Facts about the Moon:
- The oldest mountains on the Moon are considered to be its highlands. Their age exceeds 4 billion years! These hills are densely dotted with meteorite craters - so dense that you can barely find a piece of surface free from them. New impact craters are stacked on top of each other, erasing the boundaries of old craters.
- All the irregularities on the satellite, from huge depressions to the smallest craters, are the consequences of collisions with asteroids and space debris. They fall on the Moon as often as on Earth. But our satellite is not protected by an atmosphere in which most meteorites simply burn up - and when only 128 craters were found on Earth, on the Moon their number exceeded 15 thousand.
- The lunar "seas" are actually ancient plains of solidified lava. They were formed at the sites where the largest asteroids fell. Their mass generated explosions that were hundreds of times more powerful than the most powerful nuclear bomb. The impact craters were so large and deep that lava seeped to the surface and spread out into a lake.
- There are no rocks, large boulders or pronounced rocks on the Moon, like on Earth. Being exposed to the destructive influence of the Sun and outer space for billions of years, they dissipated into rock powder - the famous lunar dust that covers the entire satellite.
- Despite these destructive processes, the appearance of our satellite is changing very slowly. Dinosaurs who lived millions of years ago saw the Moon in the sky the same way we see it now. While the continents on the planet were transforming, taking on their current shapes, the surface of our satellite remained almost unchanged.
- The youngest formations on the Moon are craters with light rays. There are no visible traces of water on the surface of our planet’s satellite. Even the winding channels on the Moon, similar to river beds, were formed from volcanic lava flows.
Eclipses
A lunar eclipse is an astronomical phenomenon when the Moon enters the cone of the shadow cast by the Earth. There are different versions of a lunar eclipse: when the shadow completely covers the Moon, it is a total lunar eclipse, and when only part of the Moon is darkened, it is a partial lunar eclipse. If the Moon passes through the penumbral region but does not enter the umbra, a penumbral eclipse occurs.
Moon eclipse
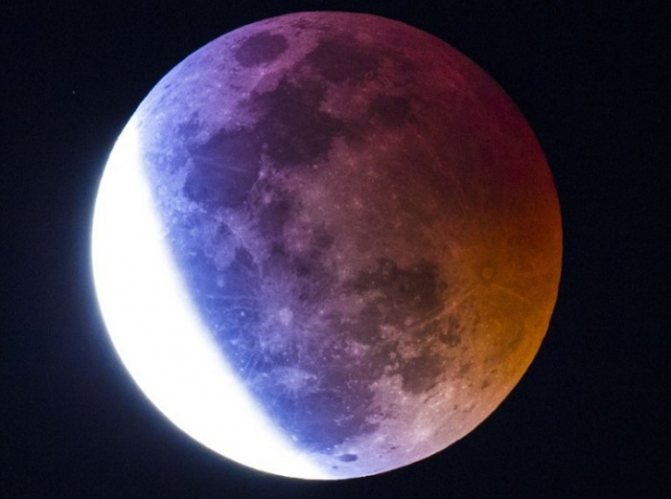

Lunar eclipses occur during the full moon, at such moments when the Moon is exactly behind the Earth and the giant shadow of our planet falls on it, obscuring the sunlight.
Questions and answers:
Why does the moon glow? — Its surface does not glow on its own; it reflects the sun’s rays like a mirror.
Why is the unlit part of the Moon sometimes faintly visible? “At such moments, it is illuminated by the Sun, the light of which is reflected by the Earth itself. This phenomenon is also called the “ash light” of the Moon.
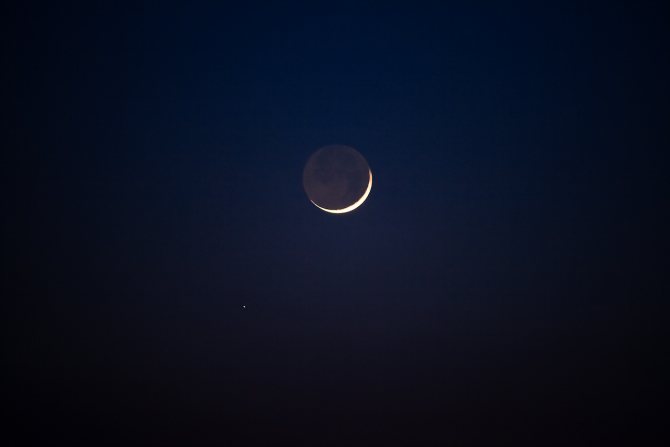

