Artistic media
Artistic media include: painting, literature, music and almost all other areas of artistic art. These works evoke emotional interest, the desire to become like the one whose works have come to us through years, centuries; on the one who works, toil, help to understand the importance, show the full significance of hard work as the most important personality quality. The use of works of art becomes especially important in preschool educational institutions.
All artistic means are effective in the pedagogical process. Their role is unique. Just listening to music or looking at pictures does not teach you how to work. Only with the observance of certain principles do the means begin to really work and provide assistance in the formation of the most important working qualities.
Literature provides basic knowledge about the emergence of professions, the process of making everyday things, famous people who made a huge contribution to the historical development of mankind. Works of fiction provide a generalization of the role, benefits of labor, and mutual assistance of professions. Children develop positive images that they begin to strive for when creating themselves.
Works of fine art show the process of labor and have a certain emotional mood. Sometimes it is joy, an upsurge of emotions, in other cases it is a calm respite, enjoying the result of the work.
The work is not easy and not easy. Children must understand this in order to learn to form an attitude towards people working for the good of society with respect, compassion, and pride. To do this, the teacher can recommend that parents visit an art gallery, exhibition with the children, or look at reproductions of paintings at home, and talk about the meaningful meaning of the works.
Music also helps to create a desire to work. Musical recordings can be used positively in a group, on a site. They can lift your spirits and give your current routine a consistent rhythm. With music, work becomes more enjoyable and much easier. It is recommended to use it when carrying out collective cleaning of groups, classrooms, during basic manual labor, and when working on site.
?
All artistic means bring maximum effect in the pedagogical process when they are used systematically, in interaction with each other, and if they are organized.
MAGAZINE Preschooler.RF
Labor activity as an important means of education in preschool ageAnnotation. The article provides definitions of the terms “labor” , labor activity”, examines the main types of labor in which a preschooler is involved, and characterizes the influence of labor activity on the comprehensive development of the personality of preschool children.
Key words: labor, labor activity, labor education, preschoolers, preschool age.
The main goal of the implementation of the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education is the formation of a general culture of students, the development of their moral, intellectual, physical, aesthetic qualities, initiative, independence and responsibility. Solving the problems of children's development should be aimed, among other tasks, at gaining experience in elementary work activities (self-service, household work, work in nature).
The end of the 20th - beginning of the 21st century is a stage in preschool education, which was distinguished by the oblivion of the problem of introducing a child to work. In many publications of preschool education programs, implemented before the release of the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education, listing the requirements for the structure of the main general education program of preschool education, labor education was not allocated to a special section. Currently, the section “Labor education” is presented in preschool education programs as an integral part of the educational field “Social and communicative development” .
Labor activity is “the process of actively changing objects of nature, the material and spiritual life of society in order to satisfy human needs and create various values. The subject of the psychological study of labor activity is the mental processes, factors, states that encourage, program and regulate a person’s labor activity, as well as his personal properties” [4, p. 117].
Labor activity, according to S.A. Kozlova, is a concept that summarizes different types of labor, consisting of labor processes (for example, dressing, undressing, washing hands, setting the table, wiping dust from furniture, etc.). The labor process is a unit of labor activity. Its structure presents all components: the purpose of labor, material and labor equipment (tools); a set of human labor actions to transform materials using tools; the achieved result of labor that satisfies human needs [2, p. 173].
Labor, according to Ya.P. Kolominsky, is “a complex activity, the implementation of which requires a certain level of physical and mental development. Preparing a child for future work begins long before he can take part in socially useful work. The mental qualities of a person necessary for work are formed under the influence of living conditions and upbringing” [3, p. 134].
The formation of elementary labor activity in preschool childhood occurs in the process of interaction with an adult.
Preschool children are characterized by subject activity, which should be considered as a prerequisite for labor activity. At this age, child labor most often finds its way into play. Imitating the work actions of adults is the main content of children's play, allowing them to master these actions and thereby contributing to the development of work activity. However, she is very unstable at first and goes back into play.
