Construction and constructive games, educational and methodological material on construction, manual labor
- Characteristics of construction games.
In the history of pedagogy, games with building materials have been described for a long time and are represented in many systems of educating preschoolers. This type of game has been studied quite well in domestic preschool pedagogy (A.N. Davidchuk, L.A. Wenger, L.A. Paramonova, S.V. Petrushina, etc.).
The peculiarity of games with building materials is that they are based on building skills and abilities, as a result of which, to a greater extent than any other type of children's game, they are closer to the creative and productive activity of a person. Constructive construction games promote the development of thinking and spatial imagination, which are the basis of design activity, as convincingly demonstrated in the studies of N. N. Poddyakov, L. A. Paramonov and others.
In the process of constructive construction games, the teacher teaches children to observe, distinguish, compare, remember and reproduce construction techniques, and focus on the sequence of actions. Children study the construction diagram of a building, learn to plan the work, presenting it as a whole, analyze and synthesize the building, and show imagination.
The content of games with building materials is the creation and reproduction of the surrounding reality using various materials.
The following types of building materials are distinguished:
– specially created (floor, tabletop building material, “Old Castle” type set, “Young Architect” type set, construction set);
-natural (sand, snow, stones, clay);
– stand (cards, boxes, boxes, etc.).
Games with building materials are associated with other types of games (role-playing, theatrical, mobile, didactic).
The presence of the concept of the game, its free development, the variability of the solution - all this determines the creative nature of games with building materials.
one
Construction.
Construction (from the Latin construo - to build, create) means construction as a whole, bringing various objects, parts, elements into a certain relative position and the process of creating a model, machine, structure, technology with drawings and calculations.
Children's design refers to the process of constructing buildings, such structures that provide for the relative arrangement of parts and elements, and methods for connecting them. As a rule, the design process takes place in a playful way to interest the preschooler.
In theory and practice, there are several types of structures:
- Pattern design is the most common type of design. It has many positive aspects: children develop various skills, master general techniques, and learn sequences of actions.
- Designing on a specific topic brings the child closer to the creative implementation of a task, but on a limited topic.
- Designing according to your own project is a complex type of design in which the child independently solves all problems, sets the goal of the activity, plans it, collects material and implements the concept.
- Conditional design: contains great opportunities for development. The child independently determines the length and height of the building.
- A model building is a type of construction developed by A. R. Luria. The child is offered a model of the building (a drawing made by the building teacher, pasted over with paper), on which the outlines of the constituent elements of the structure are hidden (model of a sofa, gate, car).
Each of the considered types of construction has its own advantages, because it is necessary to combine them in educational work, in childhood in a preschool institution.
Of all the variety of construction sets that are used in preschool institutions, I would like to focus on LEGO
2
construction set, which is “a bright, colorful and multifunctional material that opens up enormous opportunities for a child’s research and experimental activities.” With its help, you can solve complex problems through an exciting, creative game in which there will be no losers, because any child can handle it. The elements of the LEGO set have different sizes, different shapes, and simple options for attaching to other elements.
LEGO - the designer is widely used in design classes and solves the following problems: develops mental processes (analysis, synthesis, comparison, generalization, etc.). A fairly effective means of improving thinking is to design using models, diagrams, drawings, plans, samples, and from memory.
LEGO - the constructor is also used in mathematics lessons to consolidate and develop the skills of forward and backward counting, comparing numbers, knowledge of the composition of numbers, geometric shapes; the ability to navigate an airplane, the ability to classify by characteristics.
In lessons on familiarization with the environment, LEGO is used in experimental activities as the material from which the construction set is made (“What is it made of?”, “Find the same thing,” “How are they similar and how are they different?”).
With the help of LEGO, children pass on their acquired knowledge and impressions from lessons, excursions, observations and walks through buildings.
LEGO is a powerful source of developing children's interest in construction.
- Conditions for the development of games with building and natural materials.
To develop children’s play activity, it is necessary to create the following conditions:
- Organize the play environment: select the necessary building material in accordance with the objectives of developmental construction activities in the preschool institution. The material should be varied (floor, tabletop, different types of builders,
3
set and so on), beautifully designed, stable enough to suit children's abilities.
- Find time and space to play with building materials. Games require concentration of thought and attention. Therefore, play stands with tabletop building materials and construction materials must be placed so that they do not interfere with children or distract them.
