved, his horizons begin to expand, and his first ideas about the world appear.
And all this happens under the guidance of the first mentor - the educator!
Who, if not a preschool teacher, will teach you how to cut with scissors, draw, and then write? Who will teach poetry and read fairy tales? Teach friendship, honesty, attentiveness and kindness towards children, adults, animals?
It is impossible to overestimate the importance of this person in your child’s life, but sometimes, on the contrary, you can underestimate!
Motorists
Driver is also a profession. Therefore, this area also has its own words, which for the most part are known to most people. Well, simply because many people now have cars.
- The steering wheel is synonymous with the steering wheel;
- Automatic and manual – short designations for automatic and manual gearboxes, respectively;
- Spare wheel – spare wheel;
- Technical inspection is a special procedure for any car owner;
- Separate lane - a dedicated lane for public transport;
- Tuning - decorating the basic configuration through changes in design or painting;
- Tinting - darkening windows.
- Street racers are street racers.