Labor processes gradually develop into types of labor. “The first time a child masters self-service, the characteristic feature of which is focus on oneself, and the content is the ability to serve oneself (dressing, undressing, eating, hygiene procedures). Household work presupposes the ability to maintain order in the environment of a kindergarten group, on a site, at home (setting the table, preparing the necessary material for making crafts, etc.)” [ 1, p. 269]. “Labor in nature is distinguished as a special type of labor. The content of such work is caring for plants and animals, growing vegetables in the garden, landscaping the site, participating in cleaning the aquarium, etc. Labor in nature has a beneficial effect not only on the development of labor skills, but also on the education of moral feelings, laying the foundations of environmental education
Manual and artistic labor, by its purpose, is labor aimed at satisfying the aesthetic needs of a person. Its content includes the production of crafts from natural materials, paper, cardboard, fabric, wood. This work contributes to the development of imagination and creative abilities; develops small arm muscles, helps develop endurance, perseverance, and the ability to finish what you start” [2, p. 173].
At preschool age, children gain an understanding of the role of work in human life and society, become acquainted with the work and professional activities of adults, the world of professions, are included in feasible work activities in kindergarten and family, acquire initial labor skills and work experience, learn to plan, apply efforts, to bring the work started to completion, to interact with partners, to provide assistance, to appreciate the results of one’s own and others’ work.
It is also necessary to develop labor activity itself - from individual labor processes to the simplest types of labor. The solution to this problem determines the child’s inclusion in work, his ability to take part in joint activities, and achieve a common result with adults and peers. It is necessary to introduce preschoolers to the work of adults, to cultivate interest and a positive attitude towards it, hard work, independence, perseverance, responsibility, and friendly relationships with peers in the process of activity.
Bibliography
- Preschool pedagogy with the basics of methods of education and training: Textbook for universities. Third generation standard / Ed. A.G. Gogoberidze, O.V. Solntseva. – St. Petersburg: Peter, 2013. – 464 p.
- Kozlova S.A., Kulikova T.A. Preschool pedagogy: textbook. aid for students avg. ped. textbook establishments / S.A. Kozlova, T.A. Kulikova. – M.: Academy, 2000. – 416 p.
- Kolominsky Ya.P. and others. Mental development of children in normal and pathological conditions: psychological diagnostics, prevention and correction / Ya.P. Kolominsky, E.A. Panko, S.A. Igumnov. – St. Petersburg: Peter, 2004. – 480 p.
- Psychology: Textbook for humanitarian universities / Ed. ed. V. N. Druzhinina. – 2nd ed. – St. Petersburg: Peter, 2009. – 656 p.
| Next > |
Goals of labor education
?
Education through labor is an indispensable condition for the comprehensive, full development of the individual. On the one hand, physical labor stimulates mental activity, and on the other, the moral qualities of the individual.
In pedagogy, the main goal of labor education is the moral and psychological (practical) preparation of children for work. The goal is achieved gradually, taking into account the age, capabilities, and interest of the children. The global goal is a hardworking society, ready for change, capable of working for the benefit of their families and the common cause.
Labor education at school - the main tasks and their solution
Labor education begins in the family - we have talked about this more than once. But school also has a significant influence on the upbringing of a young person. For schoolchildren, work is a necessary and important means of developing moral ideas and personality traits. The goal of labor education of schoolchildren is the formation of a natural physiological and intellectual need for work. At school, it is closely connected with the polytechnic training of students, which ensures a level of knowledge of the basics of technology and organization of production.
Within the walls of a comprehensive school, labor education solves several basic and important tasks:
- Motivation to work, stimulation of interest in knowledge, the need for work as a creative process, the desire for practical activity;
- Formation of a positive attitude towards work among schoolchildren;
- Education of moral qualities: a sense of duty, hard work, responsibility, mutual assistance, determination, perseverance, honesty;
- Development of students' creative abilities through manual labor;
- Schoolchildren mastering various types of techniques, labor skills, forming an internal culture of physical and mental work.