- Respect for buildings and structures made by children. Usually the child likes to “return” to his buildings and make changes. Therefore, it is necessary to instill in all children a careful and attentive attitude towards their own buildings and the buildings of others.
- To create conditions for playing with buildings for this, you should choose small toys (cars, trains, figures of people and animals, etc.).
- Combine children for cooperative constructions from the builder. Create a situation in which a child who has acquired new construction skills will teach them to other children.
- Teach children to handle building materials carefully. Carefully disassemble the building, the craft from the designer, arrange the parts and shapes in the cells of the rack, drawers.
What else to read: Didactic games “Magic Circles” (senior group)
Games with natural materials.
These games enter a child's life early. Just having learned to walk, the child takes a shovel, a spade, tries to dig snow, sand, and loves to play with water. But without special training, children do not acquire the necessary skills, and games with natural materials are monotonous and lack content.
Meanwhile, they contain great opportunities for the development of children's thinking, will and perseverance.
These possibilities are largely determined by the nature of the natural material. It is very diverse and has different properties that dictate different ways of using it as a building material.
The child learns many properties of natural materials through the senses. Methods of sensory cognition, the ability to highlight certain properties and qualities of objects are developed in the process of meaning
4
interesting activity, especially in the game.
Games with natural materials - snow, water, sand, clay, grass, sticks, shells, pine cones, chestnuts, acorns, rose hips, maple seeds, linden, thorns, leaves, roots, bark, moss, etc. – excellent raw materials for crafts and games with them.
Every year modern pedagogy masters an increasing number of different methods and directions.
The pedagogical sandbox is a good environment for individual and group work with children for the purpose of their spiritual and moral development, personal development and cultural growth.
Sandplay cannot be interpreted. The teacher must play the role of an attentive spectator. The position of the teacher is “active presence”; she does not lead the process. The release of stored energy leads to its transformation, which allows you to direct the converted energy to personal development and further learning.
The main tasks of the pedagogical sandbox:
– Child’s self-development through creative games in the sand.
– Development of tactile-kinesthetic sensitivity and fine motor skills of the hands.
– Strengthen the skills of phonetic and grammatical structure, sound pronunciation, teaching literacy and writing.
– Development of a creative personality.
- Guidance of building and construction games in different age groups.
The teacher performs the following tasks:
– expand children’s understanding and draw their attention to the work of builders and the equipment they use; – methods of teaching the construction, education and development of independence and mental activity, constructive and creative abilities; – formation of hard work, development of correct relationships between children, uniting them into a friendly team.
First junior group
The kindergarten program for younger groups includes construction games with toys, design lessons
5
material on which the necessary actions are taught, the formation of simple, but understandable and lasting skills. Children are introduced to building materials, their shape, size, different locations on the table top (beds, supports); learn to lay one on top of the other, lay bricks horizontally (train, track); form the simplest ceiling (gate, house). The teacher finds similarities between familiar buildings and objects of surrounding life.
Second junior group
They are taught not only to distinguish the main parts of the building (cube, brick, slab), but also to give them names, and also to place bricks at equal distances from each other in a circle, in a quadrangle (fence, fence), placing them on a smaller plane . Already at this age, children are taught to purposefully inspect objects and buildings.
Teacher's manual - creating a play environment: selection of building materials.
Central group
The educational program of the kindergarten provides for the further development of children's interest in construction games, the use of created buildings in role-playing games, teaching the ability to build not only according to the proposed model, but also the subject itself, and teaching more complex methods of work. Under the guidance of a teacher, children 4-5 years old can reflect impressions of the environment in a building game. They are provided with a variety of materials (building material; builder; pieces of plywood, cardboard, materials for finishing buildings). During hikes and targeted walks, the teacher draws children’s attention to buildings, bridges, transport, roads, fences, and so on, teaches them to see the beauty of buildings, to notice not only what is common, but also what is different, and to highlight individual parts. Therefore, in the process of teaching children of this age building games, their understanding of the environment they use in the game expands.
Senior group
The educational program of the kindergarten involves teaching children the preliminary design of collective construction games, setting the goal of the game, identifying participants by prior agreement, using construction and construction skills not only for
6
a clear example, as well as from drawings and photographs of various designs. Older children's games are more focused on a combination of intellectual and practical activities. The teacher teaches them to think about the next game actions, compare with each other, develops intelligence, encourages speculation, and encourages them to implement the solution. For older preschoolers, various
Construction Materials. You must show them how to use one or another of them, how to connect its individual parts, blocks, how to make buildings mobile, durable, and beautiful. The correct conduct of the game and the active participation of all children in it determine their satisfaction with the game, their interest in it and, consequently, its duration.
