About the work of the “Health” family club in kindergarten
(From work experience)
Having analyzed the data from the questionnaires received in our preschool educational institution, we came to the conclusion that, although all parents have higher and secondary education, the level of knowledge and skills in the field of developing healthy lifestyle habits of most of them is low, and interest in this problem arises only then when their child already requires medical or psychological help. This is due to the fact that most parents do not understand the very essence of “health”, considering it only as the absence of diseases, and sees the means of improving the health of the child’s body only in therapeutic and hardening procedures, completely disregarding the interrelation of all components of health: physical, mental and social.
I believe that the most effective form of working with families on this issue is classes in a family club, which allow for a full-fledged individual approach to the physical and mental development of a child through the interaction of parents who thoroughly know the characteristics of their child, and teachers and doctors who build their work on the basis of professional knowledge pedagogy, psychology and medicine.
Classes at the family club include theoretical and practical parts. Total duration 60 minutes. So, for example, in the first, theoretical part of the “Health” family club classes, parents are offered a message or conversation from a specialist (doctor, psychologist, speech therapist, nutritionist, etc.) on a specific topic of the lesson. Duration 15-20 minutes. Then children join the second, practical part. This could be joint performance of any set of therapeutic and preventive exercises in the gym. Duration 35-40 minutes.
The third and final part summarizes the lesson. Parents are given a variety of reminders, methodological literature, and recommendations. Duration 3-5 minutes.
For example, at a lesson at the “Health” family club on the topic “Prevention of flat feet in preschool children,” nurse Ekaterina Ivanovna Shipko-Perkova introduced parents to the structural features of a child’s foot, gave the concept of longitudinal, transverse and combined flat feet, talked about the causes of flat feet, and taught diagnosis and prevention of flat feet. The children and their parents were shown how to make a plantogram, and then physical education instructor Evdokimova Larisa Vyacheslavovna offered a complex of exercise therapy for flat feet or to prevent it, paying special attention to self-massage of the feet. The lesson ended with a demonstration of equipment for the prevention of flat feet (preventive paths, massage mats, balls, foot massagers, etc., parents were given reminders on the prevention of this disease. The last lesson of the club was conducted jointly with the endocrinologist of the Nadym Health Center Nikolaychuk Oksana Viktorovna. This is wonderful a specialist who conducted an interesting conversation with parents about the proper organization of children's nutrition.Parents asked many questions that interested them, to which they received comprehensive answers.
Of course, such activities in family clubs bring tangible results. However, it should be emphasized that this effectiveness is largely determined not only by the content, but also by the quality of communication between preschool specialists and families.
Communication, as we know, is a two-way process, and all participants are interested in it. This interest concerns the content and emotional side of communication. Every family has newspapers, books, radio, TV, so we are sure that the point is not in the amount of information offered to parents during a lesson in a family club, but in the degree of its novelty, relevance and originality of presentation. Therefore, when preparing for classes, we pay attention not only to the development of the content of the message, the preparation of the necessary equipment and materials, but also the argumentation and evidence of the provisions, dynamism, the ability to take into account the position of another person, and constructively use problematic situations and controversial opinions that arise during communication. A small number of participants (no more than 10 families in one lesson) promotes active, interested contact with everyone, and a joint search for the most effective solutions to the problem for a particular child.
Classes in family clubs significantly increase both the level of development of children’s physical qualities and the speed of formation of vital motor skills. The help of parents and their individual control over their child makes this process very effective. In addition, constant supervision and insurance allow children to have greater freedom of action, which leads to the development of dexterity and the mastery of more complex movements. It is equally important that classes in a family club allow the child to come into contact with children from another group, with different adults. Such a circle of communication creates a broad environment for development and helps each child become a full-fledged member of the community.
Thus, classes in the “Health” family club not only introduce a healthy lifestyle, develop physical qualities and skills, but also contribute to the self-realization of everyone and the mutual enrichment of everyone. Adults and children get to know each other better: character traits, dreams and abilities. A microclimate is created, which is based on respect for the individual, care for everyone, trusting relationships between adults and children, parents and teachers, i.e. the relationship between the physical, mental and social components of health is ensured.
