Conversation about the forest in the preparatory group
Summary of a conversation about the forest for children 5-7 years old “A Journey through the Rooms of a Green House”
Author: Alevtina Germanovna Korobkina, teacher of the preschool educational institution “Smile” kindergarten, Perm region, urban settlement Suksun. Description: This material can be used by educators, counselors and primary school teachers, as well as parents in environmental education. Goal: to continue to form an understanding of the forest and the forester profession. Objectives: Educational.
Contribute to: clarifying and systematizing ideas about the forest and the forester profession;
strengthening cognitive interest and love for nature; aesthetic perception of the beauty of nature, through reproductions of paintings; Developmental.
Promote: the development of coherent speech, the ability to maintain a conversation, answer questions with complete answers;
developing respect for the work activity of a person in the forester profession; development of thinking, attention, memory. Educational.
Promote: nurturing love and respect for nature.
Material: reproductions of paintings by artists: Shishkin “In the Forest of Countess Mordvinova”, Shishkin “Ship Grove”, Levitan “Birch Grove” Illustrations on the topic phonogram “Sounds of the Forest” basket of hazelnuts Preliminary work: reading natural history literature to children, looking at reproductions of paintings by artists about nature , reading and memorizing poems on an environmental theme, excursions to the park, pine forest. Organization: children stand in a circle, holding hands. Round dance game “Let's go through the raspberries into the forest” 1. Let's go through the raspberries into the forest, let's go into the forest into the forest (children walk in a circle). Let's start a dance, let's start, let's start (one by one they put their legs out) Chorus: The sun is in the yard (hands are raised up, fingers are open - “sun”) And in the forest there is a path (palms folded together perform wave-like movements in front of you) My sweet you, raspberry ( sliding movements of the palms - the “Skeet” movement) 2. You, raspberry, not in the mouth, not in the mouth, not in the mouth (pinch grip of three fingers of the leading hand, move towards the mouth) Pour into the box, box, box. (a pinch grip of three fingers of the leading hand imitates picking berries into a basket, in front of the chest. Chorus: the movements are the same 3. Like picking, picking, picking raspberries. (a pinch grip of three fingers of the leading hand imitates picking berries from the ground - with the body tilted) We will bake pies, let's bake, let's bake ("pies" movement). Chorus: the movements are the same. 4. We'll bake, bake, bake pies. ("pies" movement). We'll call all the neighbors, we'll call, we'll call (movement of the hands, palms facing the face - “invitation”) Chorus: the movements are the same.
PROGRESS OF THE CONVERSATION.
Educator: What are we up to today? Children: will go on a journey through different rooms. Educator: which rooms can you travel through? Children's answers Educator: the riddle that the poet Jovan Jovanovic came up with will help us - Zmaj, listen carefully! I want to invite us to one beautiful village. He was quite lucky, who was able to visit the din. There, every house and every yard is covered with a green roof, a carpet woven with flowers lies on the street. There are no fences or doors. The windows are open to the garden. Guests will be greeted there with songs and treated to great pleasure. Those who were lucky enough to be there saw miracles! And the unusual village is called... Children: Green Forest Teacher: how did you guess that the riddle is about a forest? The children are talking. Educator: Yes, our journey to the big green house and through its rooms.




Now which forest did you enter?



The forest has become sparse. We passed the swamp. And suddenly it became light all around. What forest pleases with light and whiteness?




Here in the Urals, the Forestry Engineering University trains foresters who grow forests in all corners of Russia. So, why did people come up with the profession of forest rangers if the forest grows on its own without humans? We will find out if we go to the forestry university and become students of this university
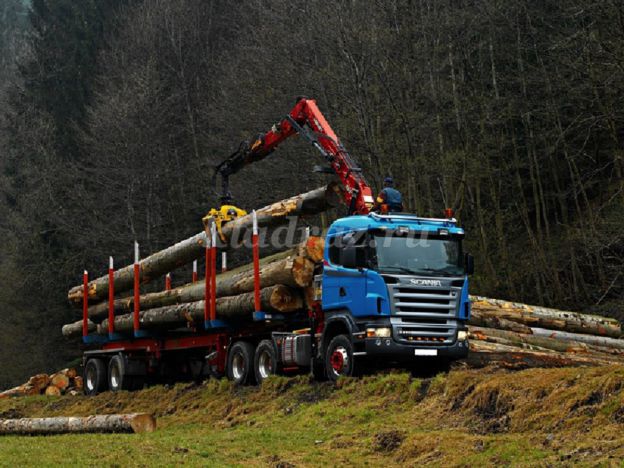