Ash Moonlight
Which side of the Moon is considered dark? — The one that is not illuminated by the Sun at the time of observation.
Are there volcanoes on the Moon? - Yes, only a few pieces. But they are either too low to stand out seriously, or too small to be considered more important than ordinary hills.
Why are there so many craters on the Moon? — Collisions with asteroids, comets and other cosmic bodies leave deep craters, like after explosions. They are called craters. The Moon has neither an atmosphere to protect it from meteorites, nor water or wind that could smooth out collision sites. Therefore, it is not strange that over the 4 billion years of the Moon’s life, so many craters have accumulated on it.
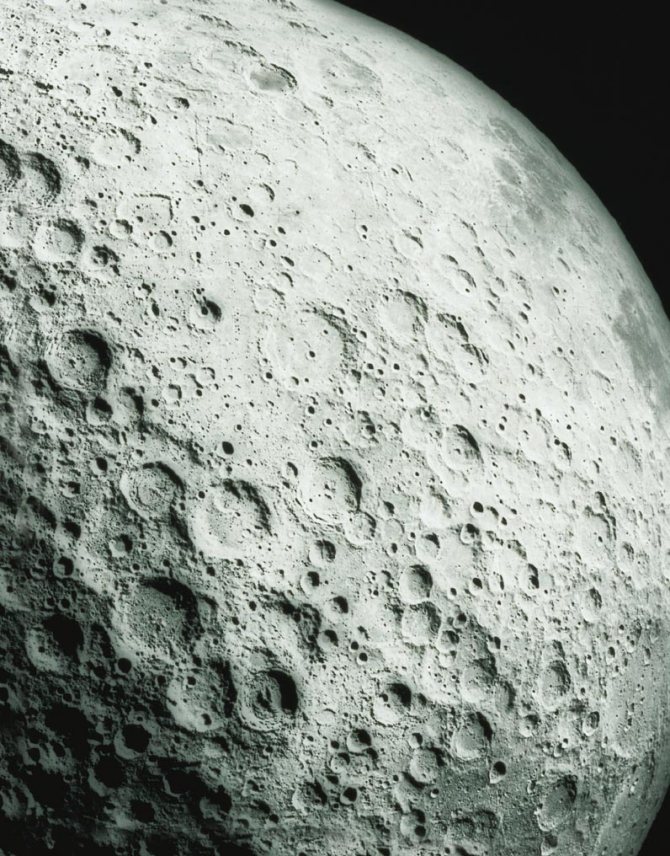

Placer craters on the Moon
Is there lava on the moon? — There is no fresh, hot and red lava on the surface of the Moon. But there is a cooled one - for example, in the lunar seas.
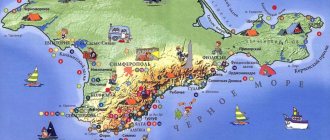
Why are there so many different faces in the craters on the map? — Inside some craters there are depicted the faces of those famous people whose names they bear.
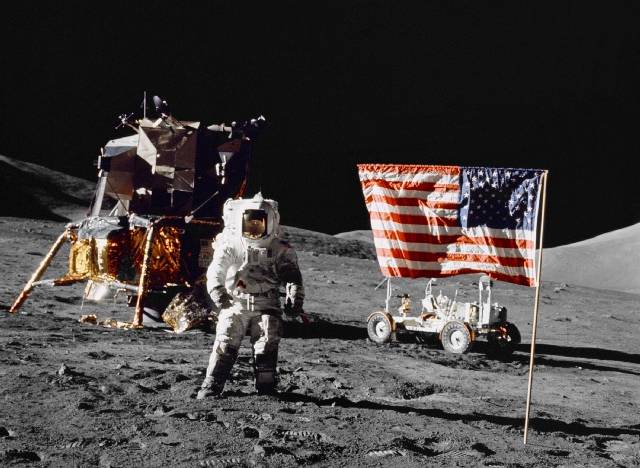