Applications: Meeting of the “Health” club on the topic: “Organization and conduct of hardening of children in preschool and family settings”
Tasks:
— involving parents in participating in the life of the group and kindergarten through the search and implementation of the most effective forms of work;
— improving the pedagogical culture of parents;
— establishing trusting relationships between parents and teachers of preschool educational institutions
- Goals:
— Training in hardening children by parents at home;
— Development of proper breathing skills in children of the fourth year of life; communication skills between adults and children;
— Formation of a positive attitude towards participation in the lesson, cooperation and interaction skills, desire to take part in the practical part of the lesson;
Equipment: TV, cassette with a recording of a fragment of hardening in the family; tape recorder, cassette recording the voices of birds, the noise of trees; mats with buttons for foot massage; sheets for hardening; reminders, recommendations for parents on the topic of the lesson, literature.
Preliminary work: learning poems about the importance of exercise and hardening on human health, learning new games “Carousel”, “Shaggy Dog”, learning a new set of breathing exercises.
Progress of the lesson
Organizing time. Creating a positive emotional mood. I invite parents for a cup of tea and a relaxation exercise.
I would like to begin my speech with the words of J.-J. Rousseau “The ideal of education is the combination of the mind of a sage with the strength and health of an athlete”
We have all been amazed for many years by the sad statistics of the incidence of the disease in preschool children. Every third person has deviations in physical development. Of course, there are many reasons for this: environmental, social, genetic, and medical.
One of them is adults’ inattention to children’s health. In other words, we love our child, diligently treat him when he gets sick, but in everyday life we do not use the entire arsenal of means and methods to prevent the disease. We should not forget that preschool age is the most favorable time for developing the right habits, which, in combination with teaching preschoolers how to improve and maintain health, will lead to positive results.
Having analyzed the morbidity rate of children in preschool institutions, we came to the conclusion that in the structure of infectious morbidity, the share of acute respiratory infections ranges from 83 to 90%. The problem is aggravated by the fact that most of the children in the group get sick every year; 30% of children suffer three or more illnesses per year. Therefore, our first priority was to reduce the high incidence of acute respiratory infections in children.
Together with medical workers, a system of comprehensive measures to improve the health of children was developed: introducing them to a healthy lifestyle, carrying out planned measures to prevent acute respiratory infections, maintaining a healthy regime in the family and preschool educational institutions, teaching proper breathing, daily hardening procedures and self-massage, and the use of anti-stress gymnastics.
We are confident that not a single, even the best physical education and health program can give full results if it is not decided together with the family, if a child-adult community (children-parents-teachers) has not been created in a preschool institution. Therefore, for the third year now, the “Health” family club has been operating in our kindergarten. Today is the next meeting of the club and it is devoted to the most relevant topic, according to a survey of parents: “Organization and conduct of hardening of children in the family and preschool educational institutions.” You, dear parents, will be offered a message on this topic, and then you and your children will go to the gym, where you will practice breathing exercises, foot massage and learn games that will help your children recover from infectious diseases. In the final part of our meeting, you will receive recommendations in the form of instructions on organizing hardening in the family, and you will be able to share your opinion on the work of the club.
So, I suggest you listen to the message: “Hardening in the everyday life of children” (speech by the head nurse of a preschool educational institution)
Part 2 of the lesson is held in the gym, where a physical education instructor teaches parents and children special hardening exercises.
Part 3 of the lesson. Summing up, reflection. Each parent is given recommendations and instructions on organizing hardening at home.
Recommendations for parents on hardening children on weekends and during vacations
Hardening is a system of activities that is an integral part of the physical education of children both in preschool institutions and at home.
The main objectives of hardening are: strengthening health, developing the body's endurance under changing environmental factors, increasing its resistance to various diseases.
When organizing hardening, it is necessary to take into account the health status of children, their age, and the level of training of parents.
Natural factors (air, water, sunlight) are used as the main means of hardening, subject to the following conditions:
1. Taking into account the individual characteristics of the child when choosing a hardening method.
2. Gradual increase in the strength of influence and duration of the natural factor.
3. Systematic hardening - it is carried out all year round, but its types and methods vary depending on the season and weather.
4. Calm, joyful mood of the child during the hardening procedure.
Hardening in the daily life of children
The first requirement for hardening at home is the creation of certain hygienic conditions: systematic ventilation of the premises, stable temperature, rational clothing for children.
