What material is given on FEMP in the senior group
FEMP in the senior group is focused on broadening one’s horizons, applying the acquired knowledge to everyday life, and having a correct understanding of the world.
Throughout the entire school year at preschool educational institutions, children learn new geometric shapes. By the end of the third quarter, children should distinguish the following shapes: circle, triangle, square, rectangle, oval. Also, ideas about a ball, cube and cylinder are introduced and reinforced. Classes are conducted aimed at training in dividing a circle and square into two and four parts.
Children in the senior group of preschool educational institutions
After division, everyone should be able to name and describe the resulting figures. The children learn to apply the acquired knowledge in geometry in life: they visually select objects of familiar shapes, tell how they are used: for example, they analyze a sheet of paper, determining what shape it is, where its corners are, where its sides are, what shape will be obtained if you bend the sheet in half.
Additional Information! Children develop ideas about the sequence of parts of the day. They skillfully determine morning, afternoon, evening and night. When asked by the teacher at lunchtime about the part of the day, they unmistakably answer “day,” and when asked what will happen after, they answer “evening,” remembering that before that there was morning.
Closer to the beginning of summer, the knowledge of the days of the week is completed. The children reinforce the concept of working days and weekends. They can easily navigate the middle of the week: if today is Wednesday, it means yesterday was Tuesday, and tomorrow will be Thursday.
Counting up to 10 is analyzed. The composition of the number and its nearest neighbors are compared. They learn to collect numbers up to 5 in units. By touch and sound they determine the number of objects (sounds), but no more than seven.

Didactic buttons for counting by touch
The skills of comparing various objects in three dimensions are developed - length, width, height. The smallest of the presented items is chosen as the measuring unit.
They train the ability to use landmarks “in front”, “behind”, “right”, “left”. To do this, they practice changing the direction of movement at the command of the teacher.
Important! Children do not acquire all these skills in one year of classes. Starting from the younger group, they gradually learned the elementary fundamentals of mathematics and the world around them. Education for the senior group is mainly aimed at consolidating the acquired knowledge and applying it in everyday life.
What is FEMP?
Definition 1
The formation of elementary mathematical concepts is a process of purposeful transfer and assimilation of knowledge, techniques and methods of mental activity.
The methodology for the formation of elementary mathematical concepts is based on the tasks, principles, conditions, content, means, methods, forms of mental education, training and development of the younger generation developed in preschool pedagogy.
The period of preschool childhood is the optimal period for the mental education and development of children. Children at this age not only learn the external and visual properties of objects and phenomena, but can also acquire ideas regarding the general connections underlying the mass of natural phenomena and social life, and master ways to analyze and solve various problems.
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
The main feature of the mental development of preschool children is the predominance of figurative forms of cognition, including perception, imaginative thinking and imagination.
Cognitive processes can manifest themselves in different types of activities.
Mental education occurs through the young generation’s assimilation of centuries-old human experience, which is imprinted in material and spiritual culture. The main function of mental education is to form cognitive activity, an activity during which children learn about the world around them through play, activities, work, and communication with adults and peers.
Perception helps the child to understand the external properties of objects and their totality; by reflecting these properties in the brain, it forms an image of the object. Thinking allows the child to comprehend the internal, hidden properties, connections of objects and phenomena. The results of thinking are expressed in words.
Perception and thinking are closely interrelated. The formation of perception occurs in the first months of a child’s life, and thinking begins to form at the age of two years. The basis for the development of thinking is perception, which provides sensory experience. Thinking has a positive impact on the development and improvement of perception, which enhances its focus and productivity.
Finished works on a similar topic
FEMP coursework at a preschool educational institution 400 ₽ FEMP essay at a preschool educational institution 260 ₽ FEMP test paper at a preschool educational institution 200 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Understanding the world begins with perception and sensation. The first source of knowledge about the world is sensations. Through sensations, children can learn individual signs and properties of objects. A more complex cognitive process is perception, which ensures the reflection of almost all features of an object.
In the first years of life, children develop the prerequisites for sensory standards. In preschool childhood, children use object standards: images of the properties of objects are correlated with a specific object. For example, green is identified as a leaf, and a circle is identified as the sun.
Types of classes in FEMP
Classes are held, according to the training manual by Pozina and Pomoraeva, once a week. In September, the first week is reserved for adaptation, so only three lessons are planned this month.
Preparing a 6-year-old child for school at home
Integrated classes
The integrated type of training is recognized as the most effective, since there is no direct teaching that can distract the child’s attention and deprive him of passion for the process. In such lessons, familiar cartoon characters are chosen as didactic material, for example, Masha and the Bear, who ask the children to help them make a difficult journey through the country of Mathematics.
The journey is accompanied by meeting new heroes who ask the guys for help in solving a task related to numbers or directions on a map.
Open classes
In open classes, embedded game technology is also used, but to a lesser extent. The lesson is more like a school one. It differs only in that it can be attended by teachers and parents of students. The purpose of the lesson is to demonstrate the skill of the teacher and the success of the children. Before the eyes of those present, a fairy tale is born, leading children through tasks and obstacles to the goal. Often in open lessons, teachers use presentations to illustrate the amount of material learned.
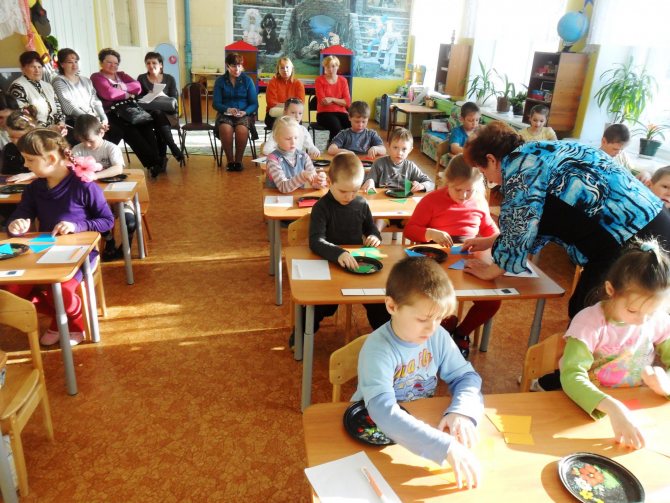