What else to read: Games on 4th
Preparatory group
Construction games in the preparatory group are distinguished by a very diverse idea, as children become familiar with the phenomena of life around them, with construction techniques on special excursions, while watching films, through books. In play, they often imitate the construction activities of adults. The interests of children in the preparatory group and their skills place high demands on the conduct of construction games. The teacher must have the necessary knowledge and show interest in technology and invention. From a wide variety of buildings, structures, design types, select those that are accessible to children and have educational and educational value.
In teaching design, the translation of a flat image (photograph, drawing) into a three-dimensional design is of great importance, which places significant demands on the child and contributes to the development of analytical activity. The teacher teaches how to analyze the results of the game. This disciplines the mind, teaches children to connect the goal and the construction process with the result.
7
Bibliography:
- Davidchuk A. N. Development of constructive creativity in preschool children. M., 1976.
- Kozlova S.A., Kulikova T.A. Preschool pedagogy: a textbook for students of secondary schools. – M.: Publishing house, 2009
- Kutsakova L.V. Design and handicraft in kindergarten. – M.: Education, 1990.
- Lishtvan Z.V. Design / Ed. THERE. Paramonova. – M.: Education, 1981.
- Paramonova T.E. Theory and methodology of creative design in kindergarten. – M., 2002.
eight
Plan “Planning games with building materials in the preparatory group
Card index of games and activities with building materials in the preparatory group according to Z.V. Lishtvan
.
Airplane construction
Target
: teach children to build an airplane, creatively using their observations, as well as photographs of the finished building, using previously acquired skills; develop in children the ability to pre-think the course of their work.
Consolidate knowledge about aircraft parts (fuselage, wings, tail, engine, propeller, landing gear)
The plane is twin-engine.
\
Progress:
suggest looking at several photographs of different types of aircraft. Clarify what airplanes are used for (for transporting passengers, cargo, mail, for the needs of agriculture, state defense).
What parts does an airplane consist of (fuselage, wings, tail, engine, propeller, landing gear); know that airplanes come with one, two or more engines.
Invite children to independently think about what kind of plane they will build, and determine what material they need, offering different constructors, determine with what parts different parts are constructed.
Please note that children may alter the design slightly. So, in the photograph there may be a twin-engine airplane, but the child is building an airplane with one or three or four engines. But all the main parts of the aircraft must be reflected in the design. Children should learn from comparison that every airplane has these parts.
Suggest that you think carefully about where to start construction.
During the construction process, it is necessary to pay special attention to the beginning of work: it is important that children correctly set the size of the structure. Those who find it difficult should be helped with questions, advice, and reminded how this is done.
When the buildings are ready, they should be carefully examined, focusing children’s attention on interesting designs, successful use of materials, and the use of previously acquired skills.
In this case, you need to pay attention to the transfer of the correct proportional relationships between the individual parts of the building, to the well-thought-out design of the fuselage, to the successful depiction of the engine and other parts, and to encourage those children who have shown creative initiative.
It is advisable to store the best versions of buildings depicting different types of aircraft in a construction corner for two to three days.
Shipbuilding
Target
: to consolidate children’s ideas about this type of transport (vessels are large and small, passenger, cargo, military. In addition, there are small ships, boats, boats.
Help children understand the relationship between the shape of ships and their purpose in life
Teach children to build according to idea and use more parts.
Move
: offer to look at several photographs of ships of different types.
Pay attention to the bases of the ships shown in the drawings or made in simplified buildings. By comparison, find out that ships for different purposes have different foundations. They have the same shape, oval (an oval can be narrow or wide), but the width of the vessels is different. Fast ships (mostly military) have a narrow, long base and a sharp bow. Heavy-duty vessels (barges) have a wide base and a blunt bow. The base shape of passenger ships is narrower than that of a barge.
First, you need to consider the construction of the bases of the boats made by the teacher, which are conveniently placed on low tables so that the children can see them from above. Compare the shape of these bases and remember why it is different. Instead of the court foundations built by the teacher, you can offer a drawing of them.
Options: (warship, barge, passenger ship, pier with ships).
Find out with the children that the ship floats faster than barges, but slower than warships. Children must decide for themselves what form of base such a vessel should have. Please note that the speed of movement depends on both the structure of the vessels and the power of the engine: a motor boat moves faster than a boat with oars. Rockets and meteors have a powerful motor and a special structure, so they move very quickly, overtaking any ships on the river.