Through ventilation, ensuring bacterial and chemical purity of the air, is carried out briefly for 5-7 minutes in the absence of children:
1. in the morning
2. before returning from a walk,
3. during daytime sleep,
After through ventilation, the temperature in the room is usually restored within 20-30 minutes.
The air temperature in the rooms of children under three years old should be - +21-23 C; three to four years old - +20-22 C; five to seven years old - +19-21 C.
To maintain indoor air temperature, constant one-way ventilation is used. It is carried out in the presence of children. To do this, leave one or two transoms open in the room (on one side). To control the temperature, thermometers are placed at the height of the child on the inner wall of the room.
A walk, if properly organized, is one of the most important moments of hardening.
A good way to harden, strengthen and shape the arch of the foot is to walk barefoot. In the summer, children should be taught to walk barefoot on well-cleaned soil (grass, gravel, sand). Hardening should begin on hot, sunny days, gradually increasing the time of walking barefoot (from 2-3 to 10-12 minutes) and continue at lower temperatures (up to +22-20 C). Then you need to teach children to walk barefoot indoors, for example, before naptime, a child walks barefoot along the path to his bed. Morning exercises for children aged 5-7 years are carried out barefoot (in a room with a parquet, plastic or carpeted floor).
The greatest healing effect is achieved when performing physical exercises in the open air. In summer, all organized forms (morning exercises, physical education classes, outdoor games, sports exercises) are best done outside.
There are practically no absolute contraindications for outdoor exercise. But children suffering from chronic diseases should start them in the summer, subject to an individual approach in dosing the muscle load as prescribed by the doctor.
After suffering from an illness that proceeded without complications, healthy children who were previously hardened are exempted from 1-2 physical education classes, and those who were not previously hardened and have functional abnormalities in their health are exempted from 2-3 classes. Children with chronic diseases, after an exacerbation of the underlying disease or the transfer of another disease, are allowed to participate in classes only with the permission of a doctor.
The use of water for hardening purposes in everyday life is combined with the formation of personal hygiene skills in preschoolers. A mandatory requirement for this is a gradual decrease in water temperature when washing and washing your feet.
Children under three years old wash their hands, face, and neck. If they splash their underwear or wet their sleeves, they must immediately change wet clothes, since when they dry on the child, they have a strong cooling effect. With age and as they get used to it, the area of exposure to water increases: children wash their arms up to the elbow, neck, upper chest and back.
Dousing has a great irritating effect. Local dousing of the feet is carried out from a 0.5-liter ladle at a room temperature of at least +20 C. When dousing, the lower half of the lower leg and foot are moistened. The vessel with water is kept at a close distance from the body (4-5 cm). The actual dousing lasts 15-20 seconds. This is followed by rubbing with a dry towel until the skin turns slightly pink.
It should be remembered that the hardening effect will only occur if cool water is poured onto the child’s warm feet. In this regard, dousing should be carried out after a nap.
In summer, it is more advisable to combine dousing your feet with washing them after a walk - first wash your feet with warm water and soap, then pour water over them at the appropriate temperature.
For children 2-3 years old, the initial water temperature during dousing is +32 C, the final temperature is +18 C; for children 4-7 years old - +30C and 16C, respectively. Thus, the water temperature decreases by 2C after one to two days.
At home, pouring feet using contrasting water temperatures can be recommended for young children when hardening begins during the cold period of the year.
Contrast dousing can be gentle when the legs are first doused with warm water (+36C-35C), and then immediately cool (+24C-25C), followed by a warm douse again (+36C-35C). Gradually, the temperature of warm water increases to +40C, and cold water decreases to +18C. Finish the procedure with dry rubbing. This method of dousing is recommended for children who are weakened or after illness. For children who are seasoned and rarely ill, it is better to carry out a contrast douse, first with cold water (+24-25C), and then with warm water (+35-36C) and again with cold water with the same gradual change in temperature. After dousing, dry rubbing is carried out.
General water procedures (dousing, bathing) are organized no earlier than 30-40 minutes after eating.
Swimming in open water is the most powerful procedure, since here there is a simultaneous influence of three factors (air, a large mass of water and sunlight) on the entire surface of the skin.
Swimming in open water is allowed for children over three years of age (no more than once a day) at an air temperature of at least +25C and water temperature of at least +23C. The duration of bathing is from 3 to 5-8 minutes.
