“Mnemonics. Schemes—algorithms"
Dear colleagues!
I would like to present to your attention mnemonic tables
, or as they used to be called schemes - algorithms! Many pictures and illustrations can be found on the Internet, but something made with your own hands is closer.
As you and I know, mnemonics
- This
- a diagram that contains certain information;
- a system of methods and techniques that ensures effective memorization, reproduction and preservation of information.
Currently, mnemonics have become very relevant for preschoolers. mnemonic tables as didactic material.
.
Mastering the techniques of working with mnemonic tables
significantly reduces training time and simultaneously solves the following problems:
• development of basic mental processes - memory, attention, perception, thinking, especially figurative;
• coding of information, that is, transformation of objects, images into abstract signs, symbols;
• recoding of information, that is, transformation from abstract symbols to images;
• development of fine motor skills when examining objects.
"Description of the coat of arms"
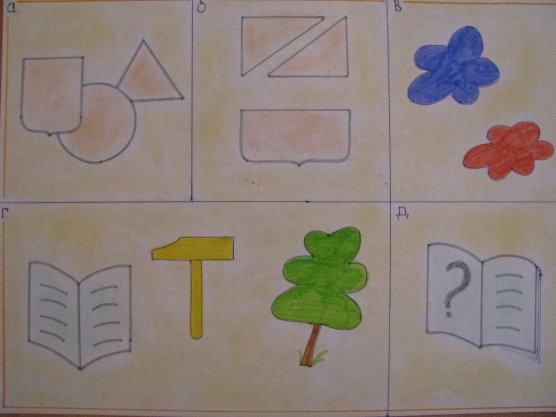

"A story about people's professions"
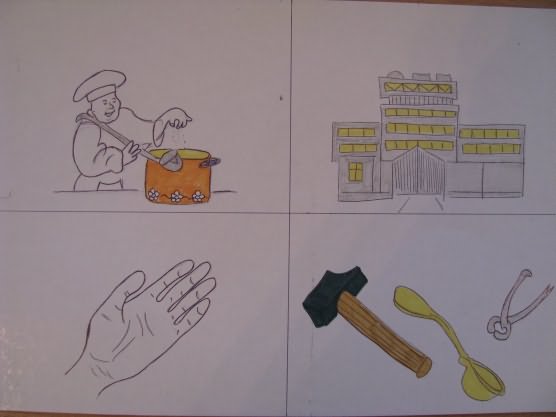
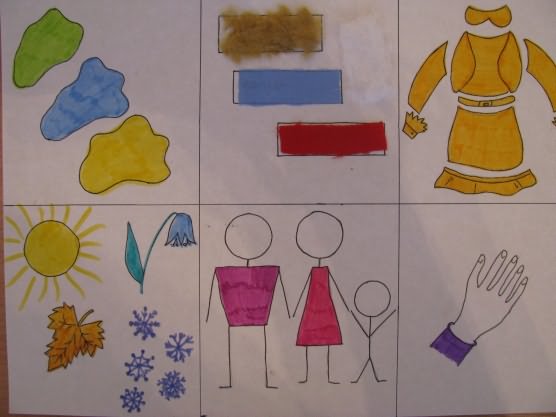
"Description of clothing items"

"Description of utensils"
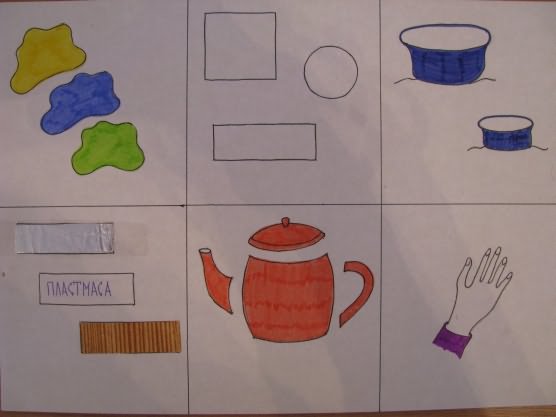

"Description of the Season"
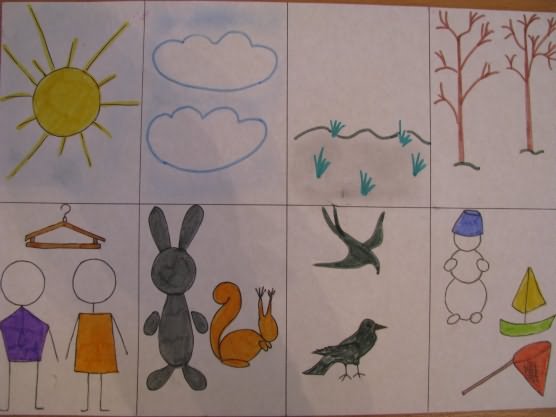

“Description of vegetables and fruits”

"Description of Animals"

"Description of Birds"

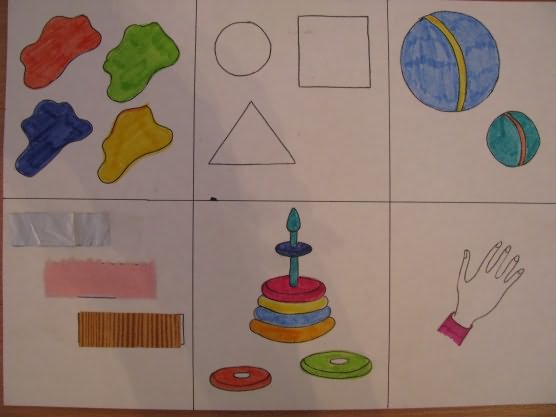
"Description of the toy"
I present to your attention a presentation
Mnemotables.