When analyzing finished buildings, you should first of all pay attention to whether the children were able to determine the shape of the base. You can invite children to determine which of the ships will have a higher speed and which will have a lower speed. The correct decision will be an indicator of how consciously they have mastered the above dependence.
Construction of urban transport
|
Target:
To consolidate an understanding of urban transport, the variety of types, and its purpose. Please note that the design of each type of transport depends on its purpose
Move
: have a conversation about urban transport after observing various types of transport in your city, pay attention to the speed of movement, determine which types of transport move faster.
Offer to look at transport toys, determine what they are intended for, how they differ from each other, why, then talk about what they have in common. Suggest what parts the main parts will be built from.
Ask them to think and say what everyone will build and in what order. Make sure that children complete the buildings in the right sequence and successfully select the necessary parts so that they can find out what the purpose of the transport is.
At the end, look through all the buildings with the children, note the successful ones and finally summarize: what types of transport do the children know, how do they differ.
Options:
freight transport (truck, dump truck, milk tanker, tanks), urban transport for transporting passengers
Construction of the bridge
Target
: Learn how to make a bridge on high, rarely placed abutments, show independence and initiative in implementing a construction plan, and negotiate with a friend about joint work.
Progress:
look at photographs, paintings depicting different bridges (railway, for cars, for pedestrians, as well as images of bridges that simultaneously serve pedestrians and cars; steamships and boats can sail under them, or trains can pass through).
Pay attention to how they are arranged, which part can be called the main one, what the bridge is supported on. Such a part is the foundations - supports. They are very durable because they have to withstand a lot of weight. The driving part is placed on the abutments. On one and the other side of the bridges there are ramps for cars or stairs for pedestrians. It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that bridges almost always have railings, and talk about their purpose and design.
Along with the building material, place toys on the tables - cars, boats, steamships. They are needed to find out the dimensions of the bridge.
Children are asked to think about what parts can be used to make a stable support (from bars, from cylinders). And if the abutments need to be higher, then they can be folded out of cubes or the cubes can be placed under bars (cylinders).
The abutments are installed on both sides opposite each other. Before making the platform, you need to connect the abutments together with long plates. If one plate is not enough, it can be lengthened by attaching another. In this case, the connection of the plates must be in the middle of the bar (cylinder) so that the platform is stable. The platform can be laid out from short plates (square, wide, narrow).
If the bridge for pedestrians is high, you need to make stairs on both sides; if it is not high, you can make a descent from long plates.
Invite the children to build the bridge themselves (the bridge design is symmetrical, so two children can build it). We need to explain to them that everyone will build one side. First, the children must agree among themselves on how to build so that the structure on both sides is the same.
It is also necessary to advise, if necessary, to replace some parts with others.
In the process of work, it is necessary to check how the children will determine the size of the bridge, where they intend to build stairs for pedestrians, how they want to connect the foundations, and help negotiate as the work progresses.
Remind that the building needs to be proportionate to the toys that are on the table (various types of transport, dolls).
When the buildings are completed, you need to examine them with the children, focus on successful designs, pay attention to the most interesting solution to the problem, the strength of the fastenings, and the finishing of the railings.
Options:
a bridge across the river, a bridge that would serve both pedestrians and cars, and trains would pass under it.
Construction of buildings
(a two-story residential building with large windows with overlap between floors)
Target
: Clarify children’s understanding of the main parts of a building (base, walls, doors, windows, roof).
Think over the sequence of construction; what parts are most appropriate to use. Carry out construction by accurately applying part to part, using the method of replacing some parts with others.
Progress:
Offer a sample of the building made by the teacher, which will serve to select parts and remind you of the sequence of work.
Construction of buildings
(beautiful doll house)
Target
: Clarify with children’s ideas about the main parts of the building (base, walls, doors, windows, roof) and the features of its design (pediment)
Think over the sequence of construction; what parts are most appropriate to use. Carry out construction by accurately applying part to part, using the method of replacing some parts with others.
Develop the ability to carry out construction from a photograph, work amicably and in concert with a friend.
Progress:
consider photographs of buildings located near the kindergarten, clarify their purpose. Draw children's attention to the architectural features of buildings. Children learn that the pediment and columns decorate them.
Showing a photograph of a building made of building material in class, ask the children if they like it and why exactly.