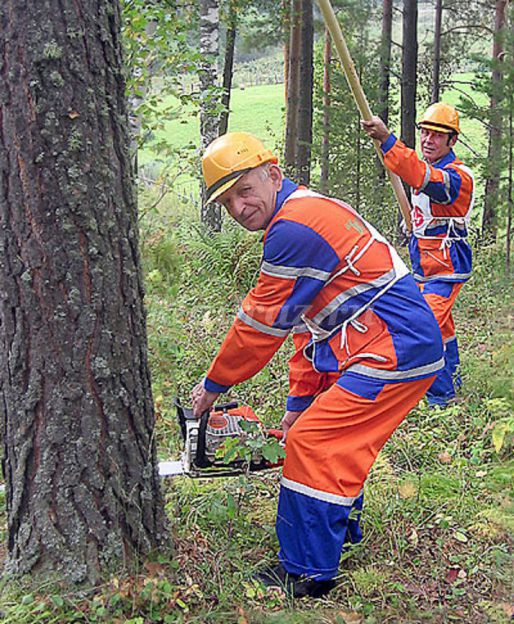
Timber trucks transport long trees with chopped off branches - they are called WHIP. They cut down trees with saws.
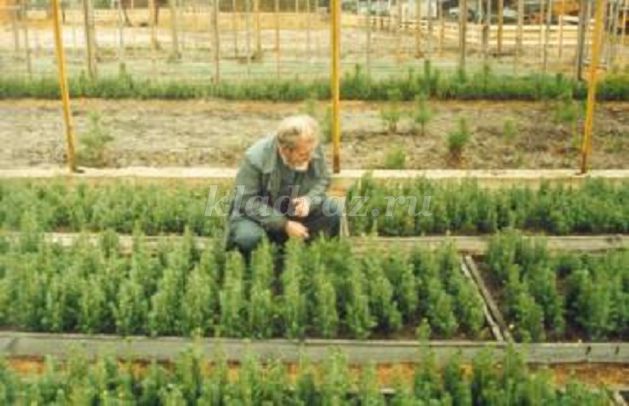


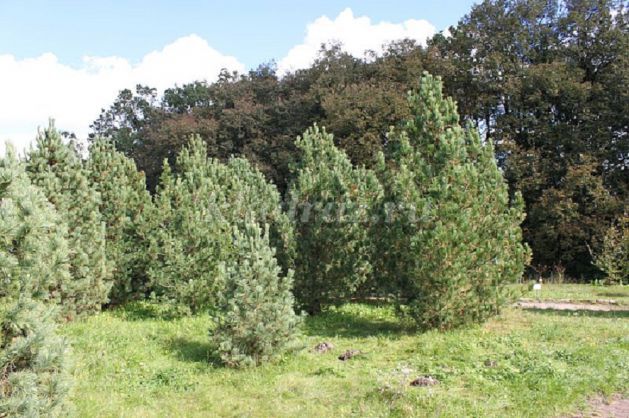
small, fluffy Christmas trees are growing! When it’s hot, they are watered, and the soil around them is also loosened with a rake. Everything is like in a garden. The soil of the Christmas trees in the beds is black. And the pines have sand. Who loves what! In the spring of this forest nursery, seedlings - very young pines and fir trees - will be brought to the cutting site. Here they will be planted and a new forest will grow.


