Air and air properties
Air is a mixture of gases: nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and others.
Gases have no shape. They spread in all directions and fill the entire available volume.
The air shell of the Earth - the atmosphere - protects us from destructive cosmic rays, from overheating by heat emanating from the Sun, and from hypothermia.

Layers of the atmosphere:
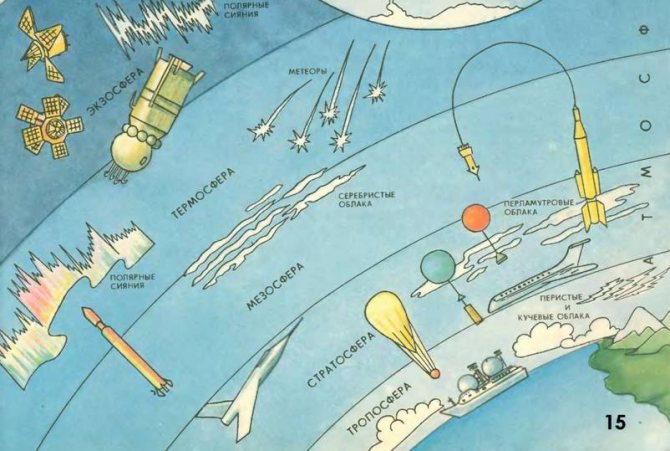
Air is necessary for all living things to breathe and to create organic substances. Watch an educational video from 5.55
What properties does air have?
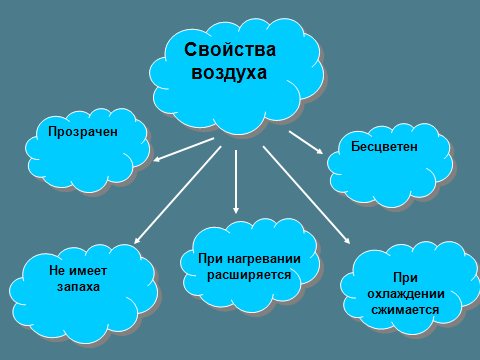
More details about the properties.
Now you see everything around you: walls, computer, closet, outside the window - houses, trees, clouds. Can we see
air? Believe me that air is everywhere around us? Does he exist at all? Maybe it was invented? Shall we prove it?
Study 1.
Take a straw and place it in a glass of water. Blow lightly into the straw. What appeared? Air bubbles will appear
Conclusion: Using vision, air can still be detected in some cases.
Look at indoor plants. What color are they? What about your walls? What color do you think the air is? We discover the first property of air: air is invisible and colorless .
Study 2 . Now take a deep breath, what did you feel?... Does the air smell anything? What about the smells in a candy store or pharmacy? ... We feel smell when particles of a substance enter our nose.
Conclusion: Clean air has no odor.
Study 3 . Can you taste the air? Lick it. What properties of air will we discover?
Conclusion: air has no taste
Study 4.
Pick up a book. What shape is it? Now try to pick up the air. Happened? Does air have a form?
Conclusion: air has no shape.
Study 5. Air is elastic
Take the ball and squeeze it with your hands. Hit the ball on the floor. What are you observing? What property of air was discovered?
Now look at these two balls. Which one is more elastic? Why?
Can I make the first ball as elastic as the second? What do I need to do?…. That's right, add air. What happens to the ball when we add air?...... (The air is compressed).
You probably have a bicycle. What property of air is used when inflating the inner tube of a bicycle wheel with a pump? ….. also jumping on sports bikes is done precisely because of the air in the tires.