Sun hardening is carried out during a walk, especially in spring and summer. You should start with light and air baths in the shade of trees, then move on to local sunbathing: children expose their arms and legs, and should always have a light cap on their head.
When sunbathing, children play in the direct rays of the sun for 5-6 minutes and then go into the shade again. As the tan appears, sunbathing becomes common, and for this, children are stripped down to shorts and T-shirts, and then to just shorts. Sunbathing starts from 5 minutes and increases to 10 minutes (during the day, the total time children spend in the sun can be 40-50 minutes).
To achieve the optimal hardening effect, it is advisable to use the combined effects of water and air.
In the summer, games with water, games in splashing pools and streams should be widely used. The water temperature should not be lower than +20C. The exposure time of the factor gradually increases from 30 seconds to 5-10 minutes.
There are a number of contraindications to using the sun for hardening purposes. Exposure to direct sunlight is not recommended for all children of the first year of life and older children suffering from severe retardation in physical development, anemia, and increased nervous excitability. In these cases, irradiation with scattered and reflected solar rays is used.
Experience in the work of the children's and parents' club "Commonwealth".
Model of social partnership of MADOU of the city of Nizhnevartovsk
DS No. 83 “Pearl” and families.
Experience in the work of the children's and parents' club "Commonwealth".
The preschool age of a child is the time when the foundations of a person’s physical, mental, and personal development are laid. Losses incurred during this period cannot be fully recovered in later life. This circumstance places a special responsibility on adults for the fate of a growing person.
In the Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated December 29, 2012 No. 273 - Federal Law “On Education in the Russian Federation” in Article 44. “Rights, duties and responsibilities in the field of education of parents (legal representatives) of minor students”, in paragraphs 1 and 2 it is indicated:
1. Parents (legal representatives) of minor students have a priority right to the education and upbringing of children over all other persons. They are obliged to lay the foundations for the physical, moral and intellectual development of the child’s personality.
2. State authorities and local governments, educational organizations provide assistance to parents (legal representatives) of minor students in raising children, protecting and strengthening their physical and mental health, developing individual abilities and the necessary correction of their developmental disorders.
In the Basic educational program of our preschool institution in paragraph 2.6. “Features of the interaction of the teaching staff with the families of pupils”, it is stated that the family is the most important social institution, which is of decisive importance both for the individual life of a person and for the social, economic and cultural development of society”, it is stated that the general requirements for preparing parents for accompanying A preschool child within the framework of his development trajectory during the implementation of an approximate basic general education program for preschool education are:
- informing parents about the compliance of the child’s development with the tasks set in the basic general education program along the following lines of development:
- health and physical development;
- cognitive and speech development;
- social and personal development;
- artistic - aesthetic.
Clause 2.9 «
The specificity of national sociocultural and other conditions in which educational activities are carried out” indicates that the educational level of parents is at different levels and presupposes the need for individual close cooperation between teachers and the family. The solution to educational problems should be carried out in close cooperation with the family, directly at various meetings with parents (legal representatives), through the activities of the parent committee.
The purpose of interaction between preschool educational institutions is to involve parents (legal representatives) in the education, training, upbringing and development of children. A preschool educational institution acts as an open socio-educational environment for parents, in the creation of which they take a direct part: interacting with educators and specialists in the process of organizing planned events with children, in the process of organizing an environment in groups.
Taking into account all these provisions, our kindergarten has built a model of social partnership with the family.
Model of social partnership between preschool educational institutions and families within the framework of the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education
The effectiveness of a kindergarten depends largely on constructive interaction and mutual understanding between preschool staff and parents.
The modern model of social partnership between preschool educational institutions and families of pupils is understood as a process of interpersonal communication, the result of which is the formation in parents of a conscious attitude towards their own views and attitudes in raising a child.