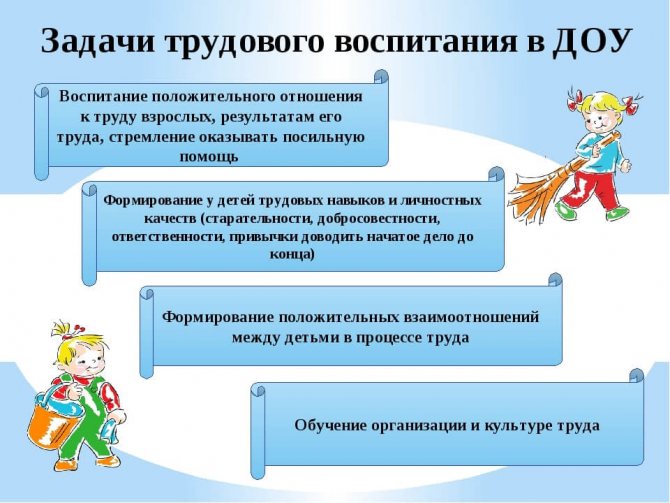
Tasks of labor education of preschool children
Labor education of preschool children begins in the family and is of great importance for the development of a little person. Preschool age is a period of imitation. Children copy everything they see. They like to work. This unique moment cannot be missed. It is necessary to encourage initiative, stimulate interest, and develop the work skills of children.
According to the Federal State Educational Standard, the term “labor education” is a system for developing in children diligence, labor skills and the desire to learn to work.
Teachers see the goal of labor education in kindergarten as the formation of the same positive attitude towards work and moral qualities. Instilling respect for the work of adults is one of its main goals.
In the work activities of preschoolers, an important role is assigned to the teacher. The teacher’s task is to help the child acquire his own experience and skills in work that is feasible for his age. Involvement in work activity allows them to demonstrate their abilities, feel like a part of the adult world, and enjoy the joy of contemplating the result of their work. The teacher organizes work activities, unites the team, teaches children to work together, help adults, and each other.
Own activities
Independent work activity is considered the main means of education. In this way, children learn basic work skills, acquire the opportunity to achieve the expected result, and satisfy the need to join the adult world.
A child’s activity is an effective means of education. It is preceded by training in basic skills. The child independently masters meaningful activities. It includes participation in socially useful work and self-service. This tool helps the development of significant motives, forms of behavior, the formation of care for people, wildlife, and surrounding objects.
The child’s activity has an educational impact provided that it has an organized form, otherwise its meaning becomes neutral.
To implement the tasks of education, conditions are created that promote the development of basic qualities from an early age, forming a culture of personal education, attitude towards work, its result, and the working person.
The child’s independent activity is used at all stages of upbringing. During the long school period, the forms of independent activity are varied. Among them are:
- labor actions, assistance to veterans, other volunteer forms;
- activities aimed at improvement and repair;
- production practice.
Independent work of preschoolers has certain requirements. There are two types of it: individual, collective.
Individual forms are characterized by the fact that most of the work is done by the child individually , but always under the supervision of the teacher. This creates optimal conditions for understanding, awareness of the social orientation, the significance of the achieved result, for the high-quality development of effective actions, and then complex processes under the guidance of an adult educator.
The material will be supplemented by an article about the problems of labor education of children.

In individual work, attention is paid to constant monitoring of the correctness, accuracy of execution, quality of the result, accuracy, discipline during work, control over order, pace, efficiency.
In preschool age, the first opportunity for collective work appears with characteristic features: a significant goal, division of responsibilities, collective result, responsibility of participants in the labor process, children’s dependence on each other. In collective work, conditions arise for the manifestation of mutual assistance, demanding of each other, and mutual responsibility.
Methods and forms of labor education
With the acquisition of initial skills and the ability to work together, the organization of a collective form becomes much more complicated.
Main tasks of labor education
In the process of labor, not only material objects are created, but also the person himself is improved. Therefore, the goal of labor education, first of all, is to educate a harmonious personality, and then to form his psychological and physical readiness for work.
Against the backdrop of social and economic development, reality places high demands when it comes to the identity of the producer. The importance of his attitude to work as a conscious need, as well as a vital need, a positive attitude towards work, respect for work (in general), and for its result is emphasized. Sociability, initiative, creativity – these are the qualities that the working world expects from a mature personality. And these qualities are formed in the process of labor education.

Readiness for work is the result of labor educational activities, which, in turn, solves the following problems:
- Formation of skills and abilities in work;
- Awareness of the goals and objectives of work;
- Formation of automotivation for work.
Labor education of preschool children in kindergarten
Considering that the economic, environmental and social situations in the country are changing dramatically, the direction and meaning of labor education is changing. New techniques, motivations and approaches are required.