Where else is this property used?…..
Study 6. Air is lighter than water, that is, less dense than water.
Fill a cup with water. Try drowning a tennis ball in it. What are you observing? What property of air was discovered?
This is why you are not afraid to swim while wearing a life preserver.
Study 7. Air is a poor conductor of heat.
Why do house windows have double glazing? What's between the frames? What property of air is manifested here?
That's right, between these double glasses there is air that keeps the cold out and the house becomes much warmer. Since air has low density, it conducts heat poorly.
If the air does not conduct heat well, why does the ground under the snow remain warm and the roots of plants do not freeze? What warms the earth, is it snow?….
There is air between the snowflakes; it does not allow the cold to pass through.
Think about how the birds sit when it’s frosty outside? Why?…. What happens to animal fur in winter?...
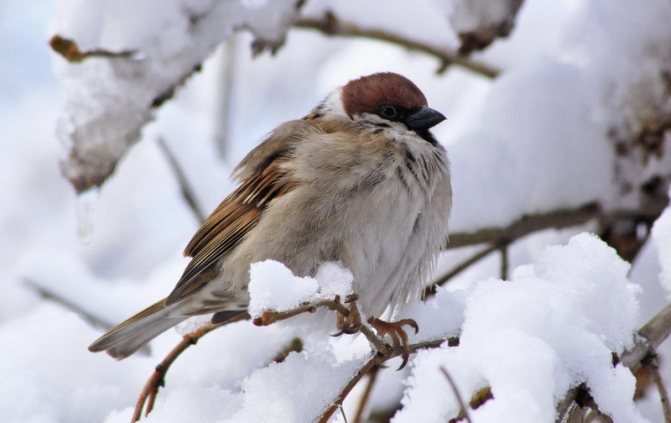

The fur of animals and the feathers of birds do not warm by themselves, but the air between them warms. When it’s cold, animals raise their fur, birds groom themselves, and people put on a warm sweater or fur coat.
Study 8.
When heated, it expands.
Why do people in a bathhouse climb onto shelves closer to the ceiling to steam? Why are batteries installed in rooms below, under the window? What happens to hot air?
Yes, when the air heats up, the air expands, that is, it becomes lighter and rises.
Now can you explain by what principle a hot air balloon flies?

What about Chinese lanterns?
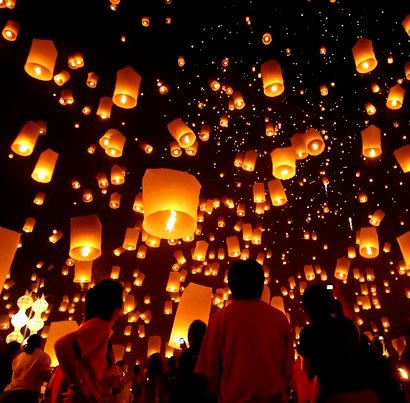

Can there be the same temperature: day and night? winter and summer? at the poles and at the equator?
What happens to heated air? (Rises). What is taking up the vacant space? (Cold air).
This means that on Earth there is a constant movement of air, and the wind simply blows.
Wind is the movement of air.

Winds bring both benefit and harm.
Imagine for a moment that there is no wind on Earth. There is no wind in our industrialized city, where there are factories, factories, mines, open-pit mines, and explosions. What will happen?
Chimneys from factories and factories emit smoke high into the sky. Powerful winds blow there at altitude. They pick up clouds of smoke and tear them to shreds, disperse them, mix them with clean air, and quickly reduce the danger of toxic gases. Tall chimneys divert trouble away from people living nearby.
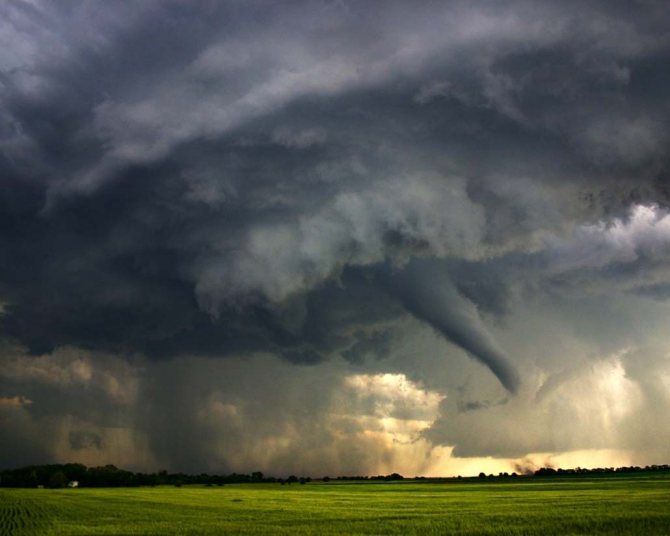
There are winds that bring a lot of trouble.
| Hurricanes typhoons cyclones | Tornadoes (tornadoes) |
| — These are all storms with wind speeds reaching 120 km/h. Such winds can demolish buildings. Usually accompanied by showers. | — These are rotating funnels with wind speeds of up to 5000 km/h. The funnel sucks in everything in its path (the case with the pink frogs). |