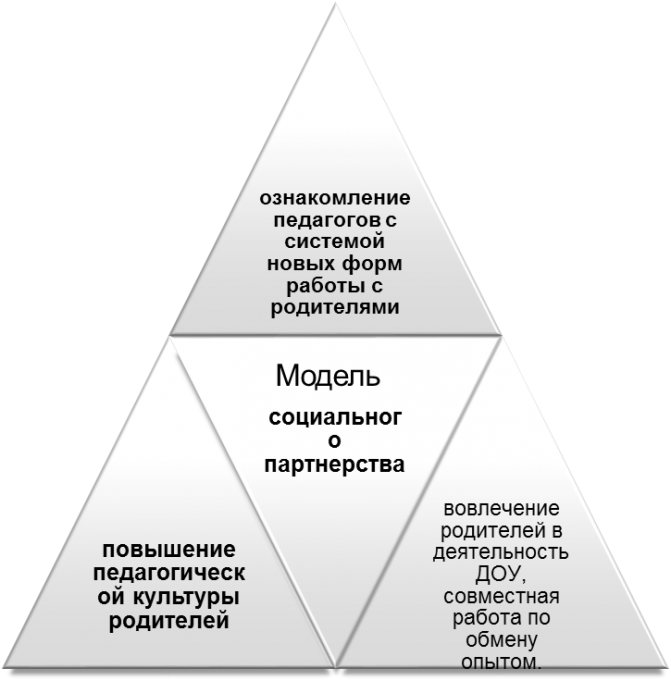
The model of social partnership Parent - preschool educational institution is solved in three directions: working with the preschool educational institution team to organize interaction with the family, familiarizing teachers with the system of new forms of work with parents;
improving the pedagogical culture of parents; involvement of parents in the activities of preschool educational institutions, joint work to exchange experience. In the process of implementing this model of cooperation, the attitude towards the “prestige of parenthood” changes radically. Parents develop the skills of conscious inclusion in a single process of raising and educating a child together with teachers, and teachers overcome the stereotype of parents distancing themselves from the education system.
MADOU of the city of Nizhnevartovsk DS No. 83 “Pearl” is an open system, the main “tool” of which is social partnership, the collaboration of the kindergarten staff with parents, operating on democratic and humanistic principles. For several years, our preschool institution has been implementing the following model of interaction between the preschool educational institution and the family:
Principles of working with parents (persons replacing them)
Family Study Methods
- Focused, systematic, planned;
- A differentiated approach to working with parents, taking into account the multidimensional specifics of each family;
- Age-related nature of work with parents;
- friendliness, openness.
- Questionnaire;
- child monitoring;
- visiting the child's family;
- family examination using projective techniques;
- conversation with a child;
- conversation with parents.
Forms of work with parents (persons replacing them)
Interactive
Traditional
Educational
- discussions;
- round tables;
- conferences;
- family chronicles;
- game trainings;
- parent clubs;
- seminars and workshops.
- theme weeks;
- parent meetings;
- leisure;
- creative joint exhibitions;
- photo exhibitions;
- competitions;
- open days.
- visual information;
- individual consultations;
- media use; stands and corners for parents.
The main idea of interaction between teachers and parents is to establish partnerships that will allow them to combine efforts to raise children, create an atmosphere of common interests, and enhance the educational skills of parents.
Building a model of interaction between parents and teachers in the educational process of a preschool institution involves solving the following tasks:
— to activate the educational capabilities of parents;
-involve parents to participate in the educational process of the preschool institution;
— use the experience of family education to implement educational programs;
- contribute to the personal enrichment of all participants in interaction through activity, its transformation and change.
The development of optimal methods and forms for developing the self-awareness of parents in a preschool institution is part of the general task of organizing work with parents.
By uniting and mobilizing the joint efforts of parents, educators and preschool specialists, we can more effectively solve the problems of supporting the personal and age-related development of children.
Combining the efforts of a preschool institution and parents in the process of raising children is a difficult task in organizational and psychological-pedagogical terms. It seems to us that the fundamental conditions for solving it are to create a special form of communication between the parents of pupils, the administration and teachers of preschool educational institutions, which can be designated as confidential contact.
At each stage, a certain relationship and movement of internal and external goals can be noted.
The first stage is broadcasting a positive image of the child to parents. Thanks to this, from the very beginning, friendly relations with a focus on future cooperation develop between parents and teachers.
The second stage is the transmission to parents of the knowledge that they could have acquired in the family (features of the child’s communication with peers).