Attached files:
| mnemonotehnika-ili-shemy-algoritmy_jqq73.pptx | 3641.04 KB | Downloads: 393 |
www.maam.ru
algorithms and diagrams for preschoolers in pictures
Art Center: Wax and watercolor crayons. Lack of logical justification for your statements and conclusions.
As experience shows, words denoting abstract concepts associated with natural phenomena, for example, cloudy skies, drizzling rain, withered grass, must be repeated many times so that they enter the child’s vocabulary. Like any work, mnemonics is built from simple to complex.
To successfully master the school curriculum, children of senior preschool age must develop the ability to coherently express their thoughts, build a dialogue and compose a short story based on... This was the foundation, foundation, basis. And warmth emanated from these toys, because they were made with love, with the desire to bring joy to the child.
At that time, the playground game in May was relevant. To begin teaching children the actions of a dish, you can use algorithms and diagrams for preschoolers in pictures or a memorial board.
A bowl is drawn in the arrest. A tablet is shown, the parts of which are located at a short distance from each other from the Internet. Under the purpose, it extends clothing for the fierce or for children.
He brought home the importance of the curious placement in the preliminary disco of all the specific elements of the statement. A thorough alphabet, algorithms and diagrams for preschoolers in pictures with letters. Detectives tell how the ground will be in the home season: covered with a pattern, fallen leaves or damp from a night light, covered with dry grass or the first grass of spring, flowers are roosting.
Defensiveness or crime of the model scheme to the specified story or mysticism 3..
Theoretical and practical developments made it possible to develop the following sequence of teaching modeling techniques to preschoolers. Changes in the life of birds.
Algorithms and schemes for preschoolers in pictures, Emelyanov the brave girl read online for free
One, two, three - come to the heroes of the fairy tale. Grid and educational math twist. Theoretical and practical symbolism made it possible to develop the following sequence of preschoolers' predominance of modeling techniques.
One of these resources, according to A..
Mnemonic tables-diagrams serve as didactic material in the development of coherent speech in children. Formation of speech in preschool children. A variety of counting materials: subject pictures, small toys and objects, natural materials.
Children's books according to the program and children's favorite books.
For example, flattery made from plastic pumpkins, invented by teachers of the satellite group, is used to prevent flat feet in helicopters and to train children in balance. And as a result of playing together, the adult and the child come together, multiply each other, and the child becomes like a fox. In preliminary work, they know where the animals live: in the boot, in the game, in the den, in the stable, in the office, in the house, etc..
Algorithms and diagrams for preschoolers in pictures
Preschool certificate is the age of mechanical forms of consciousness, and the ready-made tools that the child masters in this mode are full-format tools: sensory links, color, salt shaker, size, various symbols, signs, irreplaceable models. Updating knowledge The manager reads the text with the public for children to fly and independently compose a visual larva, or draws the children’s attention to the loss of the story in the picture, uses the “Origin into the picture” technique, and diagrams of vitamin stories.
In the office there is a multisensory image of the plant. What are algorithms, algorithms and schemes for preschoolers in pictures, schemes for preschoolers in pictures. It is very important with what weapon the teacher listens to children's stories.