Clarify that the house is beautiful because its facade is decorated with columns, there are also decorations on the roof and the whole structure is clearly symmetrical.
Consider what parts the house is built from. Introduce them to a new detail - a pediment, and explain where it can be used. Find out that there are cubes at the base of the building (count how many there are on each side),
Children name the parts from which the floor, walls, windows, etc. are made, and indicate their number. Following this, they examine the porch, beautifully decorated with railings.
Invite one of the children to talk about the sequential progress of construction. It is recommended to make the decorations on the roof and railings different, but the design of the house must be reproduced exactly.
The children will build the house together. Remind them that they need to work together, agree on how to build (one builds the right side, the other builds the left).
During the construction process, it is necessary to help children organize work, cope with difficulties in a timely manner, and correct mistakes.
Invite the children to look at their buildings and the buildings of their comrades who worked nearby. It is necessary to reward for good luck in creativity, for friendly work.
Construction of a fairy house
Target
: Teach children how to decorate structures.
Think over the sequence of construction; what parts are most appropriate to use. Carry out construction by accurately applying part to part, using the method of replacing some parts with others.
Develop the ability to carry out construction based on illustrations, work amicably and in concert with a friend.
Progress:
review illustrations for fairy tales with children, drawing their attention to the beautiful design and decoration of fairy-tale houses. The illustrations by Yu. Vasnetsov in the books “Ladushki” and “Rainbow-Arc” are good. It is advisable to consider illustrations that show arches at the bottom of the house or its side parts protruding forward, etc.
You can hang illustrations of fairy-tale houses in the construction corner, tell the children that soon they will be building similar houses and they need to think in advance what kind of house and with whom they will build (children build together), what toys they will need.
Ask the children what kind of house they decided to build, for whom, and how they distributed responsibilities among themselves. It should be recalled that the base of the house can be different (square, rectangular, with different side lengths).
At the end of the work, everyone examines the completed buildings together, finds out whether they look like fairy-tale houses, whether they are well built, and which can be considered the best.
Construction of a beautiful building
in your city
Goal:
Learn to build buildings based on ideas, think about what shape the foundation will be.
Develop the ability to carry out construction based on illustrations, work amicably and in coordination with a friend
Move
: You need to tell the children in advance that everyone will build the building they like. It is suggested that you take a good look at this building again during a walk or in a picture in order to build it better. (In the construction corner there should be albums with photographs of buildings or albums with pictures.) You should pay attention to the complex shape of the base of buildings.
You need to warn the children in advance that they will be building in twos, so you need to agree on who wants to work with whom, what they are going to build, how they plan to decorate the building, what parts will be needed.
Name the theme of the construction, what kind of building the children will build, what shape its base will be (rectangular, square, with an arch, etc.), tell whether they have agreed with their comrades, how they will build, how they will decorate the building. You need to start construction from the foundation.
During the construction process, children should be allowed to use the album if they need to clarify or remember something; should help in solving difficult design problems.
At the end, consider all the children’s buildings, ask if it is possible to find out what kind of building was built, draw their attention to the best buildings, to the fact that the children were able to build a building with the shape of the base that they themselves chose.
Theater construction
Goal: To learn to build buildings according to an idea, to think about what shape the foundation will be.
Develop the ability to carry out construction based on illustrations, work amicably and in coordination with a friend
Progress: Offer to use illustrative material (paintings, photos) depicting other theaters. You need to select photographs of finished structures made from building materials and hang them in the construction corner.
Propose a topic for construction, ask the children to choose partners and talk about their intentions.
At the end, it is advisable to examine all the buildings, note the most successful solution to design problems, and encourage children for their friendly work and ingenuity.
Construction of the station
Target:
Exercise children in depicting familiar structures from memory and imagination, encouraging them to show creativity and ingenuity, remember the main parts of the station building, the sequential progress of the construction and be guided by this in their work. Teach children to pre-distribute responsibilities between construction participants and not to suppress each other’s initiatives during work.
Progress:
Ask the children who was at the train station. Ask how it works, saw the arrival of the train, disembarkation of passengers, how boarding is carried out. It is necessary to consider the train separately in the train illustration, paying special attention to the diesel locomotive. Children in the preparatory group already know that trains carry passengers and various cargoes.
Inform the children about the topic of construction, invite them to remember what buildings they will have to build: a station building, a railway track, a train, a platform, etc., remind them that the children will work in groups of three, so they need to decide in advance who will build what, and think about the size each building.