The third stage is to familiarize teachers with family problems in raising a child. At this stage, the educational psychologist and educator maintain a dialogue with parents, in which the latter play an active role. It is necessary to clarify that this stage is the third and not the first (which would seem to be more logical) not by chance. Only after the first two stages do parents, based on the achieved trust, have a need to share with the educational psychologist information about the manifestations of the child’s individuality (his tastes, behavior, habits) at home, and not only about the positive aspects, but also the negative ones.
The fourth stage is joint research and formation of the child’s personality.
The most important result of such meaningful, emotionally rich, activity-mediated communication between teachers and parents should be the active position of parents in raising a child, their willingness to correct their own attitudes, “transmitted” to the child.
As part of this model of interaction between kindergarten and family, a parent club “Commonwealth” has been organized in our preschool institution.
To implement the basic conceptual provisions of this model of cooperation, a system of psychological, pedagogical and social support for the educational process in a preschool institution is required.
Implementing the ideas of social partnership, humanizing the environment and expanding sociocultural boundaries, the administration of the preschool educational institution is guided by the developed program of the parent club “Commonwealth”.
These and other events expand the boundaries of preschool education as a social institution of education and enrich the content of social partnership in order to humanize the socio-cultural space.
Each kindergarten employee participates in organizing work with parents and developing common goals and objectives together with parents. This work requires great personal effort from teachers, constant creative search, and replenishment of the existing knowledge base.
The implementation of the social partnership model allows us to achieve the following results:
-creating emotional and psychological comfort for keeping a child in kindergarten in conditions as close as possible to family ones;
-reducing the number of dysfunctional families and pedagogical neglect in raising children;
– increasing the pedagogical, psychological and legal literacy of parents in the upbringing and education of preschool children;
– harmonization of parent-child relationships;
– increasing the level of parental involvement in the activities of the preschool institution.
We believe that the model of social and pedagogical partnership between family and educational institution that we have developed is a promising and effective type of social interaction.
It is focused on a humanistic approach and forces a change in the traditional pedagogical worldview: the main character becomes the child, his development, the disclosure of personal potential, and the preschool institution is a mediator between the child and parents, helping to harmonize their relationships.
Increasingly, our kindergarten teachers are faced with the fact that parents are experiencing various difficulties in raising their children. There are many reasons for this, and one of them is the heavy workload of parents (physical and emotional), since they spend a lot of energy on financially supporting the family. Therefore, it is easier for them to sit the child in front of the TV or provide him with a large number of toys that replace parental communication. There are also immature parents who are not adequately involved in the upbringing and development of their children (they do not understand the importance or have no desire). Young parents experience especially many difficulties in raising children, since they have little life and parenting experience. Some of them are often confused in situations when children begin to disobey, become capricious, and persistently demand something. And sometimes it is easier for an adult to give in to a child or punish him than to try to look for adequate ways out of the current situation, to understand and accept his child. For many parents, the period of adaptation of a child to kindergarten is especially difficult. There are also many requests for help from psychologists and educators from parents during a crisis period in a child’s development (the three-year crisis).
Therefore, it is so important to work with parents, paying special attention to young mothers and fathers. Involving parents in the joint upbringing of preschool children, the kindergarten staff for several years has been searching for new effective forms of working with families that would make it possible to stimulate interest in the life of children in a preschool institution and to intensify the participation of parents in various events.
One of these forms was the organization of a parent club - “Commonwealth”.
In the first year, the Club's Regulations and a long-term work plan were developed, which presented the topics of the meetings.
The main activities of the club are providing psychological and pedagogical assistance to parents of pupils, promoting the positive experience of family education, increasing the competence of parents in matters of development of preschool children.
Activities are planned taking into account the interests and requests of parents, based on the results of a survey at the end of the school year.
During the functioning of the club, the most difficult thing for us was to involve the parents themselves in active interaction; there were problems with attendance and low activity of parents.
Careful preparation for each meeting, a clear selection of material, unconventional forms, practical activities, unobtrusive teaching of various techniques for working with children - all this contributed to the interest of parents in attending club meetings.
The parents' club specially organizes free communication, accompanied by psychological support. In this case, gaming and interactive technologies are used, as well as exchange of opinions with teachers, specialists and more experienced parents. Moms and dads get acquainted with positive examples of family education. And such principles of conducting club meetings as non-judgmental acceptance of everyone, maintaining confidentiality, and voluntary participation can increase the level of trust and emotional safety of participants.