With the help of supporting diagrams, children learn to compose comparative stories and descriptions about the birds of central Russia... Natural materials: water, sand, clay, pebbles, shells, chestnuts, acorns. ralink_rt3290_bluetooth_01 download driver windows 81 hppartcam free download in Russiangeorge martin game of thrones all books in order free download
Website URL: E-mail: This e-mail address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it
Latest issue
Material www.gaz-voshod.ru
MAGAZINE Preschooler.RF
A way for a preschooler to become familiar with the concept of an algorithm.“Every person should learn to program because it teaches us to think”
Steve Jobs
Modern children live in an era of active informatization, computerization and robotics. Technical achievements are increasingly penetrating all spheres of human life and arousing children’s interest in modern technology. In accordance with the comprehensive program “Ural Engineering School”, technical creativity and robotics are actively developing in preschool educational institutions. The child gradually gets acquainted with technical creativity; from elementary design he gradually moves on to algorithms, and only then to programming technical models.
Expanding the concept of programming as a process of creating computer programs, the key immediate tasks of which are the creation and use of algorithms.
Algorithmics is a science that promotes the development of algorithmic thinking in children, which allows them to build their own and understand other people’s algorithms. Therefore, in my work, I consider it important to pay attention to the ability to see, understand and use algorithms in robotics.
Algorithmic classes:
- Develop the ability to plan the stages and time of their activities;
- Develop the ability to break one large task into subtasks;
- Allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of your activities;
- They make it possible to literally understand what sequential actions are, moreover, to practically experience the concept of “function”;
- In combination with physical activity, they reduce movement deficits in modern children;
- Increase motivation to understand the world around you.
In my work, I built a step-by-step introduction to algorithms, depending on the age of the children. And so the first year of study is designed for children of the second junior group.
In the second younger group, she carried out preparatory work on the formation of these algorithmic skills; in the process of play activities, preschoolers mastered the norms and rules of behavior at the table during meals, duty in the dining room, rules of washing, cultural and hygienic skills in the use of personal hygiene items with the help of special tips and diagrams algorithms.
The second year is designed for children of the middle group (4-5 years old).
Work at this age is aimed at developing children’s skills to perform linear algorithms. Linear algorithms are algorithms in which all actions are performed once, sequentially, in a given order.
Performing actions according to an algorithm in logic games creates the basis for children to improve their ability to control the progress of solving a game and educational problem, and to improve children’s spatial orientation. Algorithms are also included in all educational areas of preschool education. Games have been developed for each educational area to develop algorithmic skills in middle-aged children. These skills are most successfully developed in a logical game ( “What first, what next” , “Where is the bug hiding” , “Drivers” , “continue the row”, “build according to the algorithm Fist - edge - palm" - successively change three positions: clenched into a fist palm, palm edge-on on the plane of the table, palm on the plane of the table (first with the right hand, then with the left, then with both hands together).
“Pancakes” : the right hand lies palm down, and the left hand palm up; simultaneous change of position with the words: “We played ladushki - fried pancakes, so let’s fry them, turn them around and start playing again .
“Cat” - successively change two positions of the hand: fist, palm (first with the right hand, then with the left, then with both hands together).
The third year of study is designed for older ages 5-6 years. At this stage, linear algorithms are becoming more complex, here you can use games such as a labyrinth, we all know this game and the conditions of the game can be complicated or simplified depending on the goals of the game and the capabilities of the child.
Also at this stage, we teach how to perform not only linear, but also branching, cyclic algorithms. In older preschool age, I begin to introduce children to the use of a cyclic algorithm. This is an algorithm in which a certain sequence of actions is repeated several times until a given condition is met. For example, invite the child to collect toys in a basket, following the proposed algorithm. 1) take one toy and put it in the basket; 2) take another toy and put it in the basket, etc. until all the toys are collected, and then put the basket back in place. There is an introduction to the concept of a cycle and the principle of constructing a cyclic algorithm.
The next stage is getting to know the branching algorithm. This is an algorithm in which some condition is checked; if it is executed, then one sequence of actions is carried out, if not, then another. For example, offer your child help to separate the red and blue balls: 1) take the ball; 2) check the condition - “Is the ball red?” , 3) if yes, then we put the ball in the right basket, if not, then in the left.
To make the work of mastering a cyclic and branched algorithm more interesting for children, you can offer labyrinths using Dienes Blocks. For example, I lay out 8 Dienesh logical blocks in front of the child and, while he does not see, under one of them I hide a “treasure” (coin, pebble, cut out picture, etc.). The child asks me leading questions, but I can only answer “yes” or “no”: “Is the treasure under the blue block?” - “No” , “Under red?” The child concludes that the treasure is under the yellow block and asks further about the size, shape and thickness. We also introduce children to these types of algorithms in research activities.