We recommend watching:
Scenario of summer entertainment for children of the senior preparatory group of a preschool educational institution. Entertainment in the preparatory group. Scenario Conversation with children in the preparatory group on the topic: Wildflowers Summary of summer sports activities in kindergarten for older preschoolers
Similar articles:
Dramatization of Chukovsky's fairy tale The Fly Tsokotukha for children 5-7 years old
Scenario for summer entertainment on ecology at a preschool educational institution. Senior – preparatory group
Disco in kindergarten. Scenario
Game entertainment for children of senior preschool age in kindergarten
How many forests are there on our planet?
Currently, forests occupy about a third of the land area.
The total forest area on Earth is 38 million km². Half of this forest zone belongs to tropical forests, the fourth part is located in the northern hemisphere. The forest area in Russia is 8.8 million km². Russia has almost 25% of the world's timber reserves and 50% of the world's valuable coniferous forests.
The forests of our planet are very different. First of all, they are divided into three main geographical forest zones - the equatorial forest zone, which grows along the equator, the subtropical and tropical forest zone, and the temperate forest zone. And there are also main types of forests. There are also three of them - coniferous, deciduous, mixed. In turn, deciduous forests are divided into deciduous and evergreen, i.e. non-deciduous. Evergreen forests are the healthiest and most productive: they produce 80% of the oxygen on Earth.
In Russia, forests are not the same both in different climatic zones and on different soils, in areas with different microclimates and water regimes. You can find a dark, cold spruce forest, a light larch forest, and a mighty oak forest, or you can find yourself in a honey-bearing linden forest, and in a nut-bearing pine forest, or in a copper-golden pine forest, where boletus grows best.
All forests on Earth work like green factories: on bright, sunny days they store solar energy for future use, without which life on the planet would be impossible. The main product of a green forest is wood.
Causes and consequences of forest loss
The reasons for the reduction are different. First of all, these are fires.
One of the reasons for the increase in forest fires is the sharp increase in the number of people traveling to the forest for recreation. Incidents of fires in the forest are the result of careless and inept handling of fire. Fires can also occur from spontaneous combustion of peat, sometimes from lightning. World statistics show that about 72% of all forest fires are caused by people. Hence, fighting forest fires remains one of the most important government tasks.
Also one of the reasons for forest loss is deforestation. Deforestation began at the dawn of human society and increased as it developed. Over the past 10 thousand years, 2/3 of the forests on Earth have disappeared. Therefore they say: “man is preceded by forests, deserts accompany him.” Over historical time, about 500 million hectares have turned from forests into barren deserts. Forests are being destroyed so quickly that the area of deforestation significantly exceeds the area of tree planting.
Forests are being cut down and shrinking at a rate of about 26 hectares per minute, and it is feared they will disappear within 25 years. Deforested areas are not restored; in their place, unproductive shrub formations are formed, and with severe soil erosion, desertification occurs. Due to deforestation, the water flow of rivers is reduced, lakes dry up, groundwater levels drop, soil erosion increases, the climate becomes more arid and continental, and droughts and dust storms often occur.
The next problem is forest pollution. Forests often visited by tourists are thoroughly littered with cans, bottles, rags, paper, etc.
The area of forests destroyed by industrial emissions is increasing.
Poaching always deals devastating blows to Russia's wildlife, which contributes to the extinction of many species of wild animals.
Forest protection and restoration measures
The main task of forest protection is their rational use and restoration.
It is important to increase forest productivity and protect them from fires and pests. With proper forestry management, felling in certain areas should be repeated after 80 - 100 years, when the forest reaches full maturity.
Another important measure for forest conservation is the fight against timber loss. The greatest losses occur during timber harvesting. At the felling sites, many branches and pine needles remain, which can be used to prepare pine flour and obtain essential oils. Factories for the production of furniture from fibreboards are being built near woodworking industry enterprises.
To prevent littering of forest parks with household waste, containers are installed to collect it, and littered forests are cleaned.
The most important condition for preserving natural resources is timely reforestation. Only a third of the forests cut down in Russia annually are restored naturally; the rest require special measures for their renewal.
Forests must exist in order for man himself to exist, for the sake of preserving the great wealth of the animal and plant kingdom for future generations of our Planet. Therefore, we need forest reservations, nature reserves, national parks, and resort forest areas protected by law.
What needs to be done to restore forests?
- Improve public recreation areas
- Do not litter
- Plant flowers and trees
- Create fire pits
- Install waste bins and signage signs
- Fence existing anthills
- Informing the population
- Draw fire safety leaflets, make stands