Open lesson on FEMP
Exercises with chopsticks
One of the most informative and accessible methods of teaching children to understand numbers is sticks. To understand the meaning of numbers, it is important not just to remember what it is called and looks like in writing. The whole point of learning to count is to understand how many units there are. Using sticks helps to understand the mathematical meaning of numbers. For comparing numbers with each other, Cuisenaire sticks are best suited, painted in different colors and having different lengths - in accordance with the numerical value of the stick.
Interesting! Each element of the set is visually attractive to the child, due to which acquaintance with numerical values is more effective.
Orientation on a piece of paper
Mandatory exercises on orientation skills on a sheet of paper contribute to all-round development. By the end of the year, children are able to name all the corners, specifying the location of each. Here such spatial concepts as “top”, “bottom”, “left”, “right”, “center” are combined.

Orientation practice sheet
Final lesson
The final lesson on FEPM in the senior group does not imply innovation. The lesson is conducted to consolidate the learned material. Most often, open lessons are held precisely at the final lessons, when the entire course has already been mastered by the children, and the teacher can demonstrate the fruits of his work there.
Didactic material necessarily includes elements of the game: familiar fairy-tale characters, balloons, colorful ribbons of different lengths. Summing up the training, the teacher prepares the lesson in such a way as to touch upon all previously studied topics and check each student how well he perceived the material throughout the year.
Developmental environment
The developmental environment is a system of material objects of a child’s activity that functionally model the content of his mental and physical development.
The physical and developmental environment is organized in such a way that every child has the opportunity to freely do what they love. The arrangement of equipment by sectors (development centers) allows children to be grouped into subgroups in accordance with their common interests: design, drawing, handicrafts, theater and play activities, experimentation. Materials that activate cognitive activity are required in the equipment: educational games, toys.
The kindergarten environment should ensure the safety of children's lives, promote the health and strengthening of the body of each child.
When creating a subjective development environment, you need to remember this:
- The environment must perform educational, developmental, nurturing, stimulating, organizing and communicative functions. But most importantly, it should work to develop the child’s independence and amateurism.
- 2. flexible and variable use of space is necessary. The environment must meet the child's needs and interests.
- The shape and design of the items are based on the safety and age of children.
- decorative elements should be easily interchangeable.
Each group should have space for conducting experimental activities with the participation of children.
- When organizing the subject environment in a group room, it is necessary to take into account the patterns of mental development, indicators of their health, psychophysiological and communicative characteristics, the level of general and linguistic development, as well as indicators of the emotional sphere and the sphere of needs.
- the color palette should be represented by warm pastel colors.
- When creating a developmental space in a group room, the leading role of play activities should be taken into account.
- Depending on the age characteristics of the children, the period of study and the educational program, the object environment for the development of the group should be changed.
It is important that the physical environment is an open system, not a closed system, that can adapt and evolve. In other words, the environment not only evolves, but also develops. Under any circumstances, the objective world that surrounds the child must be replenished and updated in order to adapt it to the new way of life of a given age.
Thus, when creating an object-developmental environment for any age group in a preschool institution, it is necessary to take into account the psychological foundations of constructive interaction between participants in the educational process, the design and ergonomics of the modern environment of a preschool institution, as well as the psychological characteristics of the age group for which the environment is intended.
We are talking about the age of the child, he has a need to play, and this must be satisfied, and not because business has its own time and need for entertainment, but because as the child plays, so he will work.”