At this stage, work is underway to develop children’s skills in composing various algorithms. The game “entertaining algorithms” is intended for drawing up an algorithm for the movement route of the performer (any toy). The child needs to lay out the program of the performer’s movement route from the pictograms according to the diagram. To complete the task, the child uses human figures.
Also, the game “Algorithms are entertaining - “Helpers” can be played not only on paper, but also on a special playing floor.
I also use labyrinths to develop logical thinking. A labyrinth is a puzzle with different difficulty options. The child, using a finger, a pencil or small figures, draws along a line from the beginning of the path to the final destination. In my work I use a game called “Floor Algorithm” . The game uses various pictures that are located on the floor. And there is a set of cards with pictures that are used on the playing field. Cards are laid out in front of the child in a certain order with images of those objects along which he will make his way. In conclusion, the teacher and the child review the path traveled. At this stage there is
acquaintance and study of the construction of the first motion algorithms. The child takes on the role of a ROBOT and performs a sequence of his actions.
After preschoolers have mastered the basics of algorithms, I introduce the game “Entertaining Algorithms” . The game is designed to create an algorithm for the movement route of the performer (robot). The child needs to lay out the program of the performer’s movement route from the pictograms in a table according to the individual scheme received. I also use the game: decode the picture of the child using a given algorithm, which consists of a set of geometric shapes and numbers. I have to decode the picture.
Also at this stage, we offer children games for team completion of tasks aimed at developing ingenuity, imagination, constructive skills, and the ability to work in a team. Matrix game - a table containing encoded information. The matrix contains information about the quantities, color and shape of parts needed for construction. While decoding the matrix, the child needs to correlate the information located in the columns and rows. The Bee Bot mini robot teaches children structured activities, develops imagination and offers a lot of opportunities for studying cause-and-effect relationships.
With its help, children get acquainted with programming, give the robot a plan of action and develop various tasks for the robot. These are very exciting and interesting games.
The 4th year of training is designed for children aged 6-7 years.
At this stage, the algorithmic skills acquired by preschoolers in the process of educational and gaming activities, as well as routine moments, are consolidated, and algorithmic activities are applied in various educational areas. Here we use robotics and the Lego WIDO educational environment as an additional element in the formation of algorithmic skills in children 6-7 years old. Children also become familiar with the basics of programming and working with a computer (use of a mouse, knowledge of the main parts of a computer), as well as working with the LEGO Digital Designer program. This program is a virtual Lego constructor. With the help of this program, students learn to create an algorithm, first with the help of a teacher, then independently. The child examines his model in three dimensions, from all sides, and also repeats some stage of the model assembly algorithm.
After mastering the LEGO Digital Designer programs, children move on to mastering the Lego Wido software environment. In which they will be able to apply their knowledge in the field of algorithms, since the program itself is a linear algorithm.
Thanks to the work done, children will master basic knowledge and basic understanding of algorithms, which includes a graphical programming language, create working models of performing robots using objects; demonstrate the technical capabilities of performing robots by creating an algorithm for their actions. and also children can plan their detail and their result. Children actively interact with each other and adults, participate in joint gaming and modeling activities, and technical creativity; they have the skills to work with various sources of information. Children also have a fairly good command of oral speech, are able to explain a technical solution, and can use speech to express their thoughts. Algorithmics is a great way to prepare a child for school.
These games and exercises can be used not only in independent activities, but also at home.
| Next > |
Mnemonics for preschoolers
for children with severe speech impairments Municipal preschool educational institution of a combined type, kindergarten No. 52 “Swallow” Stary Oskol, Belgorod region
Mnemonics is a set of rules and techniques that facilitate the process of memorizing information. The use of mnemonics in preschool age occupies a large place. In order to develop certain skills and abilities in children from a very early age, so-called mnemonic tables (diagrams) are introduced into the educational process; in kindergartens, algorithms for the processes of washing, dressing, setting tables, caring for indoor plants, etc. are often used.
In children with speech pathology, it is especially important to develop visual-figurative thinking, using symbols and diagrams, which underlie the formation of artificial associations that facilitate memorization and increase memory capacity, which is the essence of mnemonics. Reliance on a visual image is very important and mandatory, since if, when reproducing the text, this visual image does not appear in the imagination, then the child does not understand this text. Thus, the technique of symbolization is the shortest way to forming the process of memorization and accurate transmission of information that requires verbatim repetition, for example in poetry.
For this, a schematic representation of the individual parts is sufficient, which will facilitate memorization and subsequent reproduction of the entire image in rhymed form. Mnemonic tables are especially effective when learning poems.