Apollo 17 on the Moon
What do the red icons with numbers mean on the map? — They show the landing sites of spaceships on the Moon. The numbers abbreviate the names - the decryption key is located in the lower right part of the card.
What do the multi-colored dots mean? “They point to the places where space probes landed on the Moon (or where they crashed).
What do the rings on the moon mean? “They mark the rims of the craters.
Where do the light and dark spots on the Moon come from? “The dark zones of our satellite are “young” areas covered with solidified lava. Their age ranges around 3 billion years. The lighter areas are older - these are the crater-strewn highlands that were mentioned at the beginning. Their age is 4 billion years.
Why is the Moon gray? - In fact, the surface of the Moon is black as coal. It is caused by the strong light of the Sun to glow bright gray.
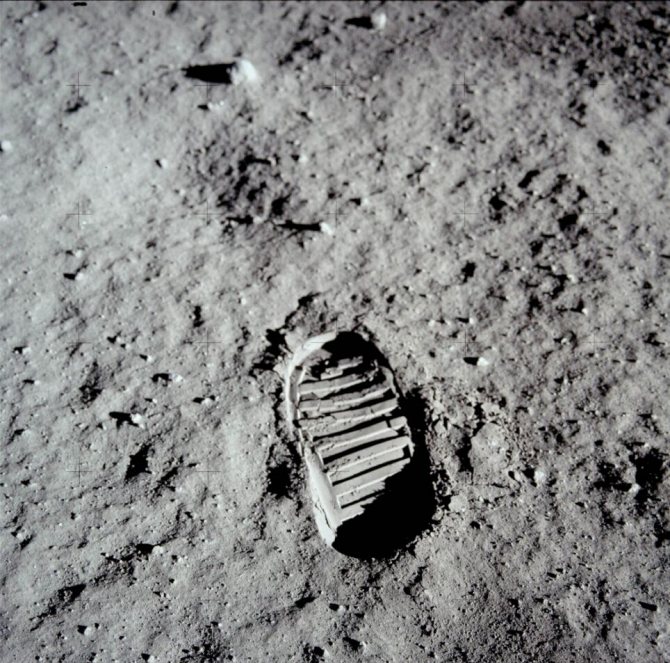

Footprint of Neil Armstrong, the first man to walk on the moon in 1969.
Have there been people on the moon? “So far, it remains the only cosmic body outside the Earth on which man has set foot. In total, 12 astronauts visited there - all Americans. 11 of them were jet fighter pilots trained for space flights. Another astronaut was a geologist. The remaining astronauts work either in lunar orbit or in near-Earth space, and have not yet been to extraterrestrial worlds.
Who was the first to fly around the Moon?
If you name the American astronauts Borman , Lovell and Anders , the first people to circle the Moon on the Apollo spacecraft in December 1968, you would be mistaken. The pioneers of living creatures who flew around the Moon were... Central Asian turtles.
They were caught near the Baikonur Cosmodrome and placed in one of the automatic lunar probes. After the flight, the “cosmonauts” returned to Earth safe and sound. This happened a few months before the flight of the American astronauts. However, due to the fact that space news was classified at that time, this curious fact became known much later.
Share link
Orbital path of the Moon - explanation for children
Children should know that the moon's gravity affects our planet by causing sea levels to rise and fall (high and low tides). To a lesser, but still noticeable, extent, this is manifested in lakes, the atmosphere and the earth's crust.
The water rises and falls. On the side facing the Moon, the tide is stronger. But even on the second one it occurs by inertia, so low tides are created between these two points. The Moon also slows down the rotation of our planet (tidal braking). This increases the length of the day by 2.3 milliseconds each eyelid. The energy is absorbed by the Moon and increases the distance between us. That is, for the little ones it is important to learn that the satellite moves away by 3.8 cm every year.