Help children correctly distribute construction sites, make sure that everyone works slowly, carefully lay out the “builder” parts so that they can be used rationally.
Finished buildings should be examined together with the children, invited to tell them who built what, what shape of the building they chose, to encourage them for having mastered the sequence of building construction, for selecting details well, for showing initiative and ingenuity, for good execution, for friendly, coordinated work.
Preparatory group Paramonova Larisa
Sample lesson notes
"Bridge for pedestrians"
Target:.
To develop in children the skills to: create design plans in accordance with specific conditions; analyze these conditions and, based on the analysis, build and control their practical activities.
Equipment.
For each child: building material, sheets of blue paper of different widths, two boats with masts, figurines of people.
Move.
First, the sample is analyzed and a short conversation is held to clarify the children's ideas about various bridge designs. The teacher asks them to remember what bridges they saw, looked at in pictures, how they differ from each other and what they have in common (common parts: supports, driving part, slopes, railings; but they have different shapes: for example, a bridge for transport gentle slopes, while the pedestrian one has steps, etc.).
Then the teacher draws attention to the available additional materials (sheets of paper of different widths, a boat, figures of people) and suggests building a bridge for pedestrians across the river (sheet of paper) along which ships sail. (The length of the bridge should correspond to the width of the sheet of paper, and the height to the height of the ship’s masts.) Children reproduce the design of the sample bridge, but at the same time independently determine how to increase its length and height in order to transform the given structure, taking into account certain conditions.
When discussing finished buildings, their compliance with the specified conditions is noted; the common and the different stand out in them. The latter is due to the different widths of the bridges.
"Bridge for Transport"
Target:
To develop in children the skills to: analyze the conditions of a task; create a design in accordance with these conditions.
Equipment.
For each child: building material, a sheet of blue paper, two cars, a boat.
Progress:
The teacher suggests remembering what they built in the last lesson (a bridge for pedestrians) and analyzing the building from memory - naming the main parts of the bridge (supports, roadway, slopes, etc.), determining their functional purpose, naming the parts from which these parts were built.
Then he says that today the children will build a bridge for transport, and gives the task - to build a bridge across the river of the same design as in the last lesson, but so that two cars can pass on it, and a ship can sail under it. He invites children to consider additional materials (cars, a ship, sheets of paper).
Children build a bridge on their own, modifying a familiar structure in width and length from memory; they make ramps for cars, positioning them differently in relation to each other, and maintain the height of the bridge.
When analyzing buildings, the teacher pays attention not only to their compliance with the given conditions, but also to the originality of individual design solutions.

Pedestrian bridge
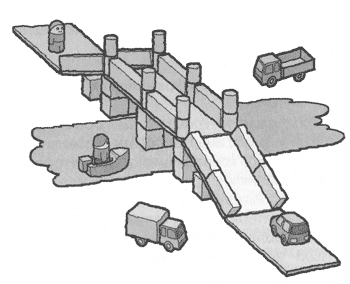
Bridge for transport
"Bridge for pedestrians and transport"
Target:
Teach children to create a design concept taking into account several conditions expressed verbally and objectively; independently select building materials in accordance with the plan; agree on joint work and plan it.
Equipment.
For each child: building material, toy ships (steamboat, boat, etc., 1–2 pcs.), sheets of blue paper of different widths, cars (2 pcs.), figurines of people (2– 3 pcs.).
Move.
First, a preliminary conversation is held, in which it becomes clear what bridges were built in previous classes (pedestrian, for transport, etc.), how they differ from each other and what they have in common, etc. It is concluded that bridges come in different designs depending on their practical purpose.
Then the teacher draws attention to the available materials and proposes to build a bridge across the river of a certain width (a sheet of blue paper) for pedestrians and vehicles so that two cars can pass on it, and vessels (a boat, a steamship, etc.) can freely sail under it. ). Children, teaming up in twos, build one bridge.
In the process of completing the task, the teacher observes whether the children consistently analyze the conditions and how they control their practical actions (visually or practically determine the compliance of the sizes of the parts of the bridge with the given conditions, for example, the length of the bridge is commensurate with the width of the river, the height with the height of the masts of the ship, etc. ).
It is important that the children agree in advance about the upcoming work (who will build what part of the bridge, etc.); however, discussion is possible during the construction process. At the same time, the teacher makes sure that the discussion is businesslike and friendly in nature.