These words belong to the wonderful teacher Alexander Makarenko, who in his teaching practice paid great attention to children's play.
Game is a type of activity of children, which consists in reproducing the actions of adults and the relationships between them and is aimed at orientation and knowledge of the subject and social reality.
A didactic game is a type of educational activity organized in the form of educational games that implement a set of principles of play and active learning, characterized by the presence of rules, a fixed structure of gaming activity and an assessment system.
Diagnosis by FEMP in the older group
Carrying out diagnostics involves monitoring the quality of education of each student individually. The lesson is based on individual communication between the teacher and the child.
Formation of cultural and hygienic skills in the preparatory group
The teacher gives each student a task in turn and observes the process of thinking and the result obtained. In the process of such diagnostics, children perform tasks of the following nature:
- Name all the geometric shapes located on the desktop. If the child finds it difficult to name the figure, the teacher poses the question differently: asks to point to the figure he is naming.
Important! Children often forget the names of shapes due to excitement, but they know exactly what it looks like when they hear the name.
- Arrange identical objects in order of increasing or decreasing length. The teacher can suggest the student an algorithm of actions by asking leading questions: “Which subject is the longest of the remaining ones?” Answering this question, it will not be difficult for the child to put them in order.
- Be able to count the number of objects, one more or less than the teacher shows. For example, when a preschooler is shown a picture of six squirrels, he must count seven nuts.
- Build a regular pyramid of cubes or cylinders so that the base is the widest object and the top is the narrowest. The teacher is allowed to hold the pyramid and adjust the placed blocks so that they do not fall.
- Carry out entertaining gymnastics without hesitation: the preschooler, at the request of the teacher, shows with his left or right hand other paired organs and parts of the body - ears, cheeks, eyes, eyebrows, etc., from the side that the teacher names.
- After forming a column, the children must name the person in front and the one standing behind. Guys should not stand closer than a meter from each other.

Children lined up in a column
- List the names of the parts of the day; leading questions are allowed, for example: “When are you going to kindergarten, what time of day is it?”
- Name the days of the week in order. When a child finds it difficult to answer or makes a mistake, the teacher can ask: “if today is the fourth day of the week, what is it called?”
GCD for FEMP in the senior group and additional material
GCD - direct educational activity. On the one hand, children in such classes are given freedom of action and thought, but at the same time, the teacher carefully guides the children, simultaneously conducting a socio-game lesson. According to the Federal State Educational Standard, it is aimed at repeating the material covered and forming independent additional development. Such lessons also imply preliminary planning, a game basis, like Pomoraeva’s notes.
Important! Without an entertaining dramatization, children will not be captivated by mathematics and knowledge of the world. Education conveyed through play is much easier for children to learn at any age.

FEPM lesson at home
Parents whose children do not attend preschool educational institutions can easily find popular notes online and independently develop their child without any special technological difficulties. The availability of educational material makes it possible to keep up with the development of those children who study with professionals in kindergartens.
Mathematical riddles will help you master terminology
Another good thing is math-themed riddles. They teach kids independence and perseverance. After all, you often need to not just say the answer, but prove it. The beauty of riddles is that they teach you to use mental operations (synthesize, analyze, compare, generalize). Here are examples of riddles:
I am a dash in grammar, and who am I in mathematics? (Minus)
I have no corners, And I look like a dish, Like a plate and a lid, Like a ring and a wheel. (Circle)
The cunning brothers live in a difficult book. There are ten of them, but these brothers will count everything in the world. (Numbers)
There are also humorous puzzles that teach you to look for answers outside the box. For example: “You and I, and you and me, how many of us are there in total?” (2). “How many ends does the stick have, two, two and a half?” (in the latter case – 6).