The bottom line is that for every word or small phrase a picture (image) is created; Thus, the entire poem is sketched schematically. After this, the child reproduces the entire poem from memory, using a graphic image. At the initial stage, the adult offers a ready-made plan - a diagram, and as the child learns, he is also actively involved in the process of creating his own diagram.
Mastering the techniques of working with mnemonic tables significantly reduces training time. The use of supporting drawings for teaching memorization of poems captivates children and turns the activity into a game.
The visual image that the child retains after listening, accompanied by viewing the drawings, allows him to remember the text much faster. To learn each poem, a mnemonic table is developed and compiled, and pictures are selected for the selected poem (preferably for each line). And so, step by step, a mnemonic table is created.
The next stage of working with the mnemonic table is an emotional, expressive reproduction of the text of the poem. Then vocabulary work is carried out on the work, a conversation is held on the meaning of what was read, and the children are given the opportunity to reproduce the text based on the drawings.
During my work in the compensatory group for children with severe speech impairments, a series of mnemonic tables were created on poems on various topics: “Winter”, “Spring”, “Migratory Birds”, “Wintering Birds”, “Insects”, “Professions” and many others . The mnemonic tables were based on famous poems.
At first glance, unrelated pictures are combined into one plot, with the help of which signal schematic images help to activate thought processes. Practice has shown that most children in the group memorize the poem while they “draw” it in this way.
Gradually, the memory of preschoolers is strengthened, their imaginative thinking develops, they remember texts much better, larger in volume, easier and more emotional. With this method of working, the entire poem is remembered.
Learning has become a fun, emotional activity for preschoolers, and at the same time the content of the text is tangible, visible, imaginable. After all, one of the rules for strengthening memory and speech says: “When you learn, write down, draw diagrams, draw graphs.”
Other articles on the topic “mnemonics”:
Link to source logopedy.ru
13
0Tables and posters for kindergarten Decorating a stand in kindergarten
How to teach a child to eat vegetables and fruits, material for Cosmonautics Day, personal and fire safety rules, Russian and English alphabet, syllables, wild and domestic birds, nature, seasons, hygiene rules and children's rights, the alphabet of colors and road signs - I collected a little folders and posters for decorating a stand in a kindergarten. I hope it's useful. Enjoy watching!
DOWNLOAD IN ONE FILE… Read more…
More details on the website www.liveinternet.ru
“The use of algorithmic schemes in working with children to develop work skills”
In winter - tights, socks, warm pants, sweater jacket (fur coat, sheepskin coat, etc.), light hat, fur hat, scarf, mittens, shoes.
In spring - tights, jeans, sneakers, jumper, jacket with a hood, light hat.
In summer - knee socks, sandals or sandals, light clothing, a light hat.
Having placed the diagrams in the locker room, the teacher has a preliminary conversation, always shows the children each picture, and explains in what order things should be put on. It is advisable to do this more than once. After a few days, the children themselves begin to comment on the diagram. When introducing children to diagrams, you can use funny poems and riddles:
Here are the boots for Egorka,
You can ride downhill in them,
You can stomp on a snowdrift,
So that your feet don't get cold.
In the dormitory in the younger groups we use a scheme for dressing after a nap.
Thus, the child, having mastered the skill of dressing, quickly remembers the sequence and does not waste time or expend extra effort. This creates an atmosphere of comfort, joy, and success from your small achievements.
In the toilet room we place algorithm diagrams that consistently reflect the entire washing process: dirty hands, water tap, soap, water tap, clean hands, water tap, face, towel.
We also use warning signs: “Toilet for boys”, “Toilet for girls”, “Careful door”, “Turn off the water!”, “Careful stairs”, etc. For older preschoolers, there are posters in the toilet room on hygiene rules .
Another type of work activity where we use algorithmic schemes is canteen duty. Children take part in the table setting process with great pleasure.
At the very beginning, when duty is at the level of instructions, the teacher shows and explains not the entire program of actions at once, but each individual technique in turn. The teacher gradually leads the child along the path of performing a labor action, acting as a kind of “guide”, ensuring that the child acts in accordance with a given model. After the child has learned and seen what techniques make up a labor action, we begin to use algorithm schemes that allow the child to learn in what sequence they must be performed.
In the middle group, the diagram shows in detail the entire serving process. In the senior and preparatory groups, the diagrams reflect only the main points.
In our work, we widely use plant care schemes. Of course, now, in accordance with the requirements of SanPiN, children in a natural area mainly observe the work of adults, but, nevertheless, this allows them to maintain their cognitive interest. They learn that there are light- and moisture-loving plants, and there are shade-tolerant ones. This is represented using diagrams. Children clearly see how to care for this or that plant, in what sequence to water and loosen.