When discussing finished buildings, children pay attention to the variety of designs if they meet all the given conditions, explain the reason for this (different shapes and sizes of objects acting as conditions), notice the originality of the solutions, etc., and the teacher notes those children who have learned do things together.
"House"
Target:
Learn to find individual design solutions based on sample analysis (building a balcony). To develop in children the ability to transform a sample in accordance with given conditions.
Equipment.
Construction material (one set for each).
Move.
First, children independently analyze a sample of a two-story house with a balcony. The teacher suggests looking especially carefully at how and from what parts the balcony is made (in this case, the children can come closer to the teacher’s desk) and talk about it.
Then some children are given the task of building a two-story house of the same design, but with three entrances, with a balcony above the central entrance, while others are given the task of building a house of the same design, but three floors with one entrance and two balconies on the second floor.
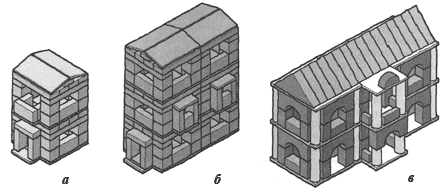
Residential buildings. a - sample; made by the children themselves: b - three-story with one entrance and two balconies on the second floor, c - three-entrance with a balcony above the main entrance
The teacher invites several children to repeat the given conditions and then begin to complete the task. Children construct each house differently, using material from their kit. Beforehand, they discuss how they will build (one - the first floor, the other - the second; or one - one half of the house, the other - the other, etc.).
If children have difficulty building a balcony, the teacher can suggest or show how best to do it.
In the process of completing the task, the teacher notes not only the level of technical skills of the children (how floors are made, how plates are laid for the floor, balcony, etc.), but also how correctly and timely they take into account the given conditions, how they are able to agree among themselves on upcoming activities.
When discussing buildings, children independently find errors in designs and tell how they can be corrected. The teacher draws attention to the fact that residential buildings are of different types, discusses with the children how the houses differ from each other and where it is better to build houses of this type (in villages, small or large cities).
"Kindergarten"
Target:
Teach children to build various buildings united by a common content; collectively create building plans and jointly implement them.
Equipment.
Construction material (one set for each child).
Progress of the lesson.
On the eve of the lesson, during a walk, a targeted examination of the kindergarten is organized. The specifics of the building are noted (how many floors, how many entrances, how they are located, what windows, etc.) and the site (it has slides, swings, gazebos, ladders, etc.).
Children are divided into subgroups (3-4 people) and discuss the design of the building of “their” kindergarten, its location on the site. Then they agree on what will be built on the site (slide, swing, gazebo, etc.), and who will build what exactly. The teacher carefully controls this moment and directs the discussion process in the right direction (each of the children defends his proposal, but the most successful one must be accepted; the tone of the discussion should be calm and friendly).
During the construction process, the teacher monitors the relationships and interactions of the children. Finished buildings are compared, original structures, their location, etc. are noted.
Then children can build a street, square, village, city, organize an exhibition on urban planning, etc.
The main ways to implement the management of construction games for preschoolers
Construction games and their optimal organization are necessary for the development of preschoolers. They are focused on the educational development of children, on developing their constructive skills. The effect of their educational influence is directly related to the rational organization of leadership, the use of optimal techniques and methods of educational influence.

Figure 1. Construction games. Author24 – online document exchange for students
In order to teach children specific construction skills and abilities, to develop in their minds a certain concept of design work, it is necessary to regularly familiarize children with the methods of construction of various buildings, the characteristics of materials and their functional purpose. This leads to a gradual expansion of the child’s knowledge, which, in turn, makes construction games more meaningful, develops the ability to build more complex structures and improves construction techniques.
Too lazy to read?
specialists and get an answer in 15 minutes!
Ask a question

Figure 2. Characteristics of construction games. Author24 – online document exchange for students
Construction game management is focused on solving the following educational tasks:
- Formation and development in children of ideas about the importance of work, the need to develop labor skills, especially in the construction industry, focusing children’s attention on the organization of work of builders, instilling respect for this field of activity, the desire to preserve the original appearance of the building, the need to treat it with care and respect it ;
- Familiarization with various construction methods. This allows you to develop the child’s creative and constructive abilities, activates his intellectual activity, develops thought processes;
- Teaching hard work, respect for work, developing teamwork skills and methods of collective interaction.
Too lazy to read?
specialists and get an answer in 15 minutes!