View of the Earth from the surface of the Moon
Perhaps it was lunar gravity that caused the formation of the Earth as a planet suitable for life. It moderated fluctuations in axial tilt, allowing a stable climate to persist for billions of years. But the satellite did not stand aside, since the earth’s gravity once stretched it to incredible shapes.
Popular message topics
- Poppy (flower)
Thanks to its unusual color shades and combinations of aromas, the world of flowers is a source of inspiration for people, an integral part of their lives. There is not a single person who is not familiar with one of the representatives of the kingdom of flowers - the poppy. - City of Togliatti
In 1737, a charter was signed on the founding of the city - a fortress that would protect Russia from the attacks of nomads, and give the Kalmyks who converted to Christianity a chance to live in a settled way. June 20, 1737 is the birthday of the city of Togliatti. - Word
Most Windows users have encountered Microsoft Office programs in one way or another, and mostly the specific program that interests us, Microsoft Word (also often referred to as WinWord, MS Word), most often simply World.
Lesson in 1st grade “Why is the Moon different?”
Irina Bodrichenko
Lesson in 1st grade “Why is the Moon different?”
Subject: Environment
Class : 1-A
Topic: Why is the Moon different ?
Goal: To develop the cognitive interests of students; to form an idea of the Moon as a satellite of the Earth; explain to children why people don’t live on the moon using a multimedia presentation; cultivate children's interest in the world around them; to form friendly relationships between students, the ability to understand themselves and others.
Objectives: Educational: Expand and deepen students’ knowledge about the Moon, the Earth’s natural satellite.
Developmental: Develop ideas about the shape, size, color of objects; speech, attention, memory, logical thinking, fine motor skills.
Educational: To cultivate a love of nature and respect for the environment.
Cognitive: general educational – conscious and voluntary speech statement orally about changes in the appearance of the Moon; logical - searching for the necessary information (from the story of the teacher, parents, from one’s own life experience, stories, fairy tales, etc.).
Personal: understand the meaning of knowledge for a person and accept it.
Regulatory: predict the results of the level of mastery of the material being studied.
Communicative: able to exchange opinions, listen to another student - communication partner and teacher.
Summary of the educational conversation “The Moon is a satellite of the Earth” with children of the preparatory group
Anna Nshanovna Uzunyan
Summary of the educational conversation “The Moon is a satellite of the Earth” with children of the preparatory group

Dear colleagues, as you know, children show great interest in planets and space. We were able to observe, more than once, the moon in the autumn-winter period, when it gets dark early and brightens late. And as it turns out, children have scant knowledge about the inanimate nature around us. I really hope that our observations of the evening and morning skies will expand the children’s understanding and horizons.
Tasks:
— continue to expand knowledge about inanimate nature, celestial bodies and the desire to learn its secrets;
- form basic ideas about the Moon,
— to cultivate the ability to see the beauty of the sky, to admire the nature around us.
Preliminary work:
observing the sky at different times of the day, looking at books, illustrations, paintings from the series “Planets”, “Space”.