PURPOSE AND TASKS OF THE CLUB
The goal of the “Commonwealth” parent club program is to create conditions for increasing parental competence in matters of the comprehensive development and upbringing of a preschool child.
Tasks:
- Expanding parents' ideas about the characteristics of the development and upbringing of preschool children.
- Contribute to the activation of the formation of reflection on parents’ own educational activities.
- To update the understanding of the importance of parental participation in the comprehensive development of their child.
- Formation of ideas among parents about the importance of maintaining mental and physical health.
- Promote increased mutual understanding between parents and kindergarten teachers.
Work with parents within the framework of the “Commonwealth” club is based on a new philosophy of interaction between family and preschool institution, which centers on the idea that parents are responsible for raising children, and all other social institutions (including preschool institutions) are called upon to help , support, guide, supplement their educational activities. ABOUT
Experience shows that parents’ positive attitude towards joint activities has enormous pedagogical value. Parents are confident that the preschool institution will always help them in solving pedagogical problems, and at the same time will not do any harm, since it will take into account the opinion of the family and suggestions for interaction with the child. The biggest winners are the children, for whose sake this interaction is carried out, which will contribute to the child’s comfortable stay in the preschool educational institution, and in the future his successful preparation and adaptation to school.
Program of meetings of the club "Commonwealth"
intended for interested parents. The group can be a team, or the parents of one group can become members of the club. The club program consists of 9-10 meetings.
Frequency of meetings: once a month. Club meetings are led by an educational psychologist. Preschool education specialists (deputy head of medical education, group teachers, speech therapist, head nurse and others) are invited to participate in club meetings for consultations on issues of interest to parents and as assistants in organizing interactive activities in subgroups.
Classes are held in the form of game training using conversations, discussions, problem situations, games and exercises. The topics and content of some club meetings are vague, as they are prepared in accordance with the requests of the participants. The preparatory stage of work with parents begins with getting acquainted with the program of the “Commonwealth” club and with teachers - kindergarten specialists. At this stage, a survey of parents is carried out in order to identify their pedagogical competence. Conversations with parents help teachers and specialists identify the most popular topics and problems in the upbringing and development of preschool children; taking into account the requests of parents, determine the work of the club for the entire school year.
In organizing club meetings, we use both proprietary methods developed by us.
At the end of the meeting, parents are offered reminders on the main topics of the meetings. Efficiency is determined through a survey of parents' opinions at the end of meetings and based on the results of the work program of the Commonwealth club.
Parents are informed in advance by teachers about the club meeting verbally, as well as through an announcement indicating the topic of the meeting.
Principles for conducting meetings:
- Voluntariness of participation.
- Maintaining confidentiality.
- Non-judgmental acceptance.
- Openness of the group.
- Leader competence.
In our opinion, the performance criteria are:
— high attendance by parents at all planned meetings,
- parents’ use of the proposed materials when working with children,
- positive assessment of the family and feedback on further cooperation with the preschool institution.
From the survey results, we can see a meaningful difference in the parents’ answers to the survey questions that they gave in October, at the first introductory meeting, and in April, when they had the opportunity to participate in the work of the “Commonwealth” parent club. If at the beginning of the year parents were more concerned about generally accepted problems: “What did you eat?”, “It is necessary to teach the child to count, write,” etc., then at the end of the school year 100% believe that the basis for the development of a preschool child - the game lies.
When organizing meetings in the parents' club, we very carefully thought through the topics, selected exercises that would help parents establish contact with each other, identify problems that concern parents, and help them find the right solution. Parents gladly came to the meetings, answered questionnaires, participated in discussions, played games, shared their experiences, impressions, and talked about their children and problems. Parents had the opportunity to ask questions of concern to the kindergarten specialists and receive qualified assistance from the staff of our preschool institution.
Thus, the cooperation of the kindergarten and the family within the framework of the work of the “Commonwealth” club helped to activate the pedagogical potential of parents, involve them in the upbringing and development of children, help them in this; parents had the opportunity to share their experience and gain new ones.
And indeed, the professionally coordinated work of the preschool staff
institutions, favorable microclimate in kindergarten, individual
approach to each family - all this contributes to increased efficiency
educational work with children and building literate
communication with parents (legal representatives) of pupils.
N.B. Shakhova, Deputy Head of VMR