Ask a question
Observation 1
By supervising construction games, the teacher creates an optimal play space that allows organizing construction work, selecting the necessary material in sufficient quantity so that all children can participate in the game.
Providing the possibility of real observation of the construction of any object is important for the competent organization of management of the construction game process. To do this, the teacher can bring illustrations of the various stages of construction work, show films on construction topics, prepare a presentation, or organize an excursion to the construction site. This will enrich children's ideas of construction, which will have a beneficial effect on the development of the game plot.
In addition, familiarity with construction based on the use of special builders is of no small importance. Children know the design details of various shapes and modifications: cubes, bricks, plates, cylinders. The teacher, in turn, shows ways to connect them and design options. Having mastered the possibilities of working with the designer, the child begins to fantasize and develop new modifications.
Construction games are held in two main areas:
- Familiarization with constructive activities in specially organized classes.
- Demonstration of construction techniques and development of the basic skills necessary for successful construction are carried out in the independent play of children.
In special construction classes, children learn to build various structures and expand the construction theme. Construction begins with individual small parts and objects and gradually moves on to the construction of larger buildings and structures. In the process of learning to design, children develop the ability to plan their work, predicting the results, based on the materials used for design and methods for modifying them. This has a beneficial effect on the development of the child’s thought processes, the formation of his intellectual abilities, the development of creative abilities and creative talents.
Card index of construction games for middle preschool age.
1.Construction of a house for a cat, dog and goat"
Goal: Develop children's ability to build a house. Learn to build in the required sequence. Promote cooperative play
Material: cubes and bricks, plates.
Progress of the game. - Look, it’s raining, and our puppy Bimka is wet, he’s sitting under a tree and shaking. He needs to build a warm house - a booth. The teacher offers to build a house for the dog. Children select the materials themselves and invent the house themselves.
2.“Building a truck, roads”
Goal: To consolidate the ability to tightly lay bricks flat to each other with the narrow short side (road)
.
Place the cube firmly and evenly on the second brick (machine)
.
Material: cubes and bricks.
Progress of the game. The teacher brings a traffic light to the group
, children remember what they know about traffic lights. Let's build a road and a car, shows how to build, plays with buildings
3.“Town for dolls”
Goal: Continue to create buildings according to the general plot. Develop the ability to design as desired
, cultivate the desire and ability to build calmly together
Material: prism cubes and bricks, plates. cylinders.
Progress of the game. - Look, our dolls were very upset, they had a fire, all the houses in the city burned down. Therefore, they need to be helped and built new houses. Let us help our toys, create our own houses, come up with our own buildings.
“Building a house for a cat, a dog and a goat”
Goal: Develop children's ability to build a house. Learn to build in the required sequence. Promote cooperative play
Material: cubes and bricks, plates.
Progress of the game. - Look, it’s raining, and our puppy Bimka is wet, he’s sitting under a tree and shaking. He needs to build a warm house - a booth. The teacher offers to build a house for the dog. Children select the materials themselves and invent the house themselves.
Card index of construction games for senior preschool age.
1.“Collect and build”
Goal: To strengthen children’s ability to recognize and name geometric shapes (square, rectangle, triangle, circle, oval). Lay out various objects from geometric shapes.
Material: cube with geometric shapes glued on, geometric shapes cut out of cardboard; contour samples of buildings
Progress:
Option 1.
The child throws the dice, names the figure he sees on the top face and takes the same cardboard one of any color. From the figures collected over several moves, the child creates any image.
Option 2.
The child chooses a shape by color. The form, in this case, can be any. For example: A green triangle appears on the top face of the cube. The child is asked to choose any green figure. A building is also made from the collected figures.
2. "Architect"
Goal: To develop the ability to compose a serial series. Train your child in the ability to create a construction plan.
Material: Strips of different lengths (up to 10 gradations); a sheet of paper, a simple pencil.
Progress:
Option 1.
Arrange the strips in disarray. Invite the children to arrange them in order: from smallest to largest or from largest to smallest.
Option 2.
Arrange the strips in disarray. Invite the children to draw a plan for the staircase without touching the stripes. Then, offer to take the strips and build the stairs according to the plan.
3."Happy Island"
Goal: Development of imagination. Skill to work in team. Reinforcing the names of geometric shapes.
Material: Multi-colored geometric shapes and their parts.
Progress: The teacher determines the topic. Children create a building together. The construction must correspond to the nature of the theme.