Introductory part.
Educator: Guys, today you will learn a lot of interesting things about one inanimate, celestial object that surrounds us and without which our Universe could not exist. To find out what this object is, you need to solve the riddle.
At night I walk across the sky, dimly illuminating the earth,
I'm bored alone, but they call me. (by the moon)
Main conversation
Educator: Are there any among you who have never seen the Moon?
What time of day did you see her? How do you remember her? (children's answers: in the evening, at night, early in the morning, when we go to kindergarten; it is round, different, half-shaped, shines at night, etc.)
For many millennia, we have been seeing the Moon in the night sky when we raise our heads up. It just looks different: sometimes it’s round, like a pancake, sometimes it looks like a sickle.
People didn’t know why this was happening, they even thought that they were seeing different celestial bodies, which is why two names appeared: “moon” and “month”

Why do you think we see her so different? (children's assumptions: there is an old moon and a new moon)
What is the Moon (children’s answers: planet)

And the path along which the Moon moves around the Earth is called orbit .
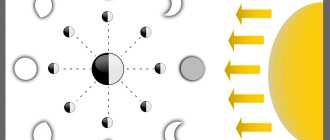
She herself does not emit light, so in the sky we see only the side illuminated by the Sun, and darkness on the other side. As the Moon moves through its orbit, the Sun illuminates the Moon differently and it seems to us that its shape is constantly changing. But in fact, it does not change its shape.
The different shapes of the Moon are called phases.

And the first person to set foot on the surface of the Moon was American astronaut Neil Armstrong.
There is no air on the Moon, so astronauts need to wear special spacesuits with a supply of air and a breathing apparatus, and a special helmet on their heads.
There is always a black sky above the Moon, so the stars are visible during the day as well as at night.
There are many versions and theories of how the Moon was formed and formed. One version is that when the Earth was almost formed, a huge meteorite the size of the planet Mars fell on it. Upon impact, fragments were thrown into space from which the Moon was formed.
You will grow up and maybe one of you will study the planets, space and find out how the planets were formed. In the meantime, we will look at the sky day and night and admire the shine of the sun, stars and moon.
Lesson summary “Moon-satellite of the Earth” Purpose. Clarify and consolidate children's ideas about the location of planets in the solar system. Form ideas about the moon as a satellite.
Summary of an educational conversation with children of the preparatory group “Slender Back” Educational conversation with children of the preparatory group “Slender Back” Lyudmila Rudenko Objectives: 1. To consolidate children’s knowledge about the spine.
Summary of an educational conversation with the children of the preparatory group “Bronzovka Beetle” While the children were sleeping soundly, a beautiful beetle flew into our window. It’s hard to say how he managed to get through the mask net, but somehow he did.
Source
How the Moon appeared - an explanation for children
for the little ones to know that there are several theories about this. But the most popular one focuses on the collision that tore material away from the Earth . Scientists suggest that the impact object had 10% of the Earth's mass (like Mars ). The pieces orbited until they formed the Moon. This idea is also supported by the fact that the composition of the planet and the satellite are very similar. This could have happened 95 million years after the formation of our system (give or take 32 million).
This is the prevailing theory, but there is also another that suggests that there were originally two moons that merged into one when they collided. Moreover, our planet could even pull over a satellite from Venus .
What's on the back?

No matter where you are on our planet, you will see the same Moon everywhere. And always only one side of it. Why is this happening? The fact is that it rotates around the earth at the same speed as around its axis. Therefore, it turns out that the satellite is always turned to our planet with the same side.
To better understand this, you can conduct a simple experiment. Ask your mom or dad to help you. Let them depict our planet. They just stand quietly. And you will be a companion. Try walking around the ground and at the same time slowly turning around yourself. It turns out that you will always be facing the ground, and the back of your head will not be visible.

But what is there, on the other side? Thanks to photographs taken by spacecraft, scientists found that on the reverse side there is a huge depression, its diameter is more than 2000 km and its depth is 12 km.
Seasons - explanation for children
The Earth's axis is tilted relative to the plane of the ecliptic (the imaginary surface of the orbit around the Sun). An explanation for children cannot do without deciphering this moment. southern hemispheres take turns pointing to the Sun. This results in different amounts of light and heat being received – the change of seasons.
The Earth's axis is tilted by 23.5 degrees, and the Moon's by 1.5. It turns out that there are practically no seasons on the satellite. Some areas are always lit, while others live forever in the shadows.